Method for detecting mutation of deafness susceptibility genes through combination of overlapping extension PCR and Sanger sequencing
A technology of sequencing and primer combination, applied in the field of gene detection, can solve the problems of gene chip method, such as many detection sites, high cost, cumbersome detection operation, etc., to reduce the number of PCR reactions and sequencing reactions, reduce the detection cost, and simplify the operation. effect of steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] Example 1 A kit for detecting deafness-related genes based on Sanger sequencing
[0074] 1. Composition
[0075] A combination of primers with nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID No.1-26, sequencing primers with nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID Nos.27-28 and reagents for PCR reactions, wherein the reagents for PCR reactions include: GeneAmp TM 10×PCRBufferI (ABI TM 4379876), 25mM Mg 2+ , 25mM dNTPs, Primers, Roche Taq Enzyme (Product No.: 03501221190), H 2 O; The reagent for Sanger sequencing is BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (including: BigDye, 5×seq Buffer).
[0076] 2. How to use
[0077] S1. Collect EDTA anticoagulated whole blood samples;
[0078] S2. extracting DNA by column method;
[0079] S3. PCR reaction, there are five independent PCR systems, using primer mix 1-5 respectively:
[0080] Primer mixture 1 includes nucleotides such as primers shown in SEQ ID No.1-6;
[0081] The primer mixture 2 includes nucleotides such as prim...
Embodiment 2
[0098] Example 2 Detection of deafness-related gene mutation sites
[0099] 1. Experimental method
[0100] A kit for detecting deafness-related mutation sites based on the Sanger sequencing method in Example 1 was used to detect the blood of a known positive sample to obtain DNA with a sample concentration of 32 ng / μl.
[0101] The corresponding relationship between the mutation status of known positive samples and primers and primer mixes is shown in Table 2 to Table 6:
[0102] Table 2:
[0103]
[0104] table 3:
[0105]
[0106]
[0107] Table 4:
[0108]
[0109] table 5:
[0110]
[0111] Table 6:
[0112]
[0113] 2. Experimental results
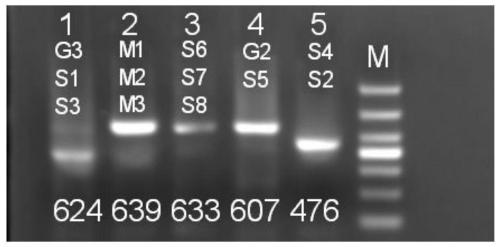
[0114] The result is as Figures 1 to 11 As shown, all the 43 sites detected can be successfully covered and detected. Separate fragment sequencing was performed on each single site of the same sample, and all sites were the same as the overlapping results.
Embodiment 3
[0116] 1. Experimental method
[0117] Utilize a Sanger sequencing method based on overlap extension PCR in the embodiment 1 to detect deaf susceptibility related four gene common loci (total 5 reactions), by the detection of 20 examples of known result samples, and with the common PCR The single locus Sanger sequencing method was used to compare the experimental results of four common loci (13 reactions in total) related to deafness susceptibility to determine the consistency.
[0118] 2. Experimental results
[0119]
[0120]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com