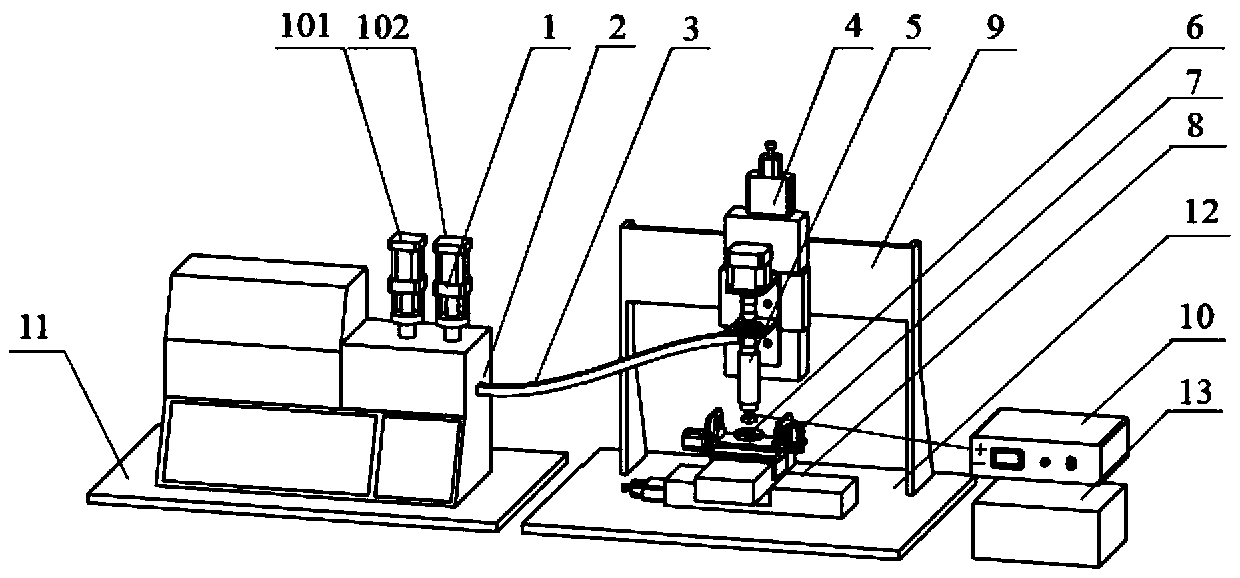
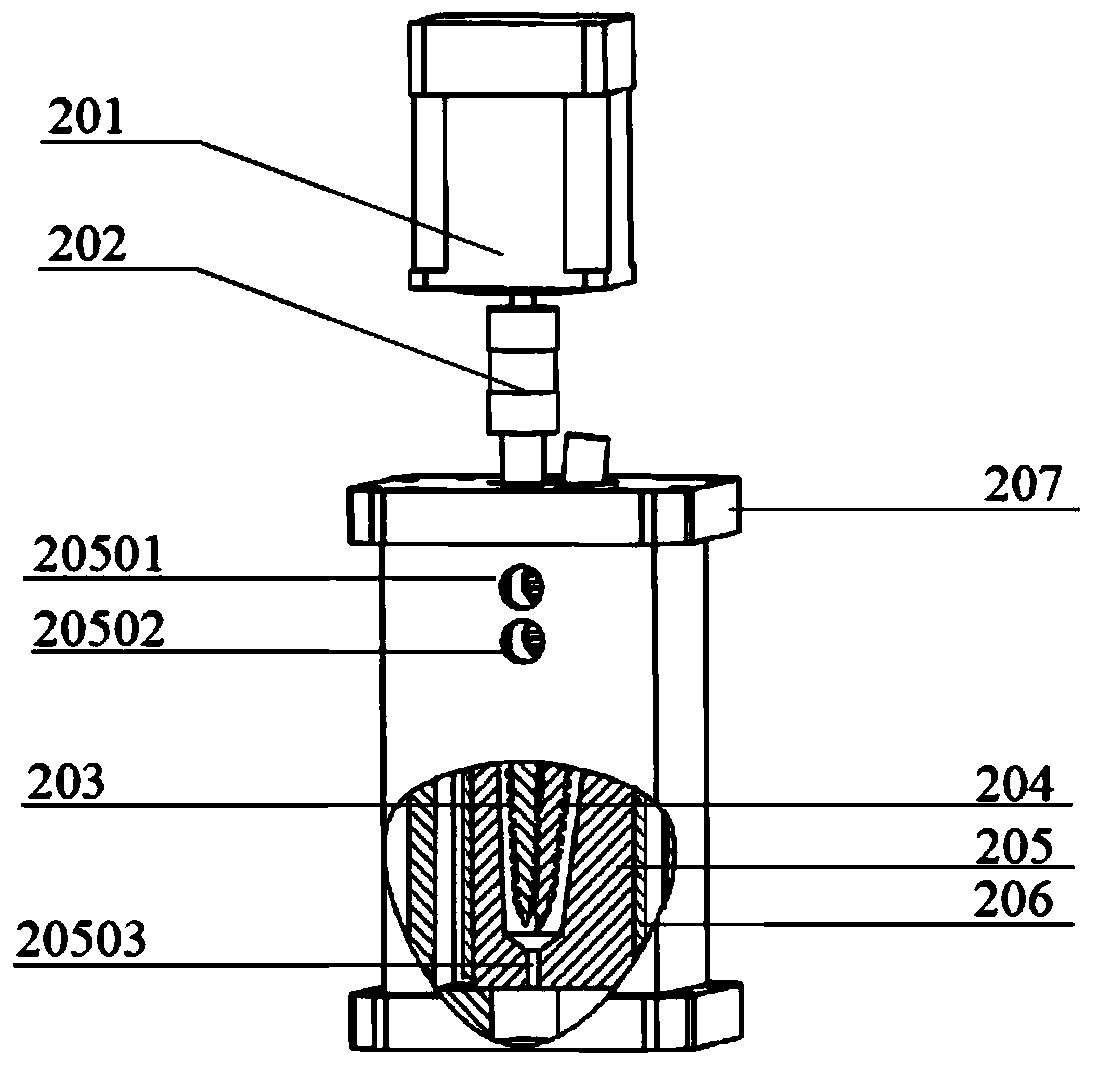
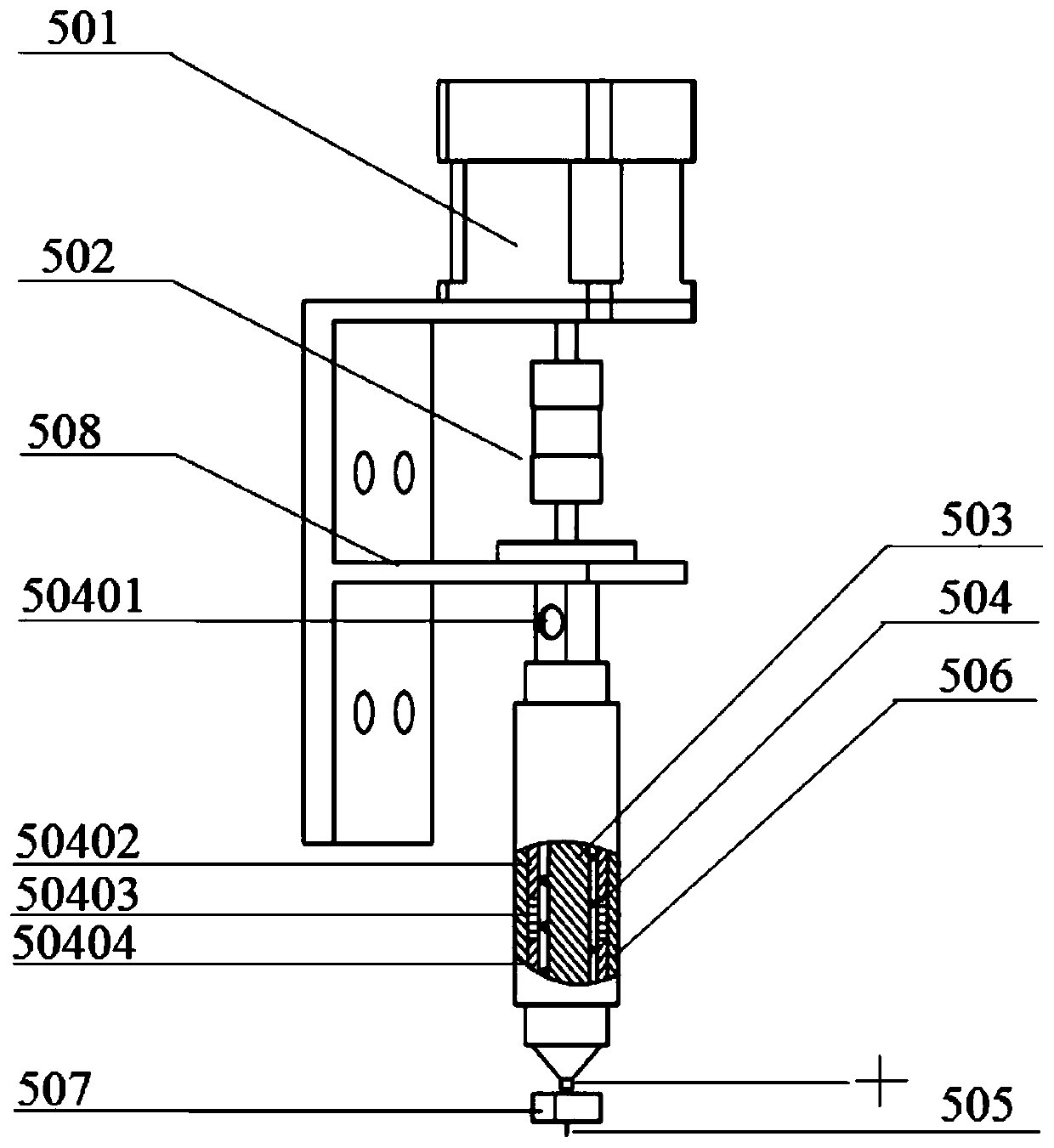
[0006] According to the existing research results and information that have been published at home and abroad, the 3D printing technologies and processes that have been proposed for the manufacture of functionally graded materials / structural parts mainly include: directed energy deposition (LENS),
laser cladding, and
fused deposition modeling (FDM). ,
polymer injection (Polyjet),
powder bed fusion, etc., but, according to the research of the inventor, it is found that these existing 3D printing technologies still have many defects and deficiencies when manufacturing functionally graded materials / structural parts: (1) Inhomogeneous mixing of ingredients
These existing technologies do not provide a dedicated mixing unit (especially
active mixing of materials), resulting in uneven mixing, which leads to the inability to prepare real high-performance functionally graded materials / structural parts
For example, the existing LENS,
laser cladding, FDM and other technologies mostly adopt the integrated
nozzle / print head structure, and it is completely impossible to achieve uniform mixing of multiple materials in the integrated
nozzle, especially LENS and
laser cladding materials are the components of materials. After spray deposition, the mixing is carried out in the
molten pool, and the
mixing effect is even worse
The multi-
nozzle structure used in the
polymer jetting process is also the mixing of multiple materials before they are solidified after deposition, which cannot achieve complete and uniform mixing of multi-component materials
The
powder bed fusion process restricts its ability to achieve uniform mixing of materials (especially for the feeding method of
powder coating), and there is a serious problem of material waste; (2) various existing 3D printing technologies cannot realize continuous functional gradient materials / The manufacture of structural parts can only realize the manufacture of quasi-continuous functionally graded materials / components, and cannot produce functionally graded materials / components in the true sense; (3) The
processing accuracy is low, and all existing processes cannot achieve micro-scale functional gradients In the manufacture of structures, the minimum feature resolution is difficult to achieve below 100 microns, especially no technology can realize the manufacture of high-resolution feature structures below 20 microns; (4) These existing technologies are difficult to achieve due to the limitation of forming accuracy The manufacture of functionally graded materials or structural parts based on
microstructure changes is mostly realized by adjusting the composition ratio of materials to realize the manufacture of functionally graded materials or functionally graded structures; (5) it is impossible to realize the integrated manufacture of functionally graded materials and three-dimensional structures, Most of them are
integrated manufacturing of simple two-dimensional or 2.5-dimensional structures; (6) it is difficult to realize the manufacture of complex three-dimensional functionally graded structural parts; (7) the production efficiency is low and the stability of the manufacturing process is poor, such as LENS, laser cladding, FDM, etc., due to During the printing process, the material ratio is constantly changing, and the printing process parameters (laser power, nozzle
heating temperature, etc.) must also be adjusted accordingly, resulting in poor process stability and low printing efficiency in the entire printing process; The mixing and printing functions are integrated, and a strict sequence and synchronization relationship must be ensured for feeding, mixing and printing, otherwise it will be difficult to successfully print out the required functionally gradient materials and molding structures, and the improvement of
processing efficiency will be greatly limited;( 8) The types and shapes of available printing materials are limited, and the printing materials need to be processed into the required shape and size in advance
For example, the current materials suitable for LENS and laser cladding processes are basically powder and wire, and there are strict restrictions on the shape and geometric dimensions of powder and wire; FDM is currently suitable for wire, and its geometry The size is also strictly limited;
polymer injection is currently only suitable for very low-
viscosity photosensitive resin materials;
powder bed fusion is suitable for powder materials, and its geometry and size have stricter restrictions; (9) Each
manufacturing technology is suitable for There are also strict restrictions on suitable forming materials. LENS, laser cladding and
powder bed fusion technologies are mainly used for
metal-based functionally graded materials and structure manufacturing. FDM is mainly used for
thermoplastic-based functionally graded materials / structures. Polyjet is mainly used for Manufacturing of photocurable resin-based functionally graded materials / structures; (10) equipment and processes are complex and production costs are high
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More