Modulation of the gut microbiome to treat mental disorders or diseases of the central nervous system
A therapeutic, disease-based technology applied in the field of modulating the gut microbiome to treat psychiatric or central nervous system disorders, able to address issues such as microbiological limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0304] Example 1: Human feces collection
[0305] Fecal samples from healthy human donors were collected using commercially available fecal collection containers. Within 5 minutes of collection, 1 gram of feces was resuspended in 9 mL of sterile 20% glycerol in PBS and homogenized using a vortex for 30 seconds. 1 mL aliquots of this mixture were loaded into cryovials and stored at -80°C for incubation.
Embodiment 2
[0306] Example 2: Culture of Helper-Uncultured Pairs from Human Fecal Samples
[0307] All cultures were carried out in a Coy Anaerobic Vinyl chamber with 5% hydrogen and 10% CO 2 , Executed in an environment of 85% nitrogen. Serial dilutions of thawed fecal samples were prepared anaerobically in PBS and beads dispersed (7-10 beads / plate) on 1X Fastidious Anaerobic Agar (Accumedia) (FAAy) plates with 2.5% yeast extract. Plates were incubated anaerobically at 37°C for one week, and the daily appearance of colonies was followed by dotting the outside of the plate with different colored marker pens. At the end of the week, serial dilutions of late-forming colonies (appearing after 4-7 days) were prepared in PBS and beads dispersed on FAAy plates. Adjacent (< 2 cm), early-forming colonies (formed in 1-3 days) were resuspended at high density in PBS. 5 µL of this suspension was spotted onto a plate with its corresponding dispersion candidate dependent and incubated indoors for u...
Embodiment 3
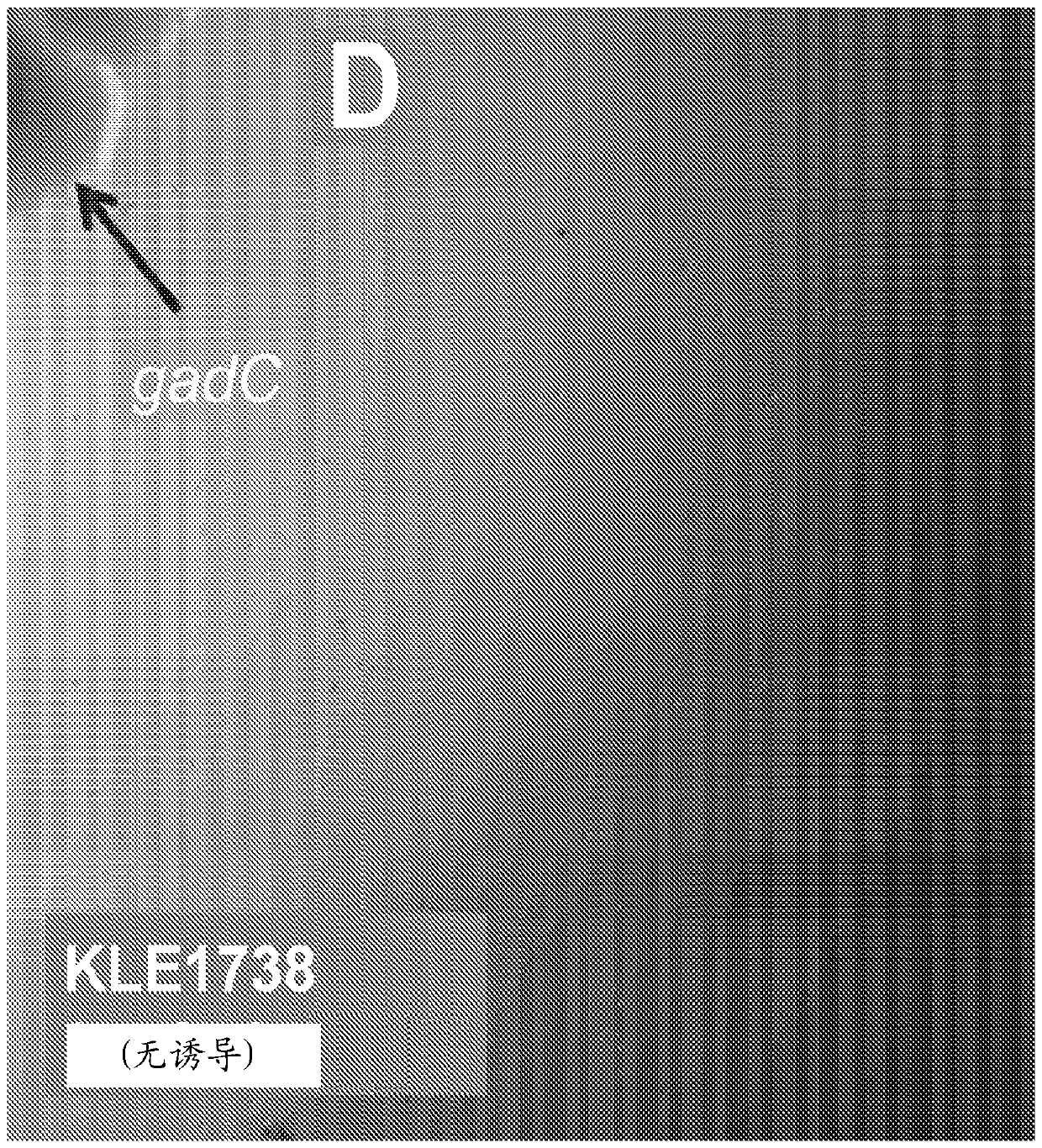
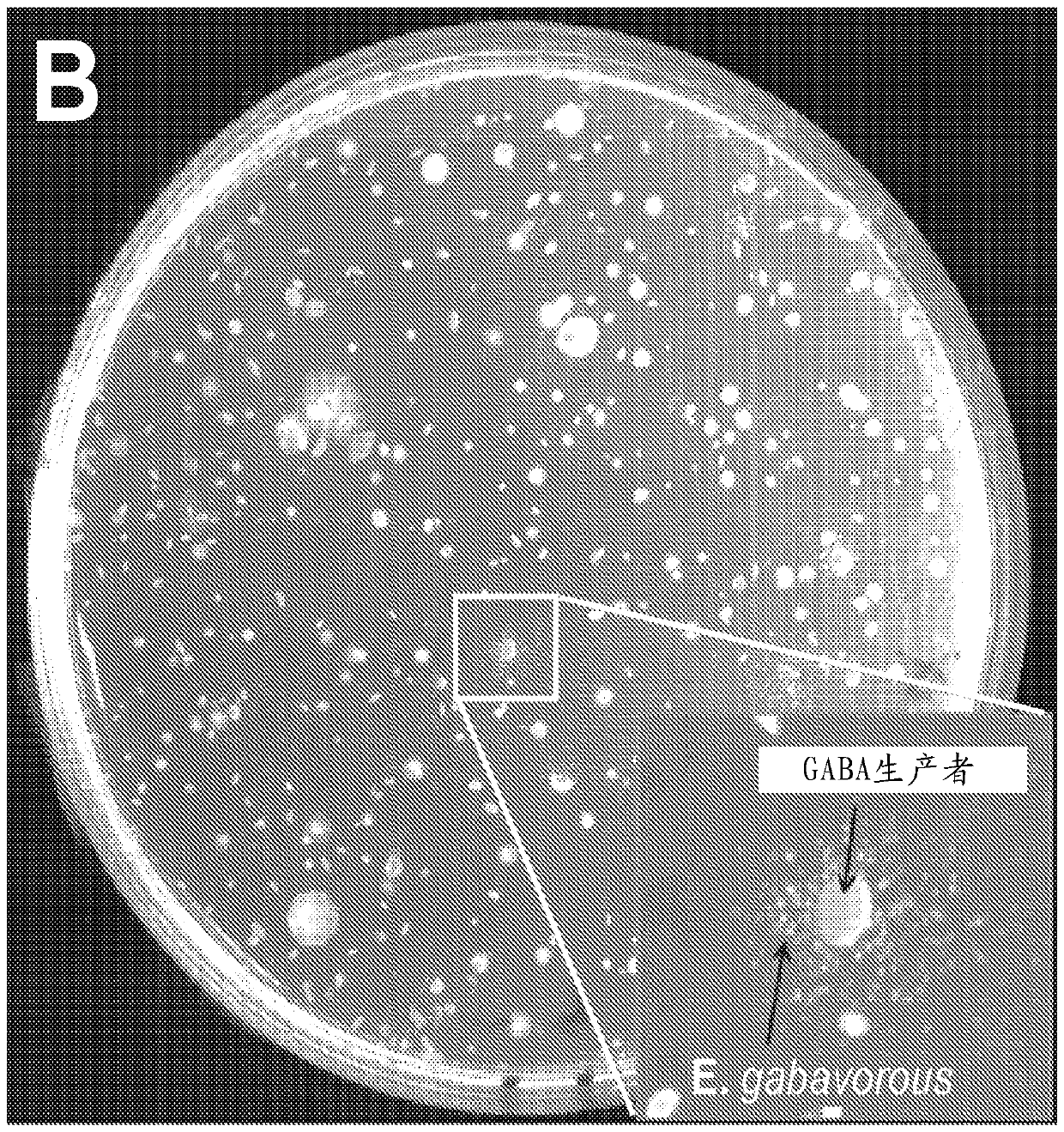
[0310] Example 3: Determination of GABA as a growth factor for E. gabavorous
[0311] like Figure 2A and 2B 48-hour cultures of B. fragilis KLE1758 grown in enriched medium are shown to induce growth of E. gabavorous, which enables bioassay-driven purification of growth factors. The supernatant was solvent-separated using ethyl acetate, and the residual fraction in water induced the growth of E. gabavorous. The aqueous fraction was subsequently purified using HP-20 column chromatography, and as Figure 2C Most of the polar fractions shown induced the growth of E. gabavorous. The active fraction was then further fractionated by preparative HPLC. HPLC yielded an active fraction and NMR showed 10 compounds, mainly GABA, threonine, lactate, valine, glutamine, malonate, succinate and alanine. All the compounds were spotted on the plate with E. gabavorous dispersed, and only GABA caused induced growth, as Figure 2E -F shown. Compounds were identified by NMR analysis, which ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com