Patents
Literature
71 results about "Functionally gradient material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
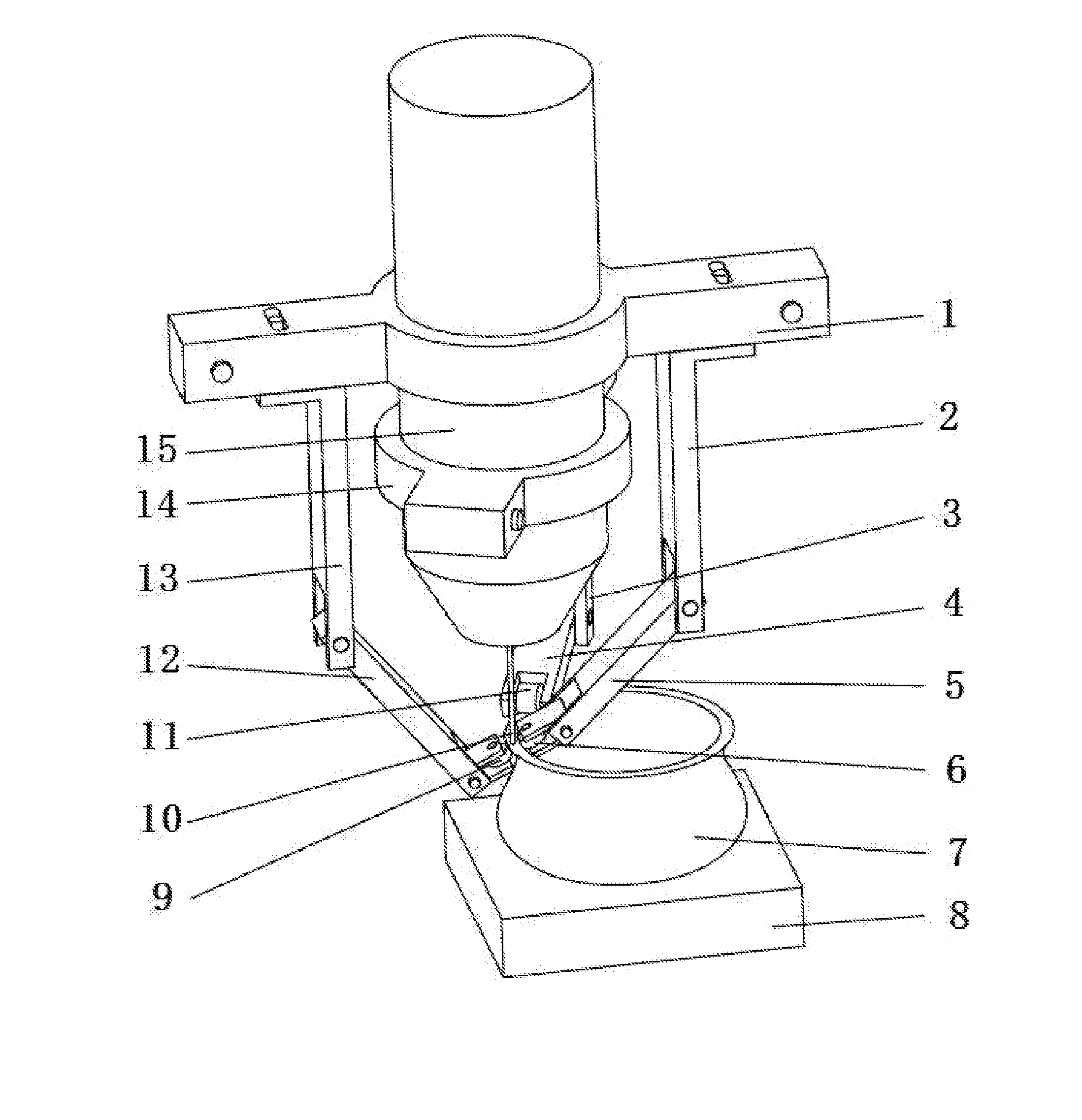
Method for manufacturing metal parts and molds and micro-roller used therefor
ActiveUS20130197683A1Formability of complexImprove accuracyArc welding apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsNumerical controlWire rod
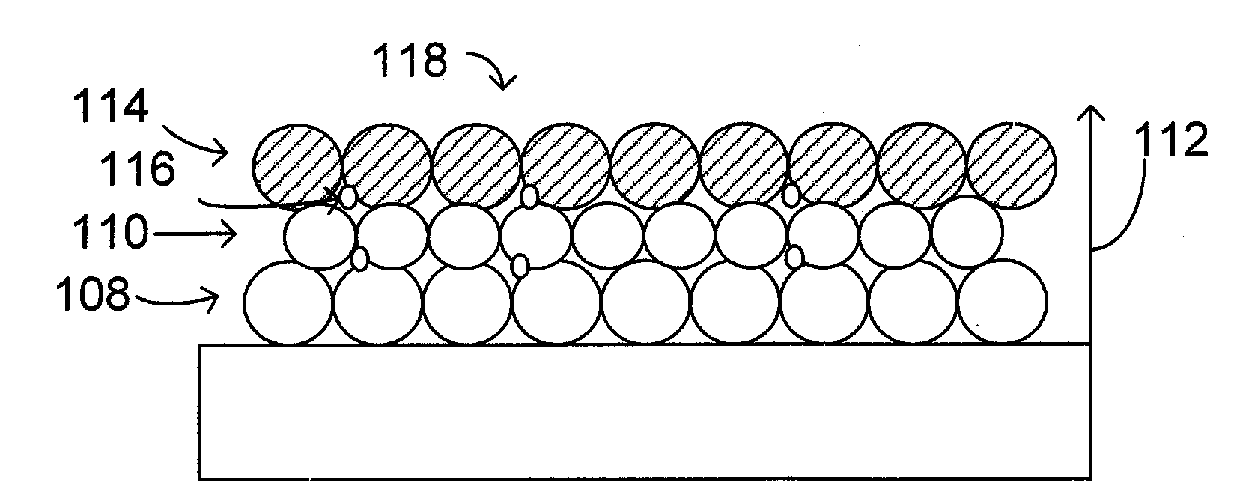
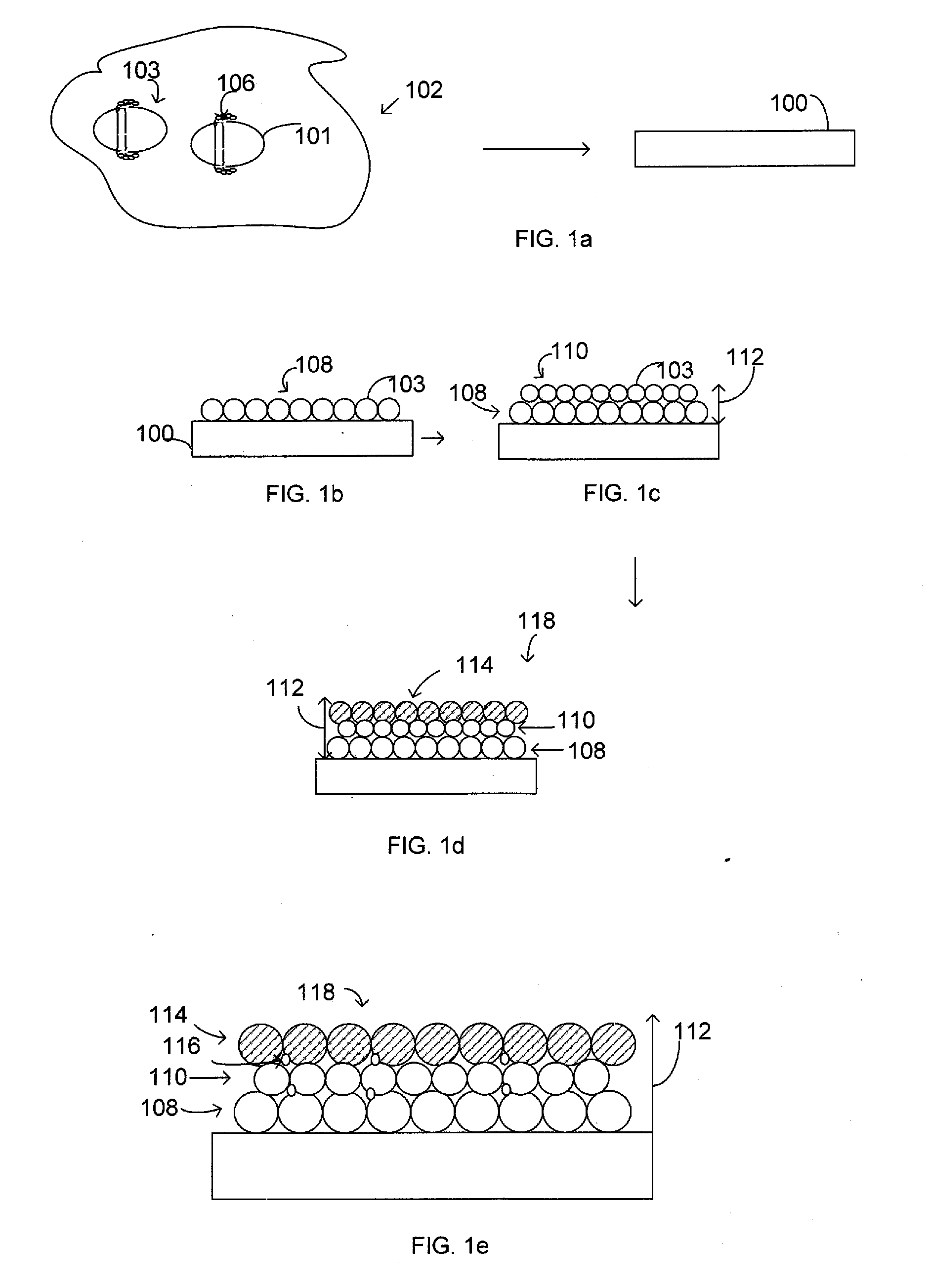
A method for manufacturing parts and molds by: 1) slicing a three-dimensional CAD model of a part or mold; 2) planning a modeling path according to slicing data of the three-dimensional CAD model, whereby generating numerical control codes for modeling processing; and 3) performing fused deposition modeling of powders or wire material of metal, intermetallic compounds, ceramic and composite functional gradient materials by layer using a welding gun on a substrate layer via a numerical control gas shielded welding beam or laser beam according to a track specified by the numerical control code for each layer. A micro-roller or a micro-extrusion unit is installed at a contact area between melted and softened areas. The micro-roller or the micro-extrusion unit synchronously moves along with fused deposition area, which results in compressing and processing of the fused deposition area during the fused deposition modeling.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing tungsten/copper functional gradient material by infiltration - weld method
InactiveCN1593818AEasy to prepare and effectiveSolve thermal stressMetal layered productsFritGradient material
The invention relates to a new method of making tungsten-copper functional gradient material, which consists of pure tungsten layer and tungsten-copper gradient transit layer. First, make the gradient hole-framework with boring fluid of percent 5~80 volume ratio and tungsten powder of 1~20 micron. Infiltrate copper fluid to make the tungsten-copper gradient transit layer. Weld the W / Cu gradient layer and the pure tungsten by hot pressure. The process is following: mix the material and mould them, then frit framework, Infiltrate copper, weld and check. The method has both the advantage of melt-casting technique and jointing technique. The tungsten-copper functional gradient material made by this method is better heatproof and suited to electric sealing material, heat sinking material, and anti-high temperature plasma scouring unit such as the first layer material in nuclear fusion.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method and device for auxiliary heating type ultrasound rapid forming
ActiveCN103600166AAvoid formingGuaranteed solid phase junction propertiesNon-electric welding apparatusNumerical controlMetal foil
The invention belongs to the technical field of rapid forming, and particularly relates to a method for achieving multilayer bead welding of metal foil strips through combination of extra auxiliary heating and ultrasonic welding. According to the method, preheating is conducted on metal foil or a base body material in rapid forming, the metal foil or the base body material is softened through preheating conducted by an external heating field, good gas protection is provided, and the welding thickness and width of a metal foil sheet are increased under the condition that the ultrasonic welding power is limited, so that multilayer one-time ultrasonic bead welding or multilayer multi-time ultrasonic bead welding of the metal foil is achieved and a three-dimensional solid block is formed in the solid-phase connection mode. Finally, a machining platform controlled by a numerical control program is applied, so that geometrical characteristic machining of a needed part is achieved. A metal piece obtained according to the method has the advantages of being low in cost, high in efficiency, compact in organization, free of casting-state structure, capable of achieving rapid forming of a functionally gradient material and the like.
Owner:WEIHAI WANFENG MAGNESIUM IND DEV
No-mold fusion stacking manufacture method of parts or mold
InactiveCN101362272AReduce or eliminate dropReduce or eliminate droolingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusNumerical controlMelting tank
The invention relates to a method for die-free fused deposition modeling of a part or a die, which belongs to the method of die-free modeling, and solves the problems of falling, flowing and collapsing of fusing material in the process of support-free and die-free fused deposition modeling of the existing method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) hierarchy slicing processing is performed to the three-dimensional CAD model of the part or the die; (2) a computer generates numerical control codes required by the shaping of each hierarchy according to the hierarchy slicing data and the characteristics of the slicing size and shape of each hierarchy; and (3) numerically controlled gas-shielded welding arc or laser bean is adopted to fuse and shape the fusing material on the base plate in sequence according to the numerical control codes of each hierarchy, until the requirements on the size and the surface of the part or the die are met; simultaneously, electromagnetic field acting on the fusing material in the melting bath is generated through an electromagnetic device. By adopting the method, the part or the die made of metal, intermetallic compound, metal ceramics, ceramics and functionally gradient material can be quickly obtained with low cost and high quality.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing functional gradient material by adopting doctor-blade casting process
InactiveCN1460661AIncrease the areaChange the strength of the magnetic fieldOrganic solventGradient material
The method for preparing functional gradient material by adopting doctor-blade casting process includes the following steps: 1). mixing ceramic powder, strong-magnetic metal powder, organic solvent and additive according to a certain proportion, stirring them in ball-grinding machine to obtain uniform dispersed slurry material; 2) in the static magnetic field with magnetic field intensity of 0.1-5.0 Tesla making the slurry material into film by means of doctor-blade casting process; and (3) drying and sintering, and forming.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
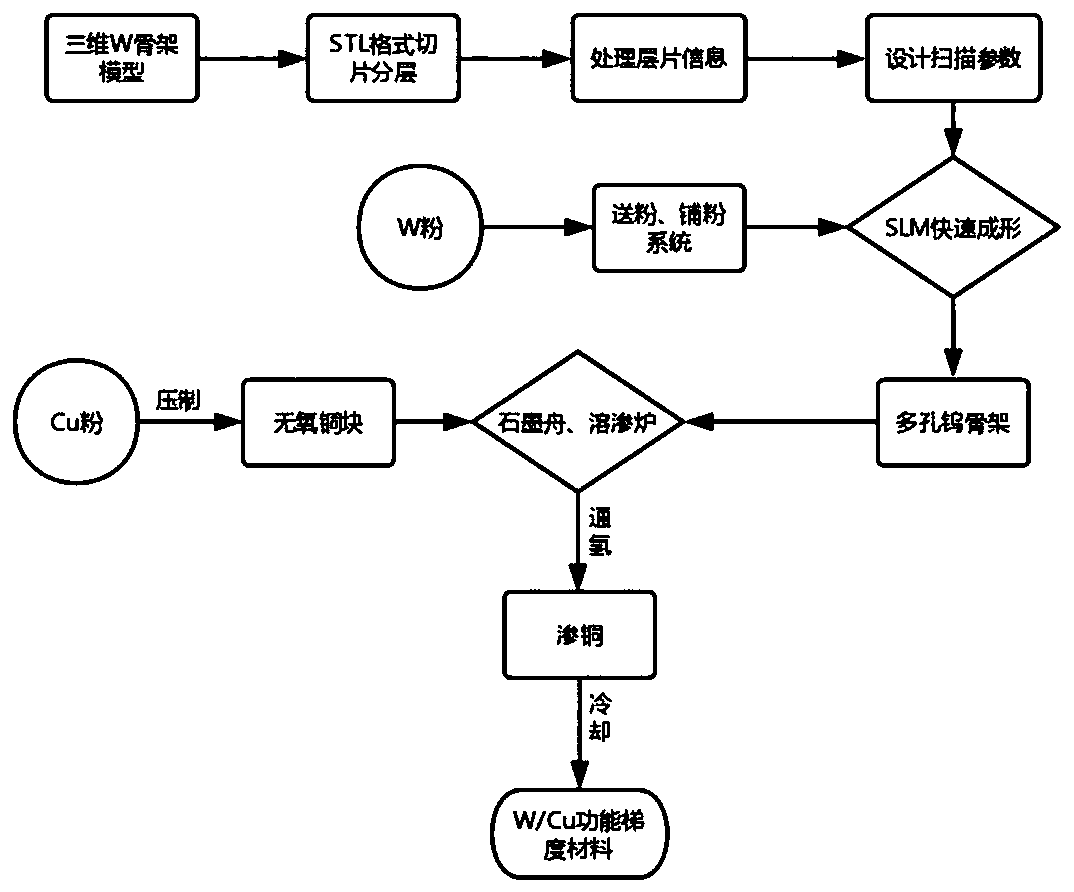
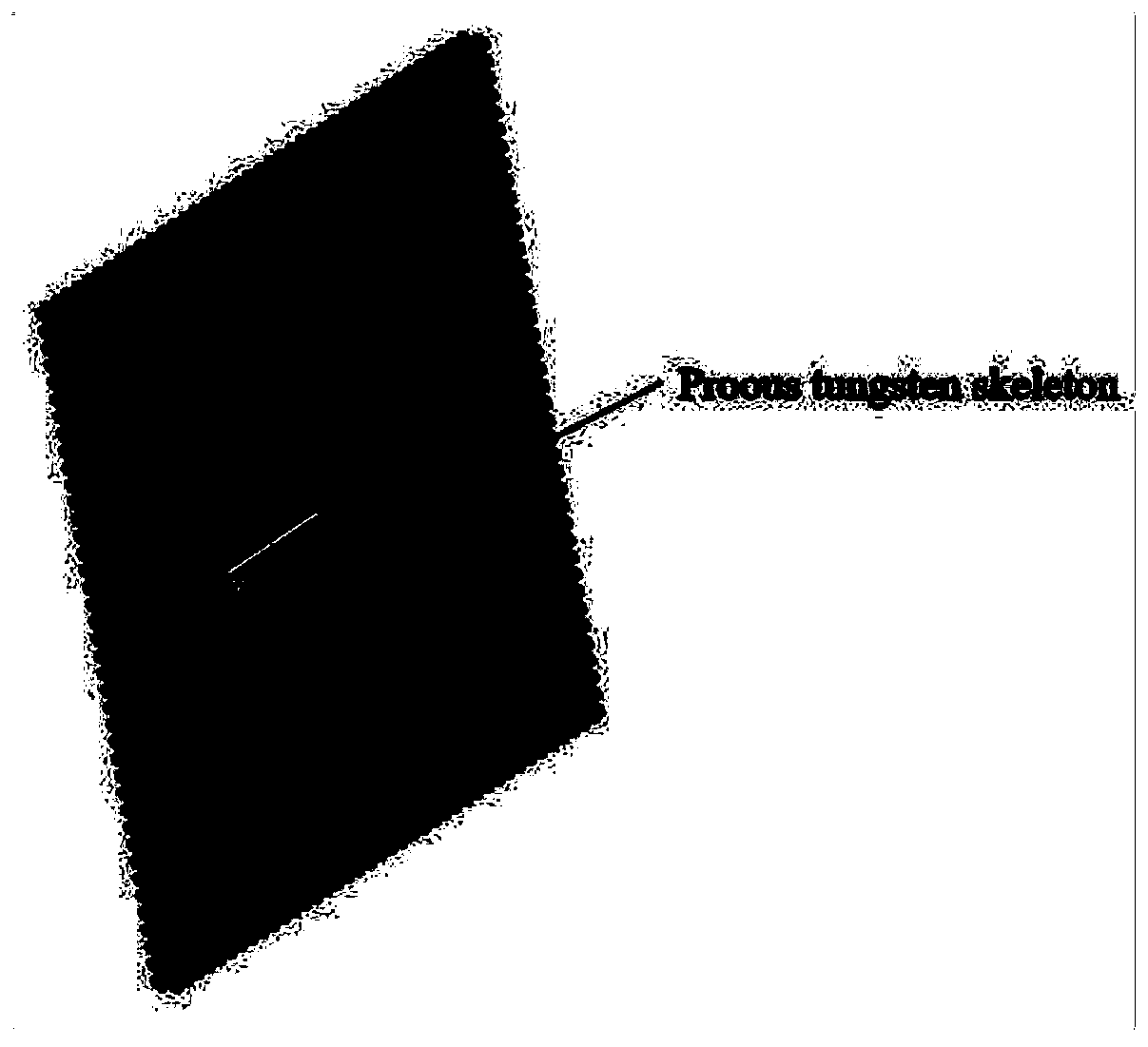
W/Cu functionally gradient material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109702200AOvercome various defects in processingImprove efficiencyManufacturing technologyGradient material
The invention discloses a W / Cu functionally gradient material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the fields of additive manufacturing technology and powder metallurgy. In terms of structure, the W / Cu functionally gradient material comprises a pure tungsten substrate on one side and a pure copper substrate on the other side, a gradient material is formed through copper infiltration ofa porous tungsten skeleton to connect the two substrates, wherein the porous tungsten skeleton is prepared by 3D printing, and then the porous tungsten skeleton copper infiltrated gradient material is prepared by a copper infiltration method; and the gradient material is prepared from the elements in percentage by mass: 50% of W and 50% of Cu. The W / Cu functionally gradient material adopts a digitalized additive manufacturing technology, a porous tungsten skeleton complex structure can be quickly formed, uniform distribution and mass gradient distribution of tungsten skeleton pores can be accurately controlled, and thus a novel technology means for preparing a properW / Cu functionally gradient material is provided.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN) +1
High-temperature polymer-based electromagnetic shielding functionally gradient material
InactiveCN103725000AImprove conductivityImprove electromagnetic shielding performanceMetallurgyWorking temperature
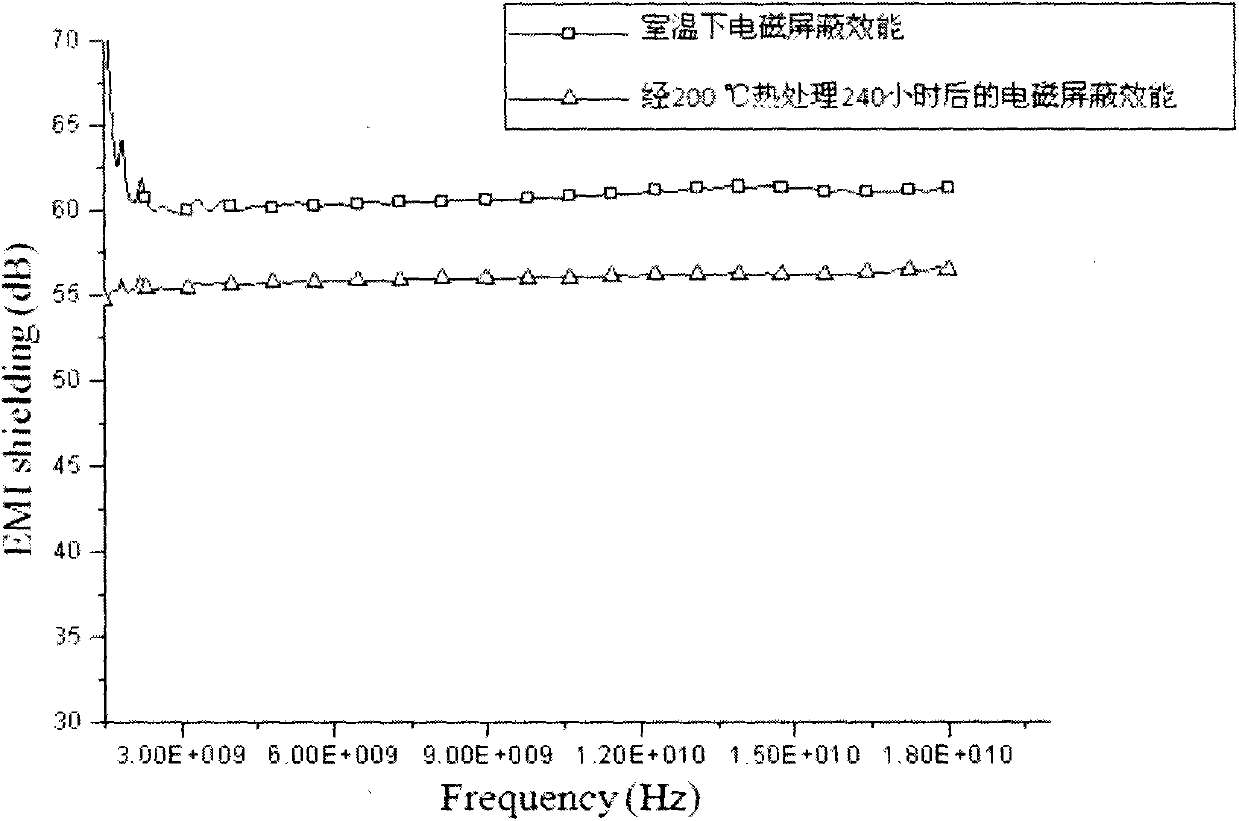
The invention discloses a high-temperature polymer-based electromagnetic shielding functionally gradient material. The material is characterized in that the content of filler changes in a gradient manner along the thickness direction of the material. The electromagnetic shielding property of the functionally gradient material can be up to 45-90dB; the long-time working temperature of the material is 150 DEG C, and over 85% of original electromagnetic shielding property still can be kept after thermal treatment at 200 DEG C for 240 hours. Therefore, the high-temperature polymer-based electromagnetic shielding functionally gradient material can be widely applied to the fields of protection of electronic equipment products with heat-resisting and electromagnetic shielding demands or other applications.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Methods to fabricate functionally gradient materials and structures formed thereby
InactiveUS20090087644A1Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFunctionalized nanoparticlesFunctionally gradient material
Methods and associated structures of forming microelectronic devices are described. Those methods may include forming a first layer of functionalized nanoparticles on a substrate by immersing the substrate in at least one of a solvent and a polymer matrix, wherein at least one of the solvent and the polymer matrix comprises a plurality of functionalized nanoparticles; and forming a second layer of functionalized nanoparticles on the first layer of functionalized particles, wherein there is a gradient in a property between the first layer and the second layer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
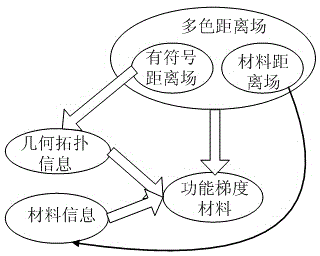
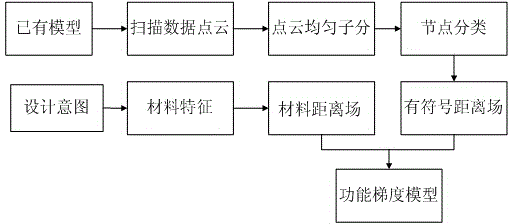
Function gradient material hidden model building method based on distance field
InactiveCN104361246AConvenience Boolean operationsSpecial data processing applicationsMaterial DesignAlgorithm
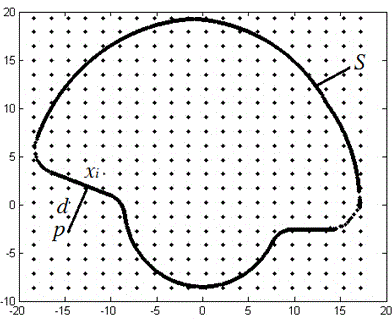
The invention provides a function gradient material hidden model building method based on a distance field. The method comprises the following concrete steps that (1) a geometric distance field is created: an entity prototype is measured, surface point cloud data is obtained, the point cloud data is a position coordinate value, a surrounding box is used for surrounding the position coordinate, the surrounding box is uniformly divided, and signed distance fields of the point cloud data of all dividing lattice top points in the surrounding box are calculated for displaying a geometric model of the entity; (2) a material distance field is created: the material features are determined according to the material design intention of the function gradient materials, so that the material distance field is calculated; (3) function gradient materials are subjected to hidden modeling. The functional gradient material geometric distance field and the material field modeling are creatively combined, and the hidden function mode of the distance field is used for completely expressing the geometric and material information. Through the self-adaptive characteristic of the distance field, the method is applicable to any complicated models, and the Boolean operation can be conveniently carried out.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
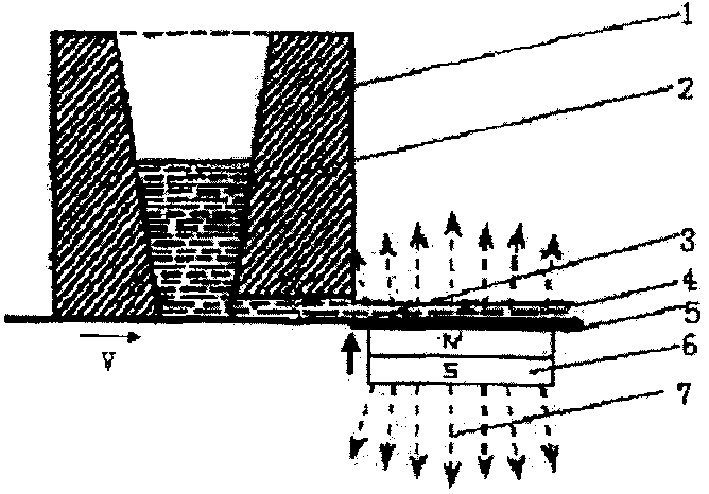
Self-spreading pre-heating powder aqueous medium bidirectional blasting and concreting device
InactiveCN101138788AReduce strong reflectionsImproving the quality of explosive consolidationShock waveSelf-propagating high-temperature synthesis
A two-way explosion concrete device of self-spread preheat powder aqueous medium is used for manufacturing a high-density hard concrete metal or ceramic compound materials and functionally gradient materials of the ceramic compound materials, which consists of a plane wave generator, a high grade energy main charge, a pressure work steel tube, a waterseal unit, a wave impedance match unit, an outer protection tub or a protective unit, a self-spread dust electrical heating unit and a protective unit of sample. The present invention is designed to provide the two-way explosion concrete device of self-spread preheat powder aqueous medium that can produce a high-energy explosive detonated by plane detonation wave produced by two plane wave generators with symmetry layout and two-way explosion by making use of aqueous medium to transfer a plane explosive shock wave and self-spread high temperature synthetic reaction preheat powder.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for ultrasonic auxiliary laser additive manufacturing of two-dimension titanium-based functional gradient material
ActiveCN111112619AEvenly distributedIncreased heterogeneous nucleation rateAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyGradient materialMolten bath
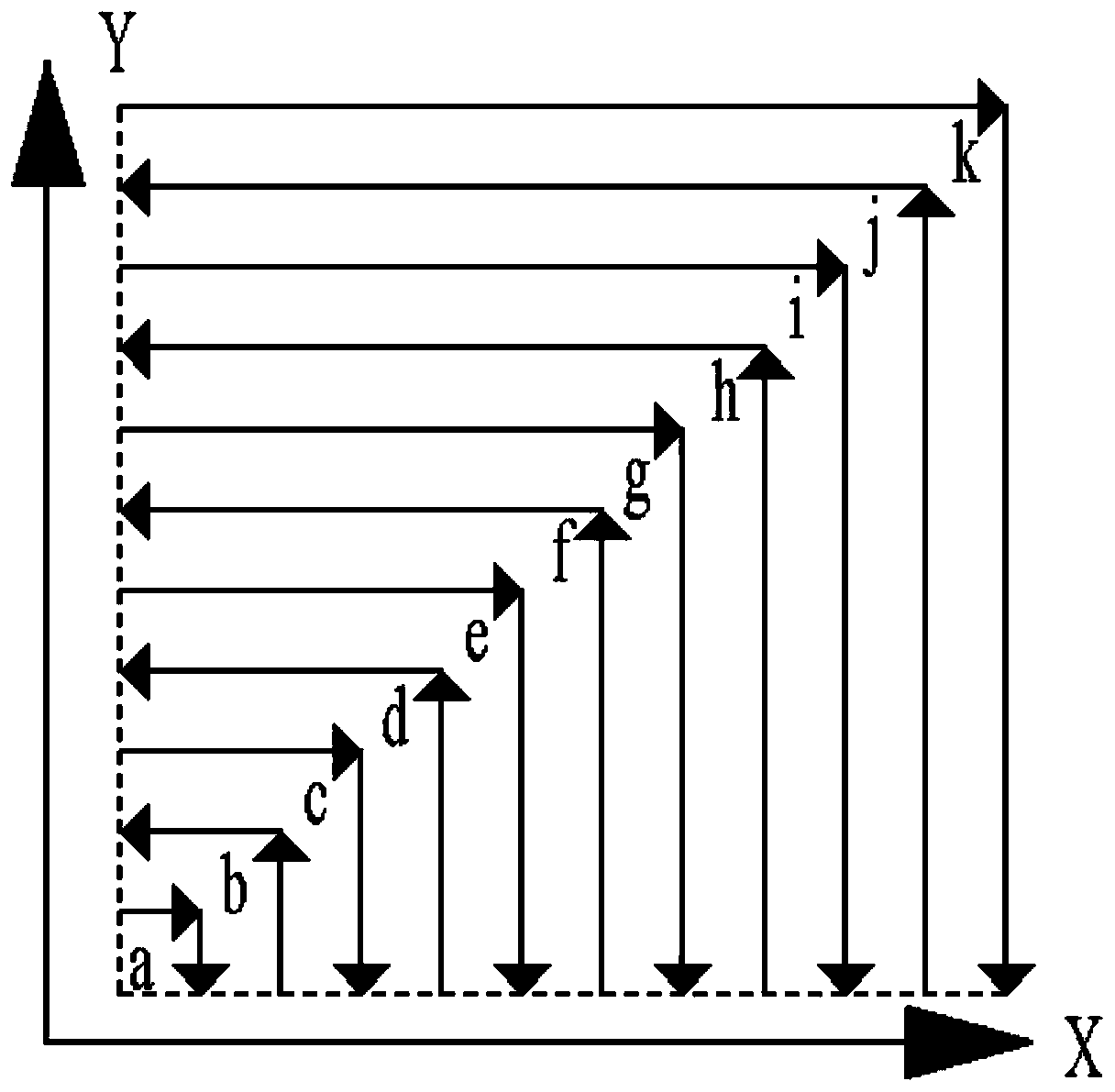
The invention discloses a method for ultrasonic auxiliary laser additive manufacturing of a two-dimension titanium-based functional gradient material, and belongs to the technical field of laser additive manufacturing. The two-dimension titanium-based functional gradient material is in one-dimension gradient transition in the XY and YZ plane and is in two-dimension gradient transition in space. According to the preset each-deposition-layer gradient transition form, the area a at the lower left corner is in 7-shaped transition to the area k at the upper right corner, accordingly, bottom ultrasonic is ensured, and sufficient interference is conducted on the molten bath flowing and solidifying process during high-proportion ceramic particle adding. In different gradient areas in the XY and YZplane, optimized direct laser deposition technological parameters and ultrasonic acting parameters are adopted, heat accumulation, the size and content of non-melted ceramic particles and the size ofa thick branch-shaped primary phase are reduced, and accordingly the integral performance of the titanium-based functional gradient material is improved. A laser head conducts scanning according to the 7-shaped path, the number of gradient combined interfaces between adjacent ways is reduced, and the integral performance of the titanium-based functional gradient material can be better improved. By means of the method, uniform distribution of the ceramic particles can be promoted, thick dendritic crystals are crushed, a microcosmic structure is refined, and accordingly the integral performanceof the two-dimension titanium-based functional gradient material is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of Ti3SiC2/SiC functionally gradient material
ActiveCN105541331AUniform and dense structureModerate combinationOxidation resistantFunctionally gradient material
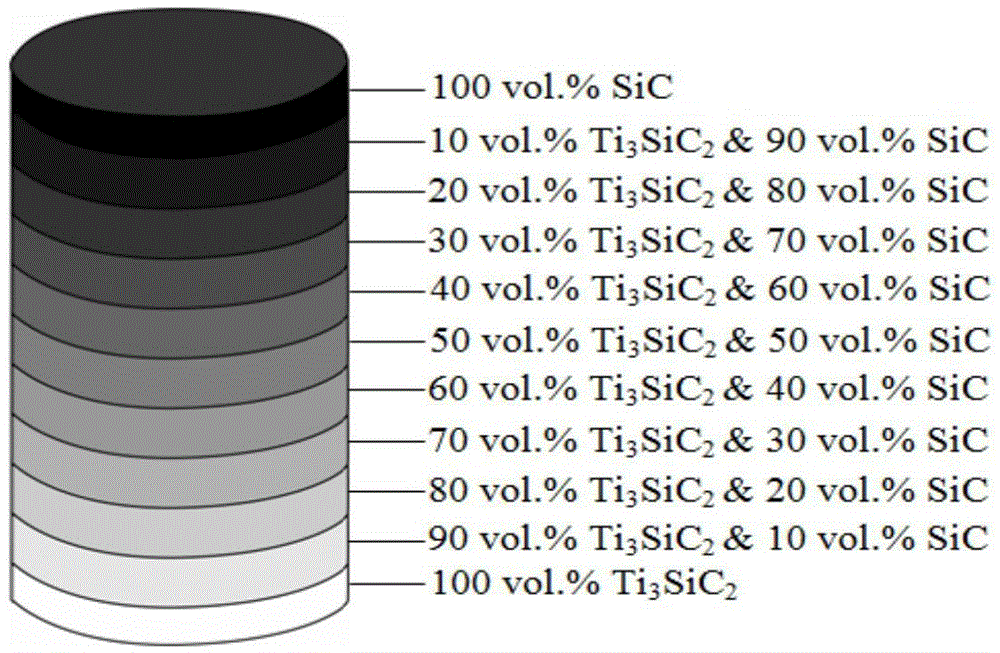
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Ti3SiC2 / SiC functionally gradient material, comprising the steps of mixing Ti3SiC2 powder and SiC powder in a die layer by layer in a gradient way, then preparing a blank, performing vacuum hot-pressing sintering on the blank to obtain a green body, and sequentially performing dipping densification and pyrolysis treatment on the green body; the SiC powder comprises micron beta-SiC powder and nanometer beta-SiC powder; the vacuum hot-pressing sintering temperature is 1600-1700 DEG C, and is kept for 3-5h, and the maximum pressure is 25MPa; the dipping densification comprises performing dipping densification on gradient layers containing 60-100 vol. percent of SiC in the green body subjected to the hot-pressing sintering in polycarbosilane liquid. The Ti3SiC2 / SiC functionally gradient material prepared by the method is high in compactness, contains multiple gradient layers along the thickness direction from Ti3SiC2 to SiC (designing can be performed as required), the structure is uniform and compact in each gradient layer, interfaces among the gradient layers are moderately combined, the mechanical strength is high, the breaking tenacity is good, under high temperature, the oxidation resistance and the thermal shock resistance are good, and the Ti3SiC2 / SiC functionally gradient material having 11 gradient layers and the thickness of 8-15mm can be prepared.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Method for molding hard alloy functionally gradient materials
ActiveCN104874797AImprove wear resistanceAccelerated corrosionTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusFunctionally gradient materialHardness
The invention discloses a method for molding hard alloy functionally gradient materials. The method includes mixing additives with alloy materials to obtain mixtures; carrying out compound pressure molding on the obtained mixtures in compound die groups to obtain blanks; sintering the blanks to obtain the hard alloy functionally gradient materials. The compound die groups comprise outer-layer dies with high expansion coefficients, intermediate transition-layer die groups and inner-layer dies with low expansion coefficients. The method has the advantages that the large and multi-component hard alloy functionally gradient composite materials which are of complicated contour structures and are free of obvious interfaces can be manufactured by the aid of the method; the sintered molded functionally gradient materials are provided with gradient grain structures along the thickness directions of the sintered molded functionally gradient materials, the gradient grain structures are provided with the different components, have different grain sizes and are free of obvious interfaces, and accordingly the molded hard alloy materials are excellent in comprehensive mechanical performance with high hardness, abrasion resistance, strength and toughness.
Owner:SEED TECH CORP LTD
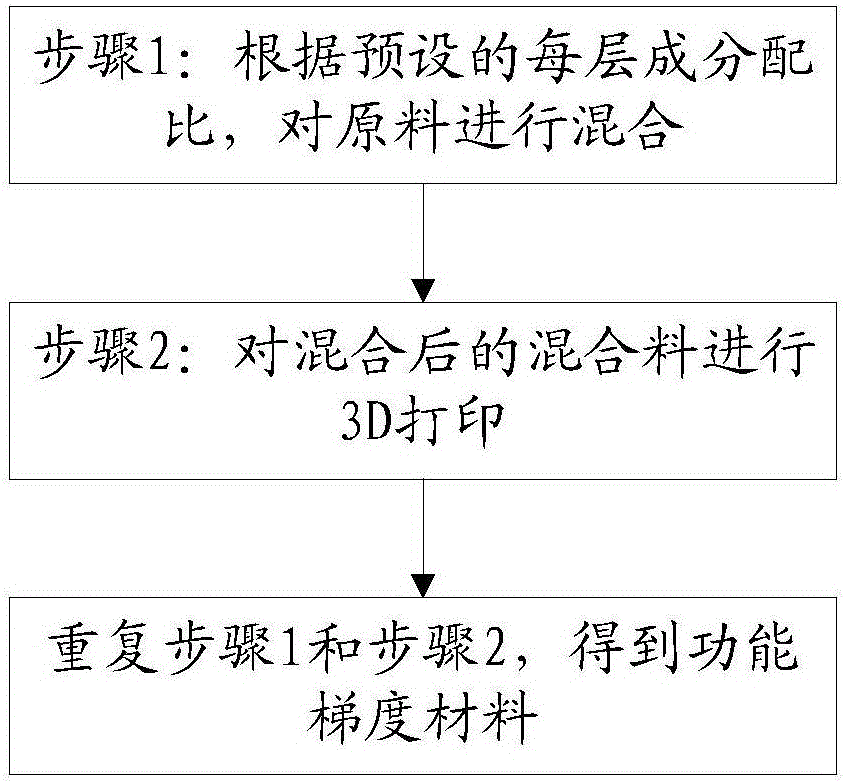
Functionally gradient material forming method and functionally gradient material forming device
InactiveCN106735211AReduce forming difficultyAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyFunctionally gradient materialMixed materials
The invention discloses a functionally gradient material forming method and a functionally gradient material forming device. The functionally gradient material forming method at least includes firstly, mixing raw materials according to a preset proportion of each layer of components; secondly, subjecting the mixed materials to 3D printing; thirdly, repeating the first step and the second step so as to obtain a functionally gradient material. The functionally gradient material forming method and the functionally gradient material forming device have the advantages that the raw materials are mixed firstly, the mixed materials are subjected to 3D printing, and complex three-dimensional processing is converted into simple two-dimensional processing, so that complex part forming difficulty is lowered greatly, and the functionally gradient material of a complex structure can be formed simply.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
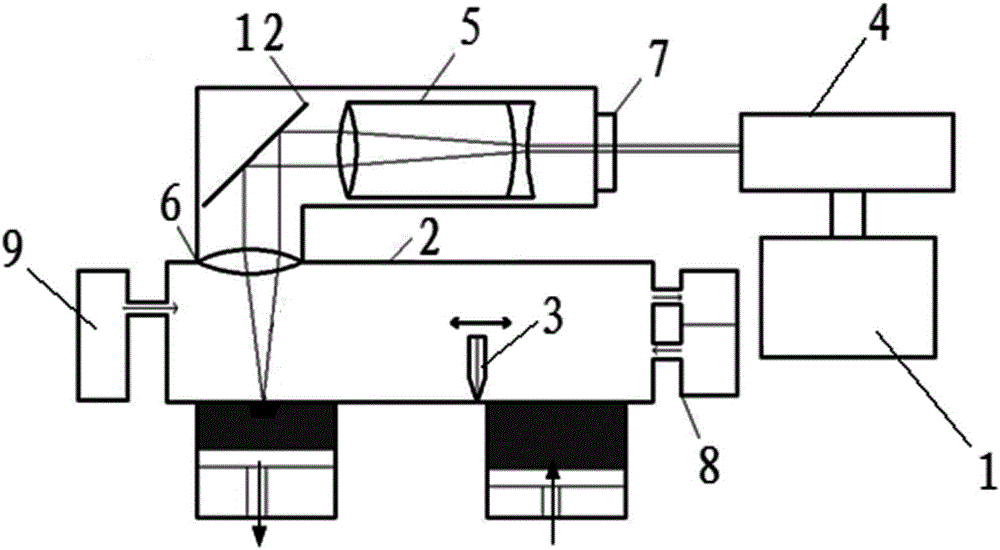
Coaxial wire-powder-gas-electric arc 3D printing method
ActiveCN105772719AReduce preprocessing timeWell mixedAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyEngineeringFunctionally gradient material
The invention relates to a coaxial wire-powder-gas-electric arc 3D printing method. The method is realized through a coaxial wire-powder-gas-electric arc 3D printing device. The device comprises a gas shield welding gun and a coaxial gas powder conveying unit. The gas shield welding gun is a consumable electrode gas shield welding gun. The coaxial gas powder conveying unit comprises a powder feeding unit, a gas feeding unit and a coaxial spiral gas powder cover. The coaxial gas powder conveying unit is of a multi-channel structure, and channels are all provided with powder feeding speed controller and a gas feeding flowmeters. According to the 3D printing method using the device, the powder adding rate can be regulated and controlled in real time, the method is suitable for additive manufacturing of conventional metal products, functionally gradient materials and composites, obtained products are even in ingredient, product machining process is short, and subsequent machining amount is small.
Owner:JIANGSU SHUOSHI WELDING SCI & TECH
Co-extrusion preparation method of polymer functionally gradient materials (FGM) and products
The invention discloses a co-extrusion preparation method of polymer functionally gradient materials (FGM) and products, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparing two or more kinds of polymers according to the certain mass percent, mechanically mixing the prepared raw materials, and then, adding the mixture into a screw extruder; (2) at the shaping phase of the co-extrusion process of the mixture, setting a certain temperature gradient field (delta T) for the blending melt which flows in a shaping mold; (3) enabling the shaped molding object which is extruded out of the shaping mold and is in the melting state to pass through a same or different certain temperature gradient field (delta T'); and (4) leading the molding object into a forming mold quickly by a traction device, and cooling the molding object below the melting point within a very short time. The invention has the advantage of providing a method capable of industrialized implementation for preparing polymers or polymer functionally gradient materials (FGM) and products by using traditional equipment and technology for processing polymers.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Cu-Ti2 AlC functionally gradient material and preparation method thereof
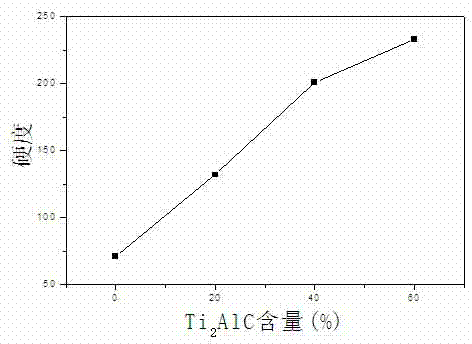
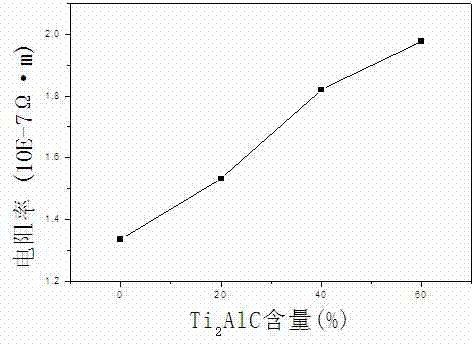
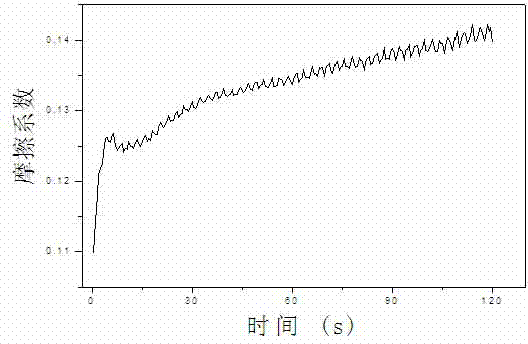
InactiveCN103085395AAdvantages and Notable ImprovementsImprove thermal shock resistanceCeramic layered productsMetal layered productsAdditive ingredientGradient material
The invention relates to a preparation method of a Cu-Ti2 AlC functionally gradient material. The preparation method is characterized in that a composite material which contains pure Cu or main ingredient Cu is formed at one side of the prepared gradient material; the compound which contains pure Ti2AlC or main ingredient Ti2AlC is arranged at the other side of the prepared gradient material; 1-4 interlayers are arranged; the contents of Cu and Ti2AlC change in gradient along with the thickness direction, and gradually change along with the performance; the hardness and strength of the material are obviously improved along with the direction from Cu to enriched Ti2AlC; the oxidation resistance and the anti-high temperature performance are improved; the wear-resisting property and the elastic modulus are gradually improved; and the toughness, the electric conductivity and the thermal conductivity are obviously improved along the direction from Ti2AlC to enriched Cu. The material has significance as to a special environment which has different operational performances as to different contact surfaces; the material is prepared from Cu and Ti2AlC powder used as raw materials in a manner of hot-pressed sintering under certain atmosphere after evenly mixing and layered charging, wherein the sintering temperature is 800-1000 DEG C; the heating rate is 8-20 DEG C / min; the pressure is 20-40 MPa; and heat preservation time is 0.5-3 hours. By adopting a hot-pressed sintering method, the prepared gradient material is high in compactness, excellent in performance, and good in industrialized prospect.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Geometric analysis method based functionally gradient material part modeling method
ActiveCN106682286AAdaptableOmit node interpolationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALPartial differential equation
The invention discloses a geometric analysis method based functionally gradient material part modeling method and aims to solve the technical problem of low efficiency of an existing functionally gradient material part modeling method. According to the technical scheme, the method includes: adopting a Poisson equation for precisely describing part internal material distribution; adopting a tensor product NUPBS parameter entity for coupling expression of functionally gradient material part geometry and materials; adopting material information appointed by a designer as boundary conditions; solving the Poisson equation according to an isogeometric analysis algorithm to finally realize functionally gradient material modeling. Since the Poisson equation is a partial differential equation and a computational domain of the Poisson equation can be any complicated geometric spaces, high adaptability is realized; part geometric expression and material space calculation can be brought into a unified framework according to the isogeometric analysis algorithm, so that procedures of node interpolation, model conversion and the like are avoided, and material space calculation efficiency is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
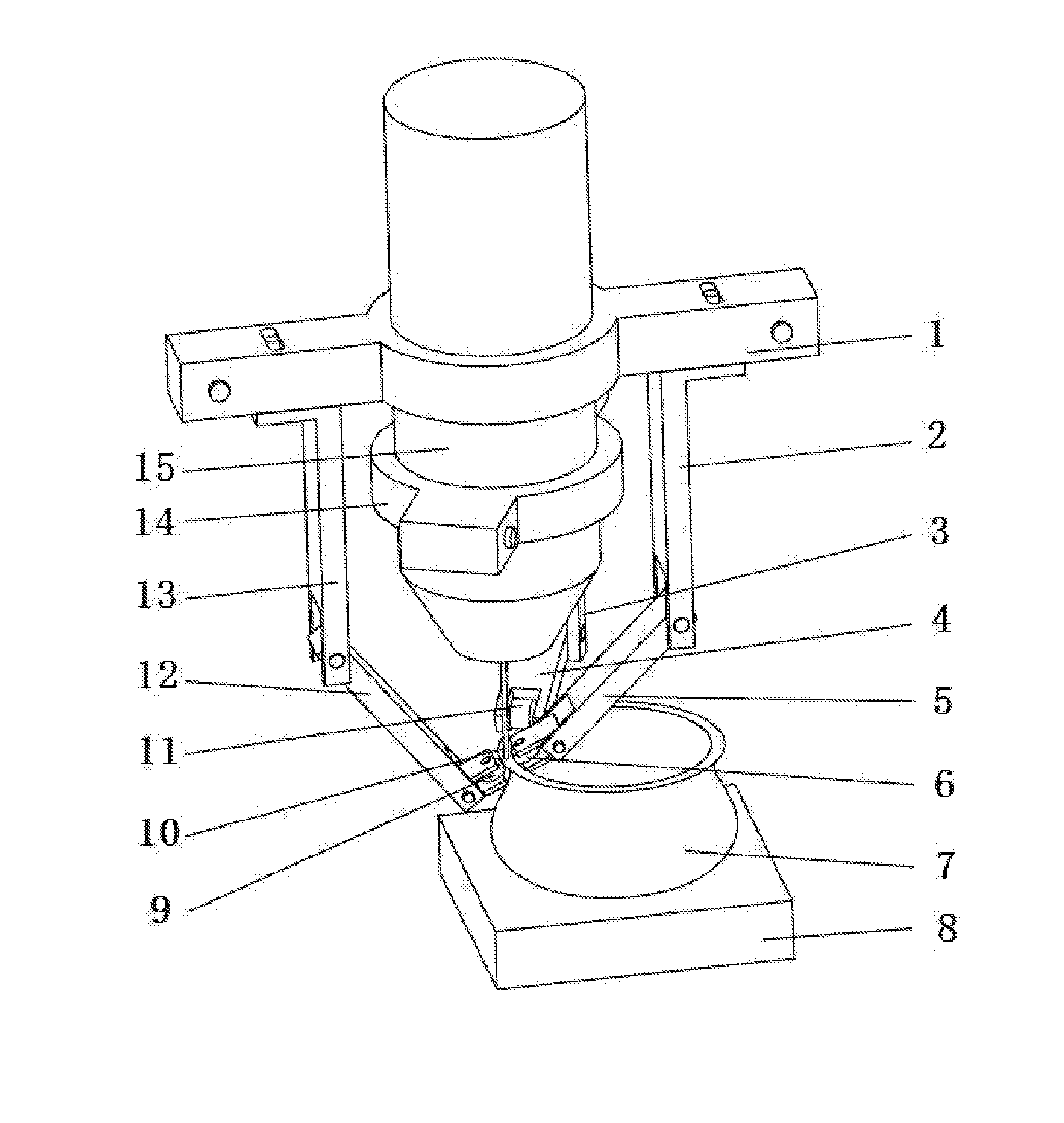
Method for manufacturing metal parts and molds and micro-roller used therefor
ActiveUS9302338B2Formability of complexImprove accuracyArc welding apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsNumerical controlGradient material
A method for manufacturing parts and molds by: 1) slicing a three-dimensional CAD model of a part or mold; 2) planning a modeling path according to slicing data of the three-dimensional CAD model, whereby generating numerical control codes for modeling processing; and 3) performing fused deposition modeling of powders or wire material of metal, intermetallic compounds, ceramic and composite functional gradient materials by layer using a welding gun on a substrate layer via a numerical control gas shielded welding beam or laser beam according to a track specified by the numerical control code for each layer. A micro-roller or a micro-extrusion unit is installed at a contact area between melted and softened areas. The micro-roller or the micro-extrusion unit synchronously moves along with fused deposition area, which results in compressing and processing of the fused deposition area during the fused deposition modeling.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
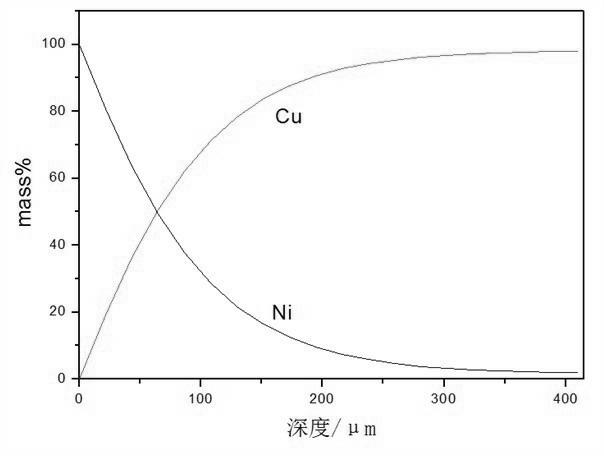
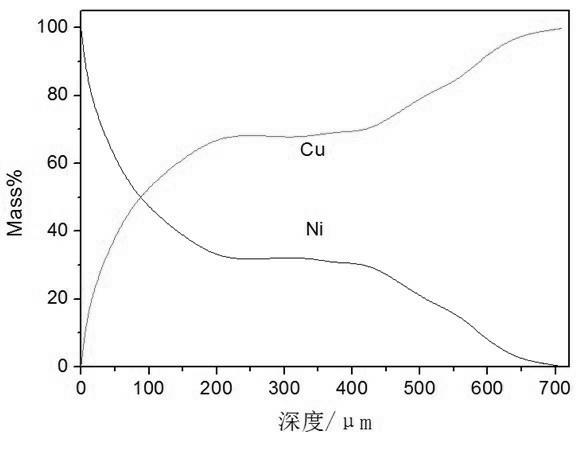
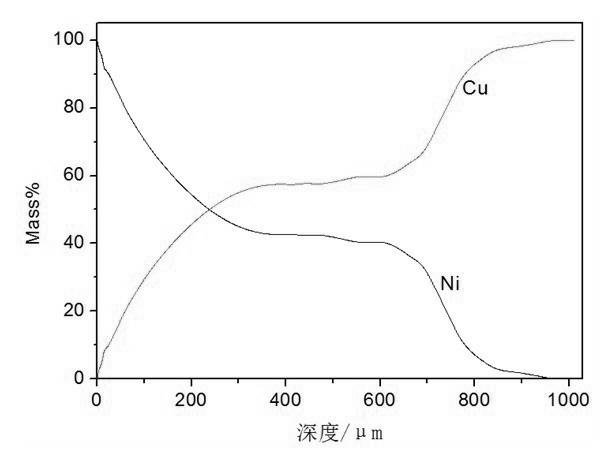
Cu-Ni functionally gradient material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102673040AStrong bending resistancePrevent oxidationMetal layered productsHigh surfaceFunctionally gradient material
The invention discloses a Cu-Ni functionally gradient material and a preparation method thereof. The functionally gradient material comprises an intermediate copper layer and two side nickel layers, wherein a gradient distribution layer is arranged between the copper layer and each nickel layer; and the copper content of the gradient distribution layer is decreased gradually and the nickel content is increased gradually to the directions of the nickel layers. The material is high in bending resistance, electric conductivity, heat conductivity and mechanical performance; various parts of the material are linked closely; the surface structure of the material is dense and flat; a stable NiO protective film can be formed on the surface of the material in the air at the temperature of 700 to 900 DEG C, so that substrate copper is effectively prevented from being oxidized; and therefore, the material has the characteristic of high surface oxidation resistance. According to the preparation method, aiming at the characteristics of the conventional Cu-Ni functionally gradient material, according to a diffusion basic theory, the method of electrodepositing Ni and interfusing Ni and Cu at the same time under the action of an electric field is adopted to accelerate the thickening of a gradient layer. The preparation method has the advantages that the formation speed of the gradient layer is high; the time required for preparing a thick gradient layer is short; and the method is easy to control and simple in process and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
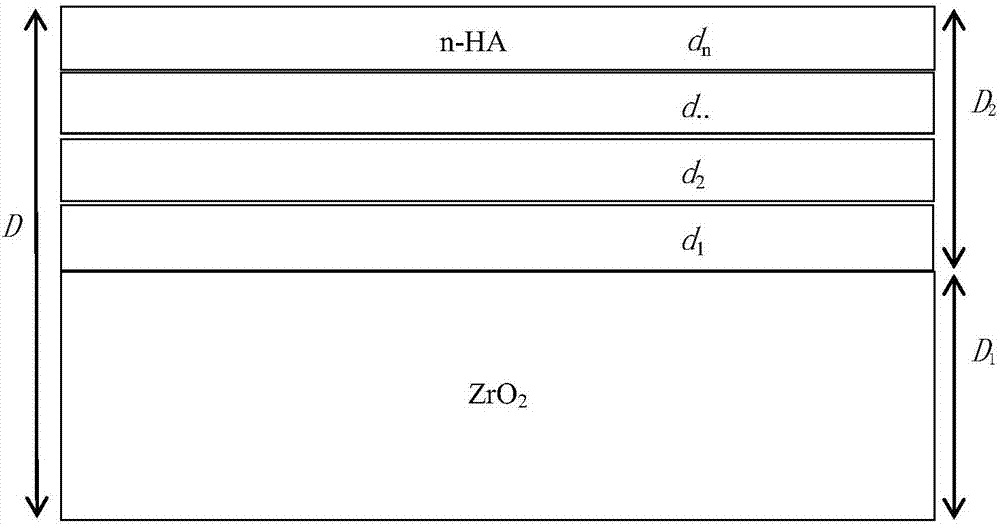
Preparation method for functionally gradient materials (FGM) of ZrO2-based nano-hydroxyapatite (n-HA)
InactiveCN107311654APracticalStrong theoretical significanceTissue regenerationCoatingsBiocompatibility TestingFunctionally gradient material
The invention discloses a preparation method for FGM of ZrO2-based n-HA. The method comprises the following steps: preparing FGM powder; preparing a green body specimen; sintering the specimen. The materials disclosed by the invention fully utilize the advantages of good biocompatibility and biological activity of n-HA and high mechanical strength of biological inert materials, namely ZrO2, and further have strong practicability and theoretical significance.
Owner:王青山
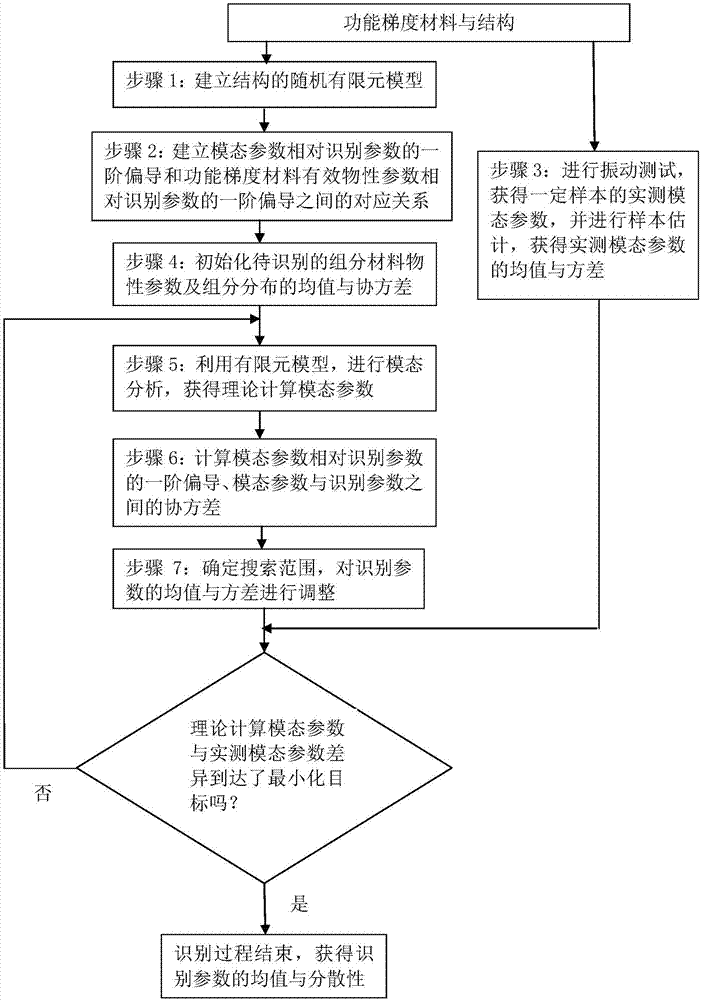
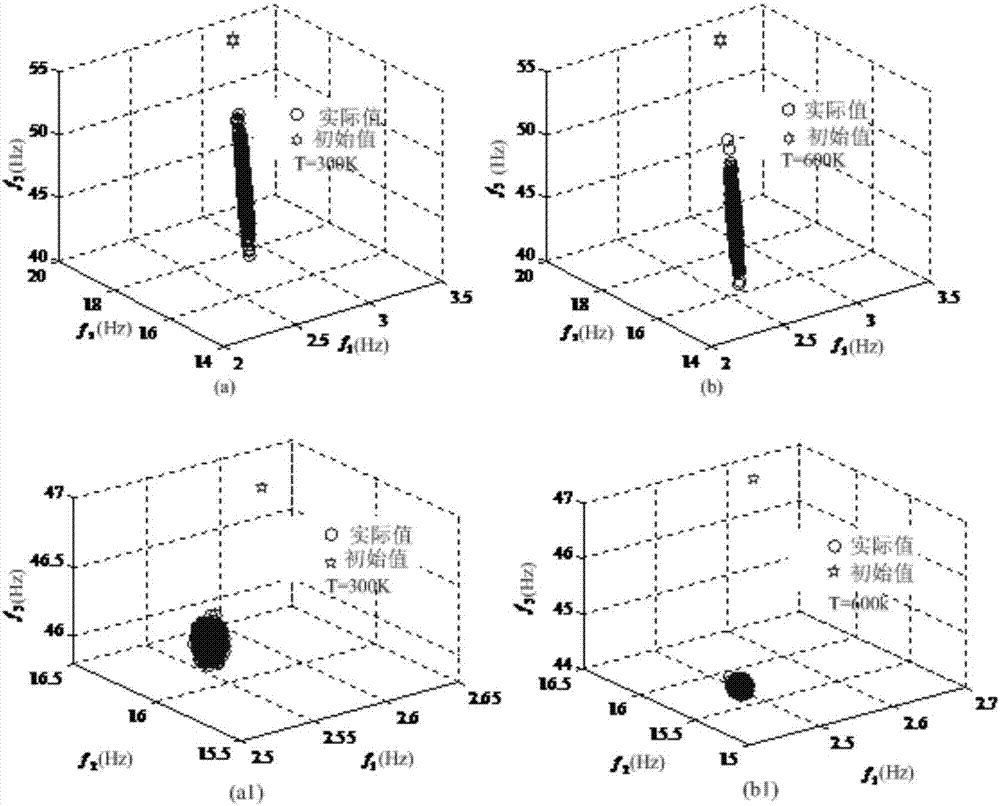
Functionally gradient material and structure parameter statistics recognition method
ActiveCN107958111AFast recognitionAvoid non-convergenceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionFunctionally gradient material
The invention relates to a functionally gradient material and structure parameter statistics recognition method. The method is used for statistics recognition based on functionally gradient material component material physical property parameter and component distribution corrected by a functionally gradient structure random model. On one hand, the method for adjusting the search range for each step iteration is adopted for increasing the recognition speed; on the other hand, propagation from the material recognition parameter randomness to the structure modal parameter randomness is achievedby building the corresponding relation between first-order partial derivatives of relative recognition parameters of functionally gradient structure modal parameters and first-order partial derivatives of relative recognition parameters of functionally gradient material effective physical property parameters, and misconvergence caused by accumulative errors in the iteration recognition process isavoided.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Infinitely-variable-speed ultrasonic microdroplet jetting additive manufacturing device and method for multiple materials
ActiveCN106142571AAvoid cloggingAvoid it happening againAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusSprayerFunctionally gradient material
The invention relates to an infinitely-variable-speed ultrasonic microdroplet jetting additive manufacturing device and method for multiple materials, and belongs to the field of additive manufacturing. A delta sport substrate device is fixed inside a rack and located below a top plate of the rack. A focused ultrasound system is fixed inside the rack and located above a bottom plate of the rack. A material pool device is located above the focused ultrasound system and fixed to the rack. Feeding devices are fixed to supporting posts of the rack. According to the infinitely-variable-speed ultrasonic microdroplet jetting additive manufacturing device and method for the multiple materials, the focused ultrasound technique and the additive manufacturing technique are combined, the size of jetted liquid drops is not limited by sprayers which are not needed, sprayer blocking is avoided, and the manufacturing cost is lowered; microdroplets are jetted from bottom to top, satellite droplets are prevented, and the printing precision is improved; mixed additive manufacturing for the multiple materials and additive manufacturing for functionally gradient materials can be achieved; and in the printing process, the microdroplet jetting frequency is adjustable, the microdroplet diameter is adjustable, and infinitely-variable-speed microdroplet jetting additive manufacturing can be achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Manufacturing method for functionally gradient material capable of reinforcing tuyere
InactiveCN104404186AReduce crackingExtended service lifeMolten spray coatingArc welding apparatusFunctionally gradient materialHardness
The invention relates to a manufacturing method for a functionally gradient material capable of reinforcing a tuyere. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: firstly, cleaning oil stain and dust on the inner wall and the small end of the copper matrix tuyere, and pre-heating to about 500 DEG C; overlaying a Ni202 transition layer on the copper matrix tuyere; overlaying a CoGrW reinforcing layer on the transition layer; performing sandblast texturing treatment on the reinforcing layer for enabling the surface to be flat, wherein the whole overlaying layer is 3 mm in thickness; plasma-spraying a ZrO2 thermal barrier coating with the thickness of 0.5 mm after the CoGrW reinforcing layer is preheated, in order to prevent the phenomenon that cracks exist in the CoGrW reinforcing layer during the use due to the different heat conductivity coefficient. According to the invention, the transition layer and the reinforcing layer are overlaid, the thermal barrier coating is plasma-sprayed, and the overlaying layer can reach the thickness and metallurgical bonding strength required for use, so that falling can be prevented during the use, the copper matrix tuyere can be protected by the thermal barrier coating during use, the cracking or falling of the reinforcing layer caused by thermal stress is reduced, the hardness is high, the abrasion resistance is excellent, the cost is low, the production efficiency is high, and the service life can reach 10 months.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司 +1
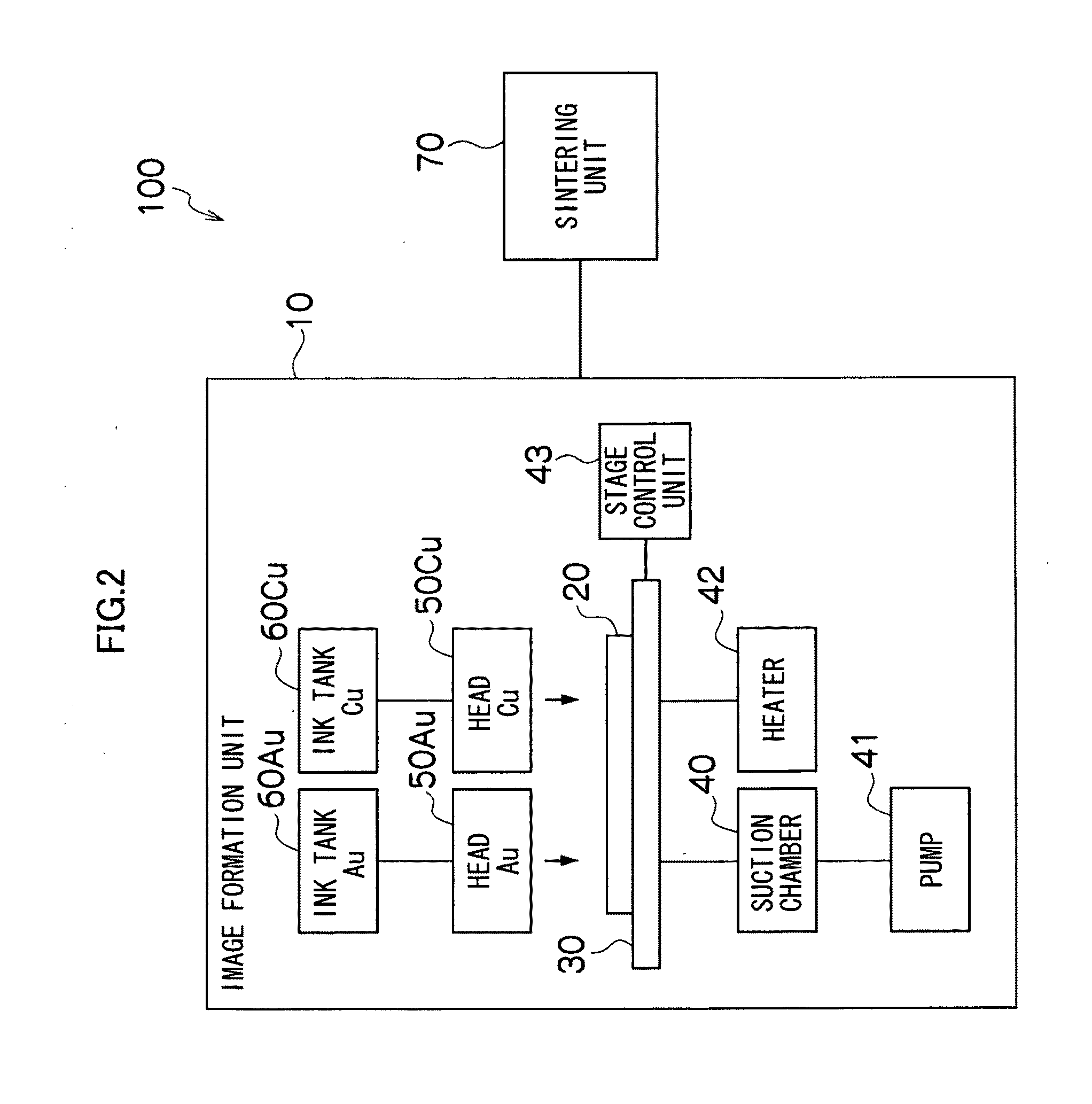
Method and apparatus of manufacturing functionally gradient material
InactiveUS20110284158A1Liquid surface applicatorsLamination ancillary operationsEngineeringFunctionally gradient material
A method of manufacturing a functionally gradient material having a gradient from a first material to a second material different to the first material by ejecting inks onto a base material from a plurality of inkjet heads, includes the steps of: supplying a first functional ink containing the first material to a first inkjet head; supplying a second functional ink containing the second material to a second inkjet head; specifying a ratio between a volume of the first functional ink ejected from the first inkjet head and a volume of the second functional ink ejected from the second inkjet head; causing the first inkjet head to eject the first functional ink and / or causing the second inkjet head to eject the second functional ink, in accordance with the specified ratio, so as to form one layer; and stacking a plurality of layers onto the base material by repeating the forming step, so as to obtain a laminated body, wherein in the control step, the ratio between the first functional ink and the second functional ink is specified in such a manner that respective layers of the plurality of layers progressively have a smaller ratio of the first functional ink and a larger ratio of the second functional ink, toward an upper layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Composite coated positive pole material of lithium ionic cell and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN101308925BSimple processOptimal control programElectrode manufacturing processesChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesPower flowLithium metal
The invention discloses a coated composite lithium ion battery anode material and the preparation method thereof, aiming at improving the electrochemical property of the coated composite lithium ion battery anode material. The invention takes Li0.8-1.2Ni0.7Co0.2Mn0.1O2, and Li-0.8-1.2Ni0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2, or Li0.8-1.2Ni0.9Co0.05Mn0.05O2 as the substrate, and adopts hexagonal crystal structure; the surface of the substrate is coated with a functionally gradient material layer which is 1-20%of the quality of the substrate. The preparation method includes the steps of preparing powder, mixing the materials, sintering, coating the surface, heating, and coating with organic material coating. Compared with prior art, the anode material can be combined with lithium metal and assembled to an analog battery; if the battery is charged or discharged at current density of 0.3C under 2.5-4.2V, the discharge capacity is more than 190mAh / g, the first coulomb efficiency will reach 90% and the capacity retention is more than 95% after 100 cycles. The coated composite lithium ion battery anode material is simple in technique and low in cost and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:BTR NEW MATERIAL GRP CO LTD
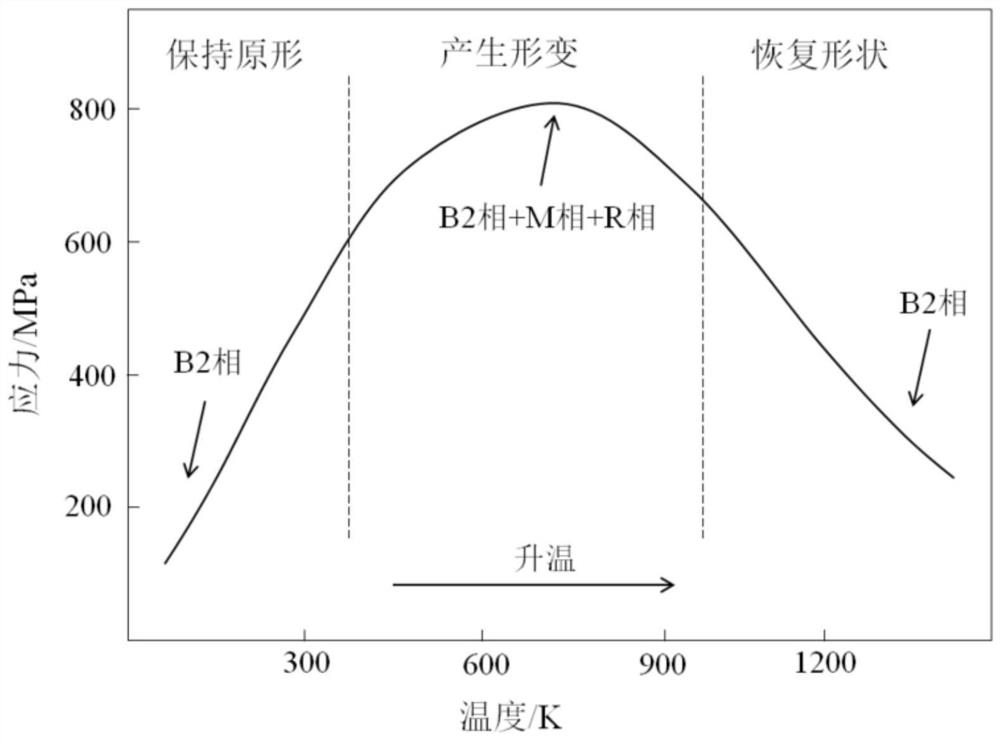
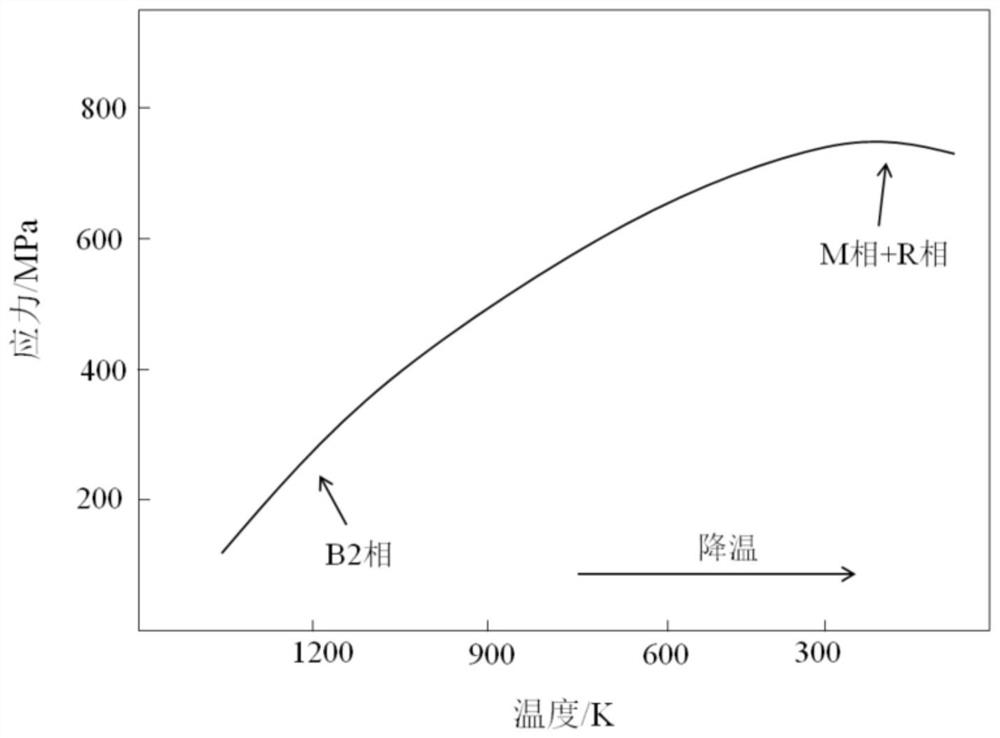
Method for 4D printing of functionally-gradient titanium-nickel shape memory alloy components
InactiveCN113210626AExert superelastic effectReduce the effects of phase transitionsAdditive manufacturing apparatusStructural deformationGradient material
The invention relates to the field of 4D printing of intelligent components and functionally-gradient materials, in particular to a method for 4D printing of functionally-gradient titanium-nickel shape memory alloy components. According to the method, direct metal deposition is carried out on titanium-nickel shape memory alloy powder through laser additive manufacturing equipment, function division is carried out on different areas including a stress bearing area and a structural deformation area when three-dimensional modeling is carried out on a workpiece, and different laser process parameters are set for the different functional areas during additive manufacturing. The reasonable titanium-nickel alloy component proportion is selected, and the gradient materials with the function, the structure and the microstructure changing continuously are prepared. According to the method, the gradient materials with the function and mechanical property changing along with the change of the internal positions of the workpieces can be prepared, reasonable function partitioning can be achieved, and the method is simple in process, easy to implement, good in applicability and high in functionality.
Owner:JIANGSU HAIYU MACHINERY +1
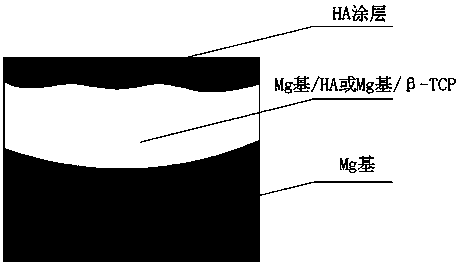
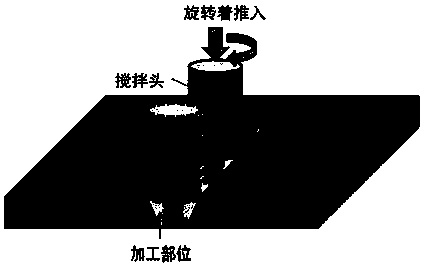
Controlled degradation magnesium-based functional gradient material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108103546AGood biocompatibilityHigh bonding strengthElectrolytic coatingsMetallic material coating processesPhosphateHydroxyapatite coating
The invention discloses a preparation method of a controlled degradation magnesium-based functional gradient material. The method comprises the steps of (1) annealing treatment of a magnesium alloy; (2) drilling of the annealed magnesium alloy; (3) HA or beta-TCP loading of the drilled magnesium alloy; (4) friction stir processing of the magnesium alloy loaded with hydroxyapatite or tricalcium phosphate, specifically, under the conditions that the rotary speed is 300-1700 r / min, the feeding speed is 10-50 mm / min and the press amount is 0.5-3 mm, 2-6 passes of friction stirring are conducted, and an Mg-based / HA layer or Mg-based / beta-TCP layer which is 0.5-3 mm thick is obtained; and (5) surface grinding, cleaning and drying with the Mg-based / HA layer or Mg-based / belt-TCP layer as the substrate material, and then electro-deposition so as to obtain a hydroxyapatite coating being 1-12 [mu]m thick on the surface of the substrate material, so that the controlled degradation magnesium-basedfunctional gradient material is obtained. The controlled degradation magnesium-based functional gradient material has good biocompatibility, bone inductivity, corrosion resistance and degradation controllability, and achieves the sequential degradation and controlled degradation of the magnesium alloy as a bone implanting material.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Light curing preparation device of gradient material and light curing preparation method
ActiveCN106217869AControllable ratioIncrease profitAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusGradient materialFunctionally gradient material
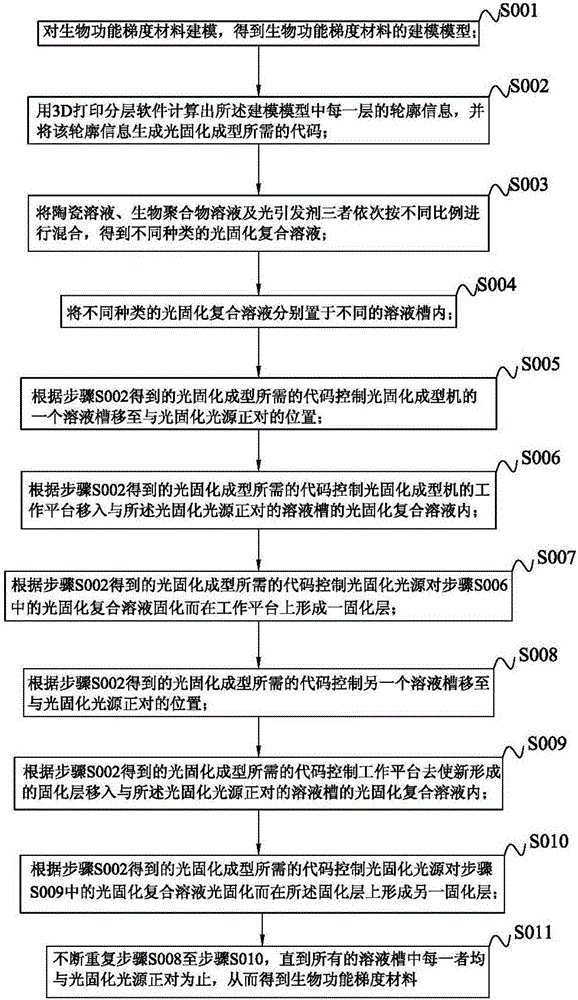
The invention discloses a light curing preparation device of a gradient material. The device comprises a horizontal motion table, a light curing system, a horizontal driver, an upper and lower mobile station, and an upper and lower driver. The invention also discloses a light curing preparation method based on the device. The method is as below: first, modeling a biological functionally gradient material to obtain a model; then calculating the contour information of each layer of the model by the 3D printing layered software, and generating light curing code by using the contour information; then, placing different light curing composite solutions in different solution baths; and at last, controlling the light curing device according to the code for light curing molding to prepare the graded material, so as to realize proportion control of the gradient material.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Making method of silicon carbide/carbon functional gradient material
A making method of a silicon carbide / carbon functional gradient material is as follows: a carbon graphite material is used as a base material for silicon infiltration treatment at 1500-1700 DEG C, and then is put in a high temperature vacuum graphitizing furnace for reacting with silicon to produce the silicon carbide / carbon functional gradient material; the silicon carbide / carbon functional gradient material is prepared by successive combination of two materials with different properties into one, wherein one material is continuously transited to the other material, and no obvious interface is produced among various parts of the material. The silicon carbide / carbon functional gradient material has self-lubricating property, good heat conductivity and electrical conductivity, good thermal shock resistance and high temperature strength of the graphite material, and high hardness and high strength, high temperature oxidation resistance, strong corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance and other properties of silicon carbide.
Owner:成都润封电碳有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com