Vaccine for treating chronic hepatitis B and preparation method and application thereof
A chronic hepatitis B and vaccine technology, applied in the field of vaccines for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B and their preparation, can solve the problems of inability to induce antibody responses, complicated preparation methods, and clinical data with no therapeutic effect, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0136] Example 2 Preparation of the vaccine containing TLR4 agonist and QS-21 liposome complex adjuvant Preparation of various ingredients:
[0137] Monophosphoryl Lipid A, Monophosphoryl Lipid A (MPLA) is purchased from the market, and the concentration after being dissolved in 100% alcohol is 1.0 mg per milliliter. QS-21 is purchased from the market, and the concentration of its aqueous solution is 1.0 mg per milliliter.
[0138] Weigh 0.0489g of cholesterol, measure 4.89ml of chloroform in a fume hood, add it to the EP tube containing cholesterol, pipette to dissolve, and mix well.
[0139] Weigh 0.0676g of dioleoyl lecithin 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DOPC), absorb 1.352ml of chloroform in a fume hood, add to DOPC, mix with a pipette, and make a mark 4 ℃ and protected from light.
[0140] Antigen preparation: HBsAg is a virus-like particle expressed by yeast, its purity meets the standards for vaccine production, and it is diluted with normal saline to a con...
Embodiment 3
[0146] Example 3 Immunogenicity of therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine formulated with TLR4 agonist and QS-21 liposome complex adjuvant
[0147] Eight mice per group were treated with C57 (about 6-7 weeks). According to the method of Example 1, 3 days before the vaccine injection, the hepatitis B virus plasmid (paav-HBV1.2) was injected into the tail vein under high pressure to infect C57 mice. On day 1, day 14 and day 28, each mouse was subcutaneously injected with 0.3 ml of the vaccine three times. See Example 2 for the preparation method of the vaccine. Set up a control group without infection, a control group with infection but no immunity, and a control group with only antigen immunization (without adjuvant) after infection.
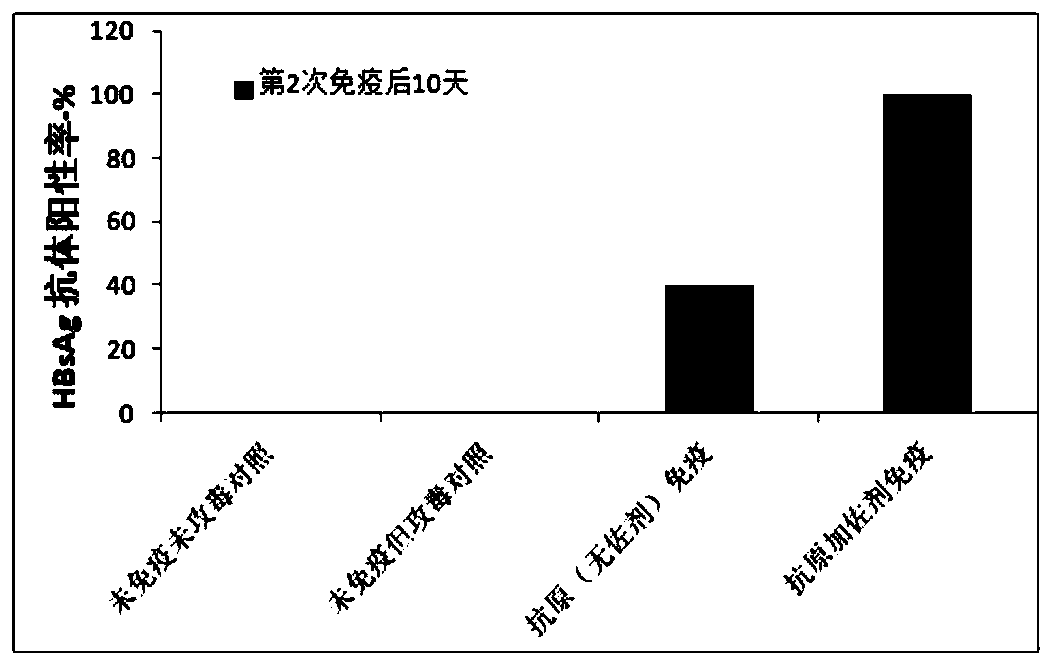
[0148] On the 10th day after the second immunization (that is, the 24th day of the experiment), blood was collected from the vein, the serum was separated, and the antibody titer of HBsAg was detected by ELISA (results in figure 1 ). 100% of mice imm...
Embodiment 4
[0151] Example 4 The therapeutic effect of the therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine formulated with TLR4 agonist and QS-21 liposome complex adjuvant in the hepatitis B mouse model
[0152] Eight mice per group were treated with C57 (about 6-7 weeks). According to the method of Example 1, three days before the vaccine injection, the hepatitis B virus plasmid (paav-HBV1.2) was injected into the tail vein under high pressure to infect C57 mice. Each mouse was subcutaneously injected with 0.3 ml of the vaccine on day 1, day 14 and day 28, respectively. See Example 2 for the preparation method of the vaccine. A control group without infection, a control group infected but not immunized, and a control group immunized with antigen without adjuvant after infection are set.
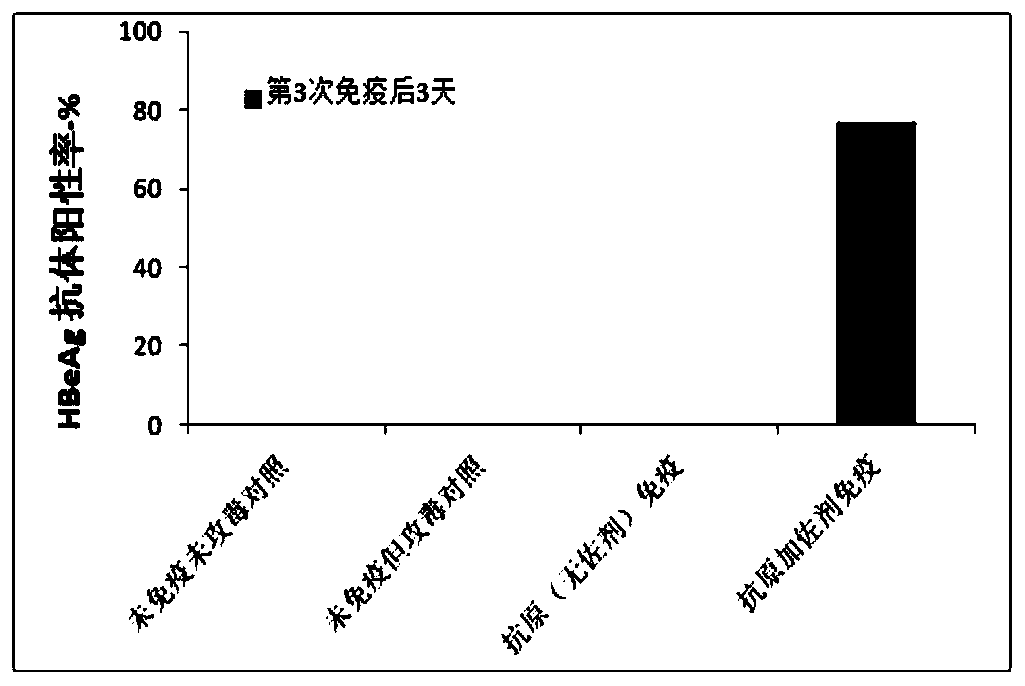
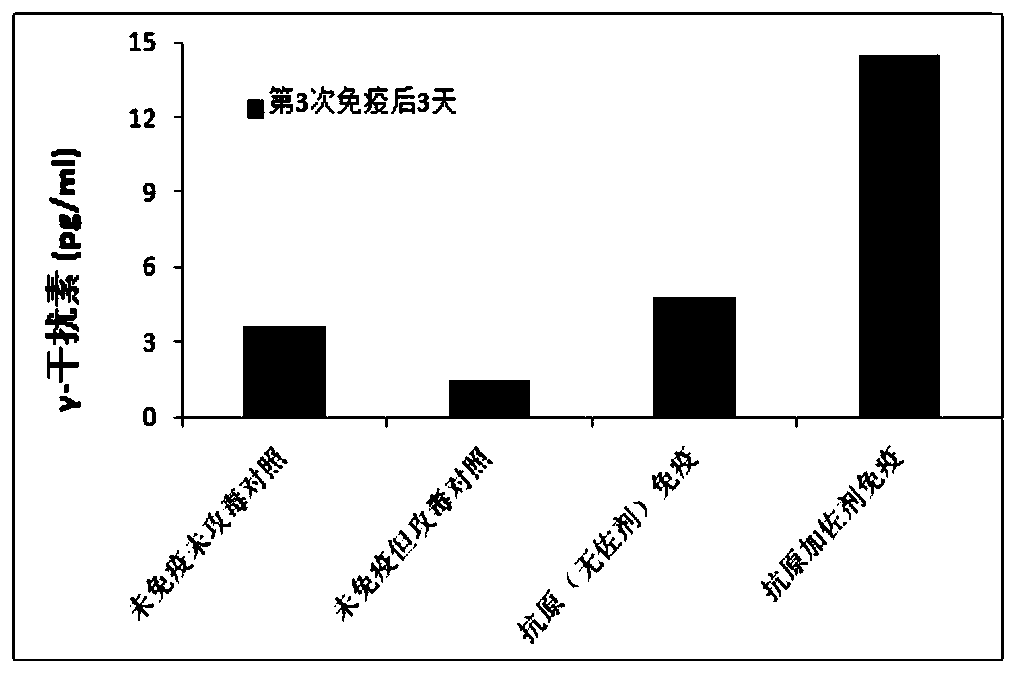
[0153] Blood samples were collected before the first immunization and on days 3, 10, 17, 24 and 31 after immunization. The virus components of HBsAg and HBeAg in serum were detected by ELISA method.
[0154] There w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com