Method for detecting E6 or E7 nucleic acid of HPV16 or HPV18 virus based on RPA
A detection method and nucleic acid technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve problems such as physical trauma, uterine loss or bleeding, false negatives, etc., to achieve convenient use and detection. The effect of short time and mild detection conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] This example is used to verify the RPA reaction amplification effect of the screened RPA primers directed against the E6 or E7 nucleic acid of HPV16 or HPV18 virus.
[0076] In this embodiment, a plasmid DNA containing E6 or E7 nucleic acid against HPV16 or HPV18 virus was selected as a template for detection. The specific sequence is as follows:
[0077] E6 of HPV16:
[0078]
[0079] E7 of HPV16:
[0080]
[0081] E6 of HPV18:
[0082]
[0083] E7 of HPV18:
[0084]
[0085] The sequence with a horizontal line is the screened RPA primer for E6 or E7 nucleic acid of HPV16 or HPV18 virus.
[0086] Select the corresponding primers to configure the RPA reaction system according to different target genes. RPA reaction system includes 2.4 μl pre-primer (10 μM), 2.4 μl post-primer (10 μM), 29.5 μl RPA buffer (from TwistDx company), 2 μl detection sample (containing 10 ng plasmid DNA), 11.2 μl double distilled water, 2.5 μl magnesium acetate (280mM); Once ...
Embodiment 2
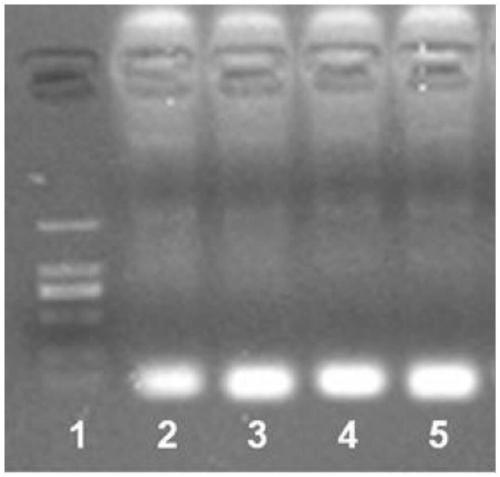
[0095] This example is used to verify the specificity of the RPA primers screened against the E6 or E7 nucleic acid of HPV16 or HPV18 virus.
[0096] According to different target genes, select non-corresponding primers to configure the RPA reaction system. RPA reaction system includes 2.4 μl pre-primer (10 μM), 2.4 μl post-primer (10 μM), 29.5 μl RPA buffer (from TwistDx company), 2 μl detection sample (containing 10ng plasmid DNA or 1000ng human genomic DNA), 11.2 μl double distilled water , 2.5 μl of magnesium acetate (280 mM); once the magnesium acetate is added, the reaction starts timing.
[0097] The RPA reaction was carried out at 37°C for 30 minutes. After the reaction, it was observed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Such as image 3 As shown, the screened primers could not amplify non-corresponding HPV nucleic acid components and human genome, demonstrating the specificity of the method.
[0098] Such as image 3 As shown, the specificity verification of the RPA...
Embodiment 3
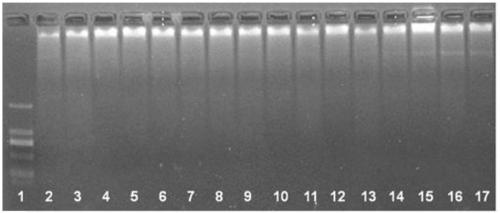
[0105] This embodiment is used for the sensitivity verification of the RPA primers screened against the E6 nucleic acid of HPV16.
[0106] The RPA reaction system includes 2.4 μl pre-primer (10 μM), 2.4 μl post-primer (10 μM), 29.5 μl RPA buffer (from TwistDx company), 2 μl detection sample (containing plasmid DNA with different copy numbers), 11.2 μl double-distilled water, 2.5 [mu]l magnesium acetate (280 mM); once the magnesium acetate was added, the reaction was timed. Both primers and templates are directed against E6 nucleic acid of HPV16.
[0107] The RPA reaction was carried out at 37°C for 30 minutes. After the reaction, it was observed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the method can amplify plasmid DNA containing 10 copies of the target nucleic acid, demonstrating the high sensitivity of the method.
[0108] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the schematic diagram of the sensitivity verification of the screened RPA primers against the E6 nucl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com