AB5-base hydrogen storage alloy, electrode for Ni-MH battery, secondary battery and method for preparing hydrogen storage alloy
A hydrogen storage alloy and nickel-metal hydride battery technology, which is applied in the direction of secondary batteries, battery electrodes, alkaline storage battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of affecting cycle life, difficulty in adjusting the balance voltage of element ratio, and reduced life of nickel-hydrogen batteries, etc., to achieve Effect of improving corrosion resistance and cycle life, improving corrosion resistance and economy, and improving high-rate discharge performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
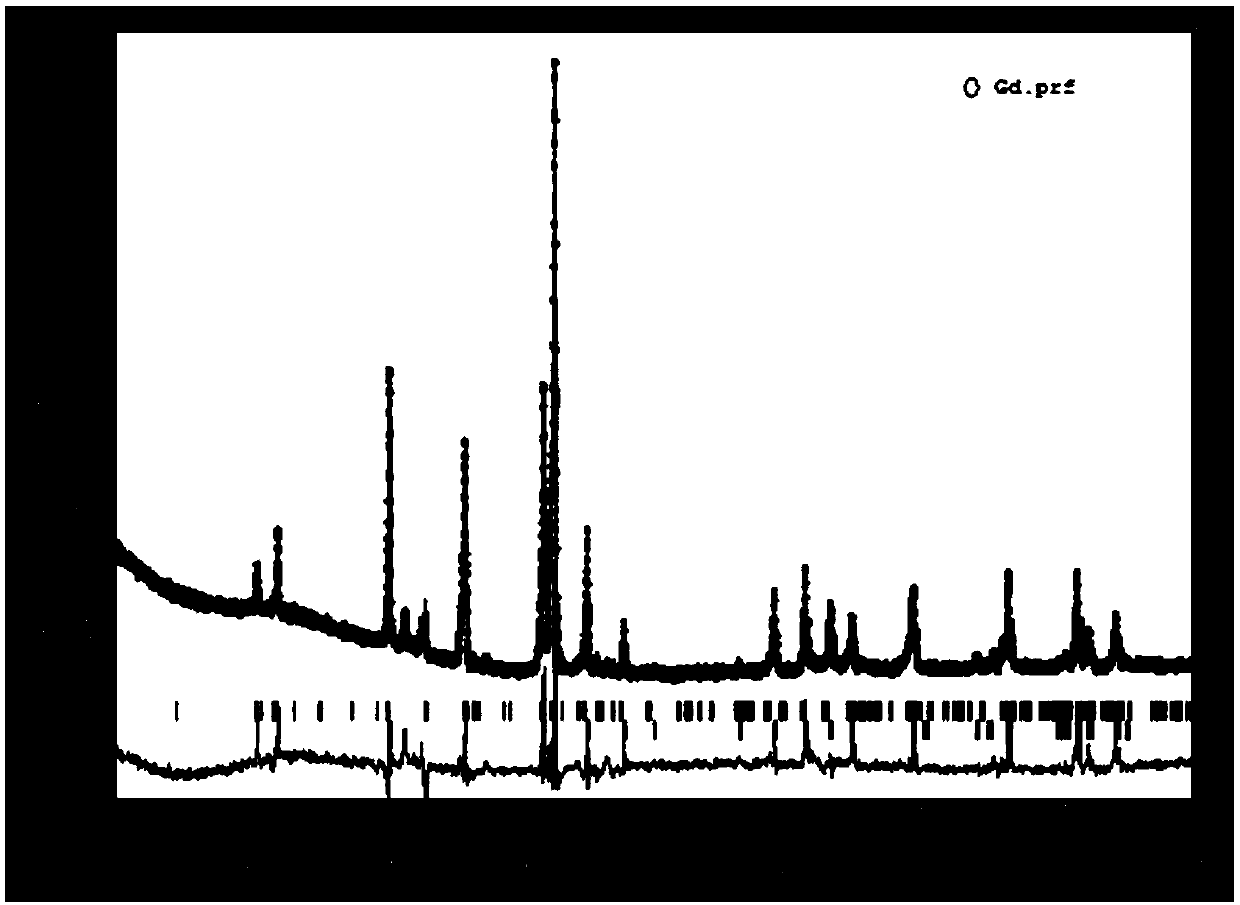
[0030] Set La(3.0~3.2)x Ce x Zr y SM (1-(4.0~4.2)x-y) Ni z co u mn v Al w The hydrogen storage alloy contains La 7.79at%, Ce 2.49at%, Zr 0.46at%, Sm 5.39at%, Ni 71.60at%, Co 2.63at%, Mn 4.08at% and Al 5.64at%, among which the elements La, Ce , Zr, and Sm are A-side elements, and elements Ni, Co, Mn, and Al are B-side elements, thus forming AB 5 Type hydrogen storage alloy La 0.50 Ce 0.16 SM 0.34 Zr 0.03 Ni 4.57 co 0.17 mn 0.26 Al 0.36 . Among them, by fixing the atomic number ratio of La and Ce to about 3.1 to meet the overcharge performance of the electrode material, a large number of Sm elements are replaced on the A side, that is, the Sm atomic ratio accounts for about 33% of the A side, thereby overcoming the low The problem of reduced lifespan caused by Co; use the ratio of Sm to La and Ce to adjust the equilibrium voltage to meet the charge-discharge kinetics of the electrode material; the A-side element is added with an atomic ratio of about 2.9% relative...
Embodiment 2-18
[0037] The hydrogen storage alloy is obtained by low vacuum induction melting method, cooling method and annealing treatment.
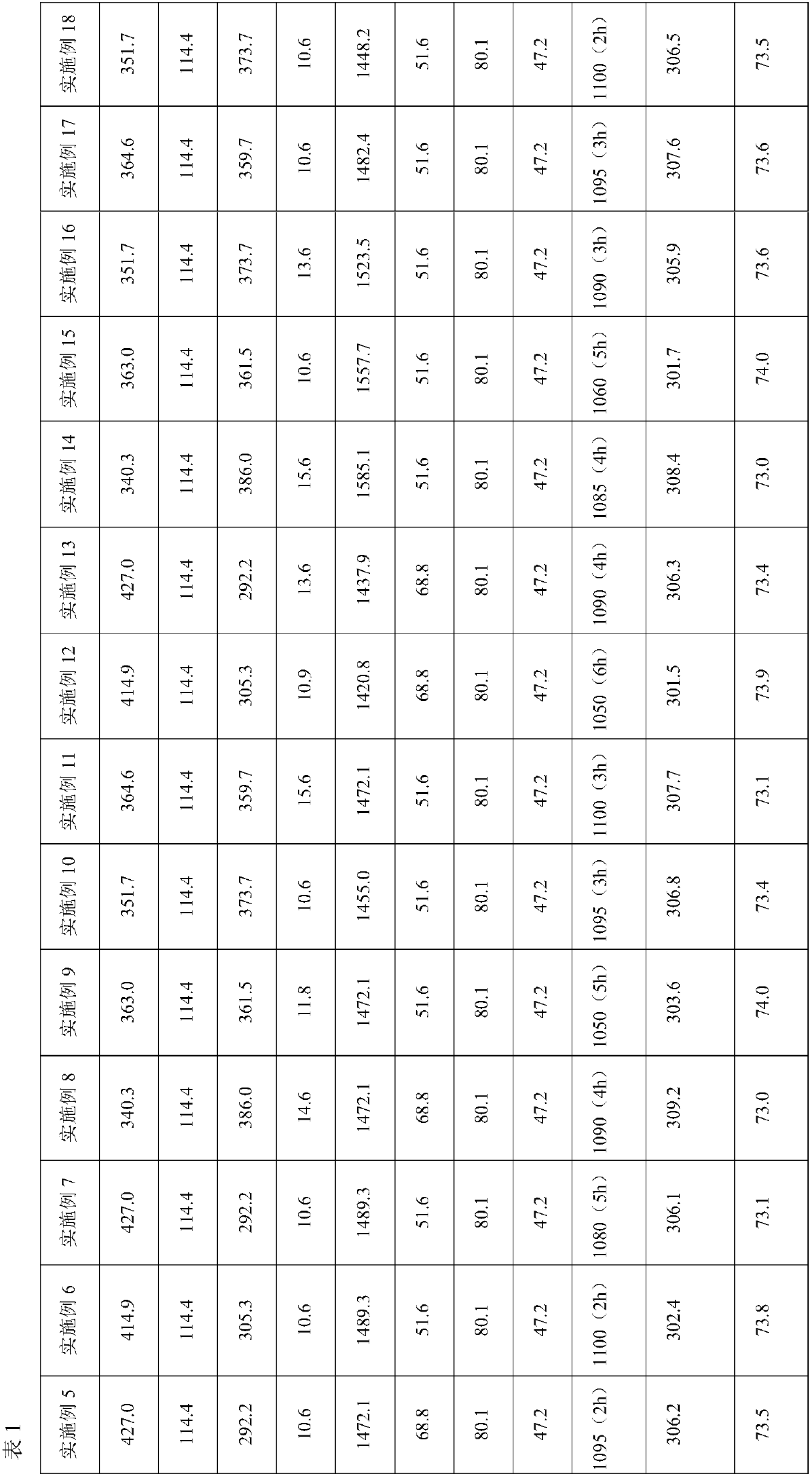
[0038] Weigh each element according to the composition of following Table 1, carry out heat treatment to its alloy ingot with ZG type vacuum induction melting electric furnace in argon atmosphere, then cool, the specific steps of this heat treatment and the step of cooling are the same as the steps of embodiment 1 ( 1), then carry out annealing treatment, in the specific process of annealing treatment, except heat treatment temperature, other process conditions are identical with the step (2) of embodiment, its heat treatment temperature, time, 120mA / g discharge capacity and 5C discharge capacity The percentages are shown in Table 1 below:
[0039]
[0040]
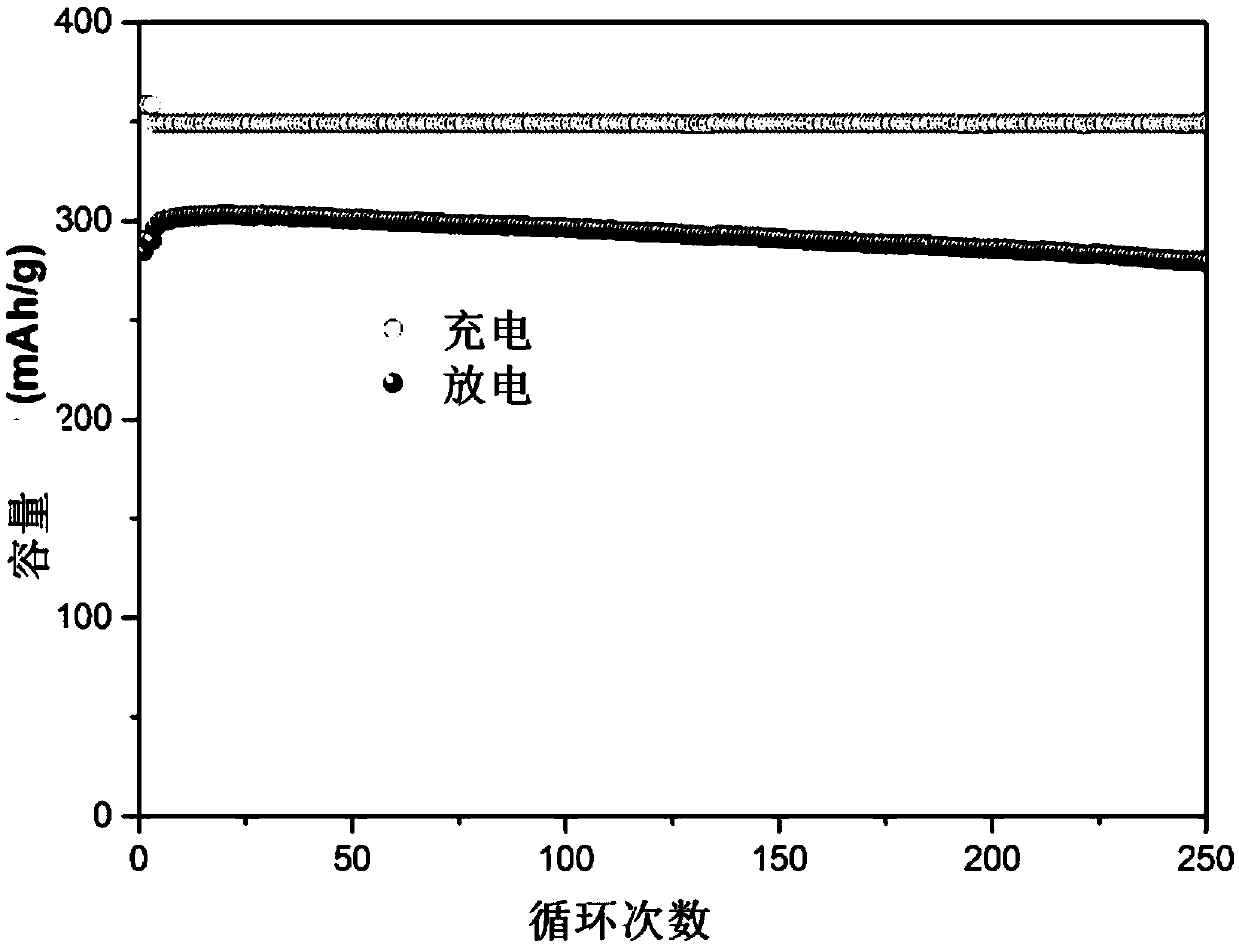
[0041] To the nickel-hydrogen battery negative electrode material La prepared in embodiment 1 0.50 Ce 0.16 SM 0.34 Zr 0.03 Ni 4.57 co 0.17 mn 0.26 Al 0.36 The charge and discharge t...
Embodiment 19
[0045] Step (1) Place pure metals 362.0g La, 120.0g Ce, 395.0g Sm, 11.4g Zr, 1429.0g Ni, 50.0g Co, 82.8g Mn and 50.0g Al in an induction melting furnace (ZG type vacuum induction furnace, The same below.) In the crucible, cover the furnace cover and evacuate until the vacuum degree is 10 -1 Pa, filled with argon to a pressure of 0.07MPa, smelted at 1550°C for 2 hours to obtain a metal smelting solution; pour the metal smelting solution into a water-cooled ingot mold, cool it out of the furnace, and obtain an alloy ingot;
[0046] Step (2) Place the alloy ingot of step (1) in a protective atmosphere furnace, and vacuumize to a vacuum degree of 10 -1 Pa, filled with argon to a pressure of 0.08MPa, and annealed at 1020°C for 10h to obtain a magnesium-free A 2 B 7 Type Catalyzed AB 5 Ni-MH battery anode material La 0.42 Ce 0.14 SM 0.42 Zr 0.02 Ni 3.92 co 0.14 mn 0.24 Al 0.30 ;
[0047] the above La 0.42 Ce 0.14 SM 0.42 Zr 0.02 Ni 3.92 co 0.14 mn 0.24 Al 0.30 Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com