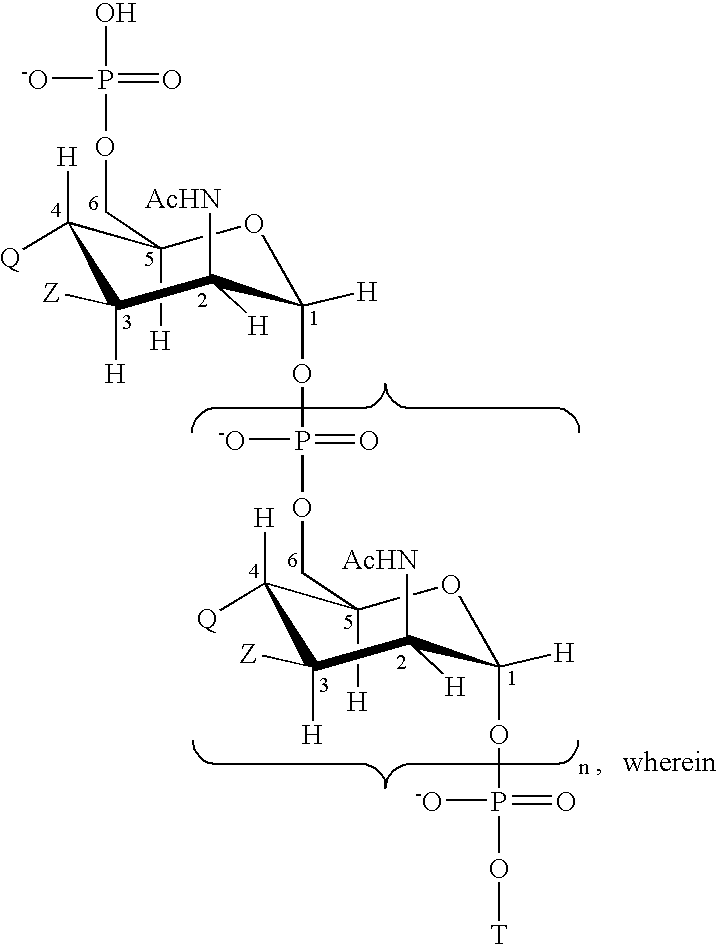
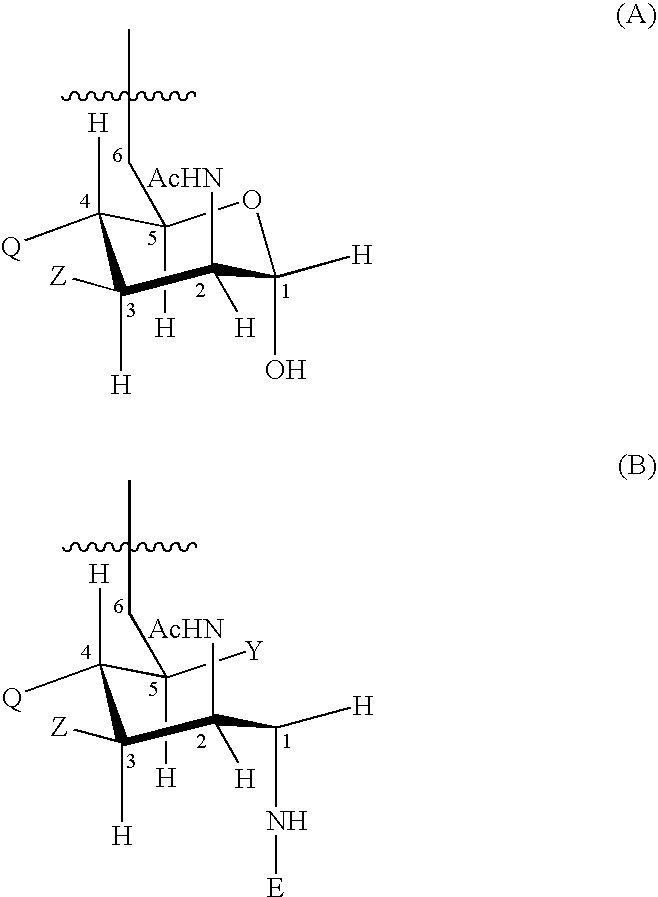
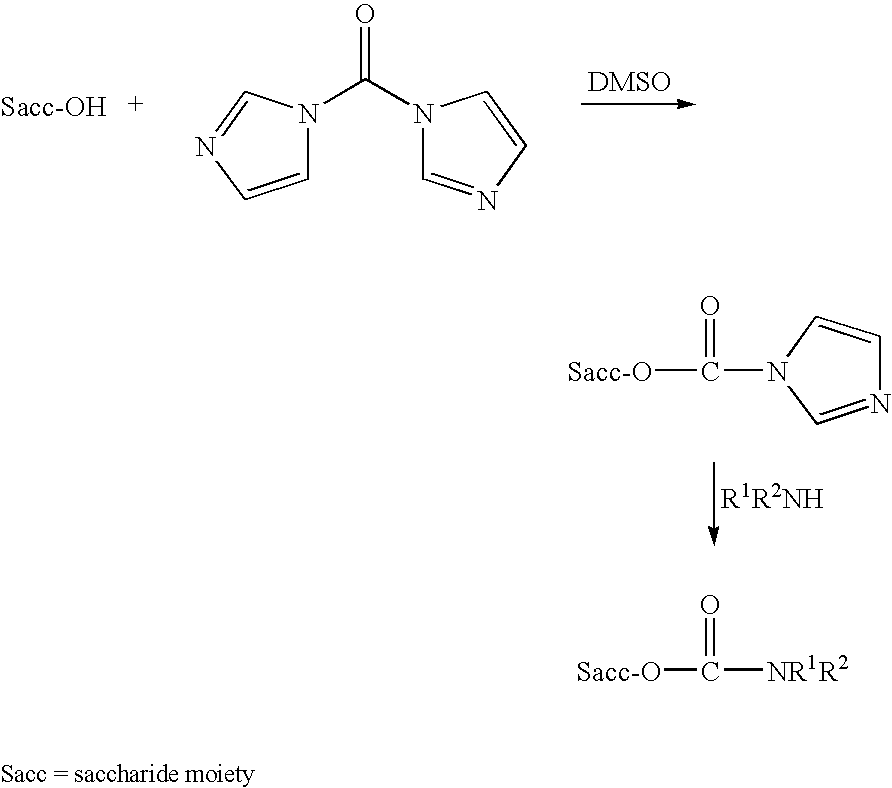
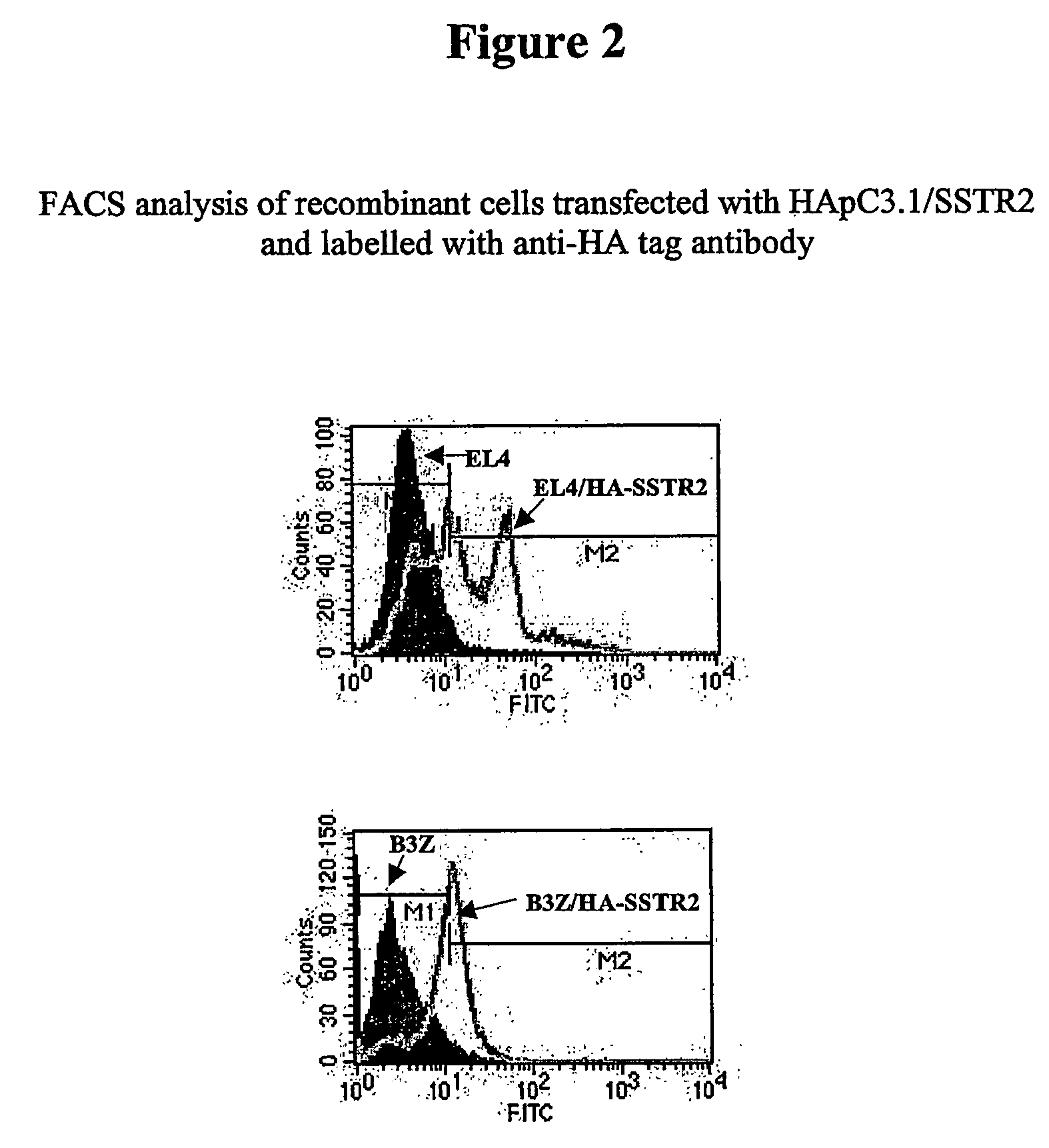
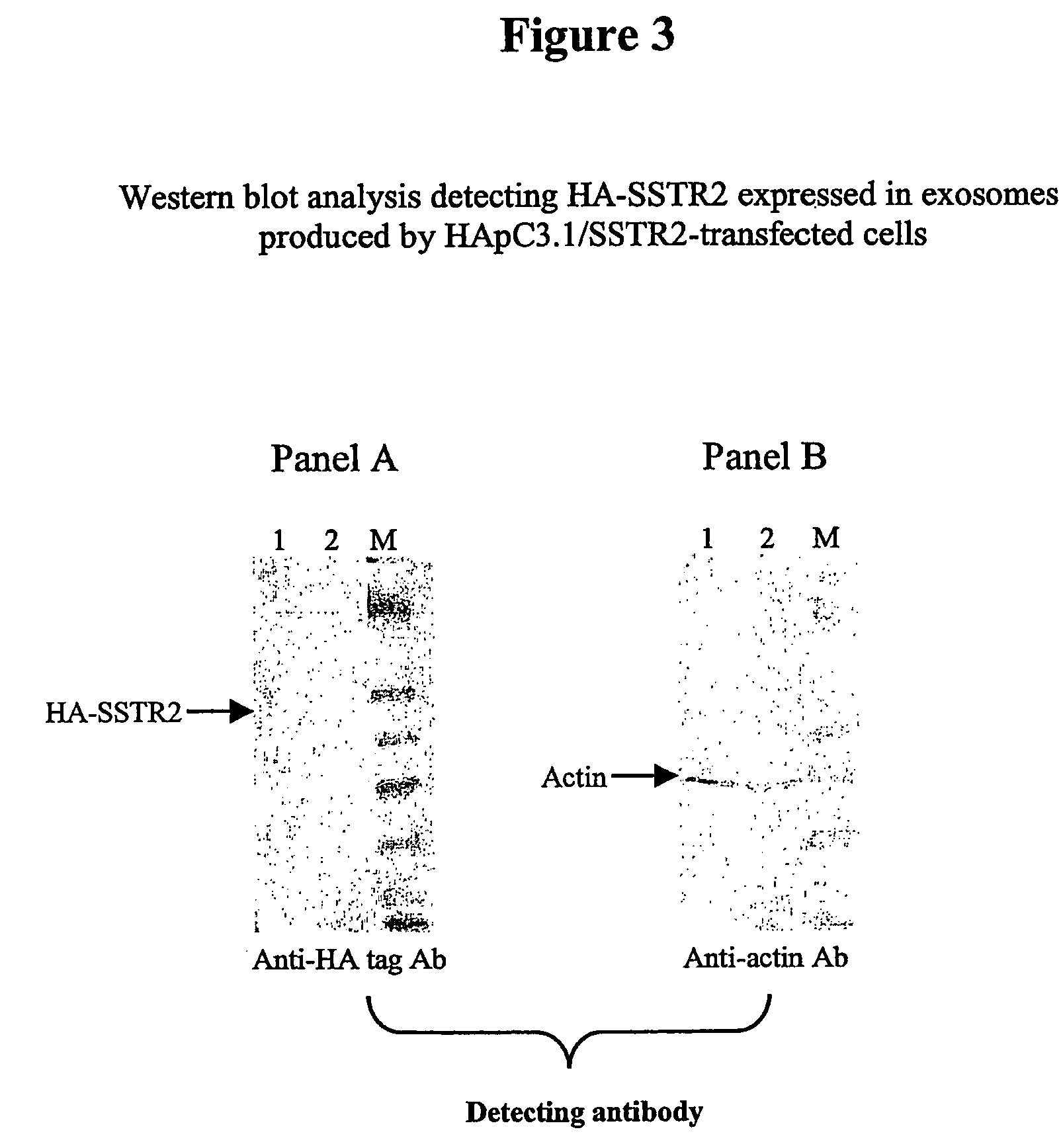
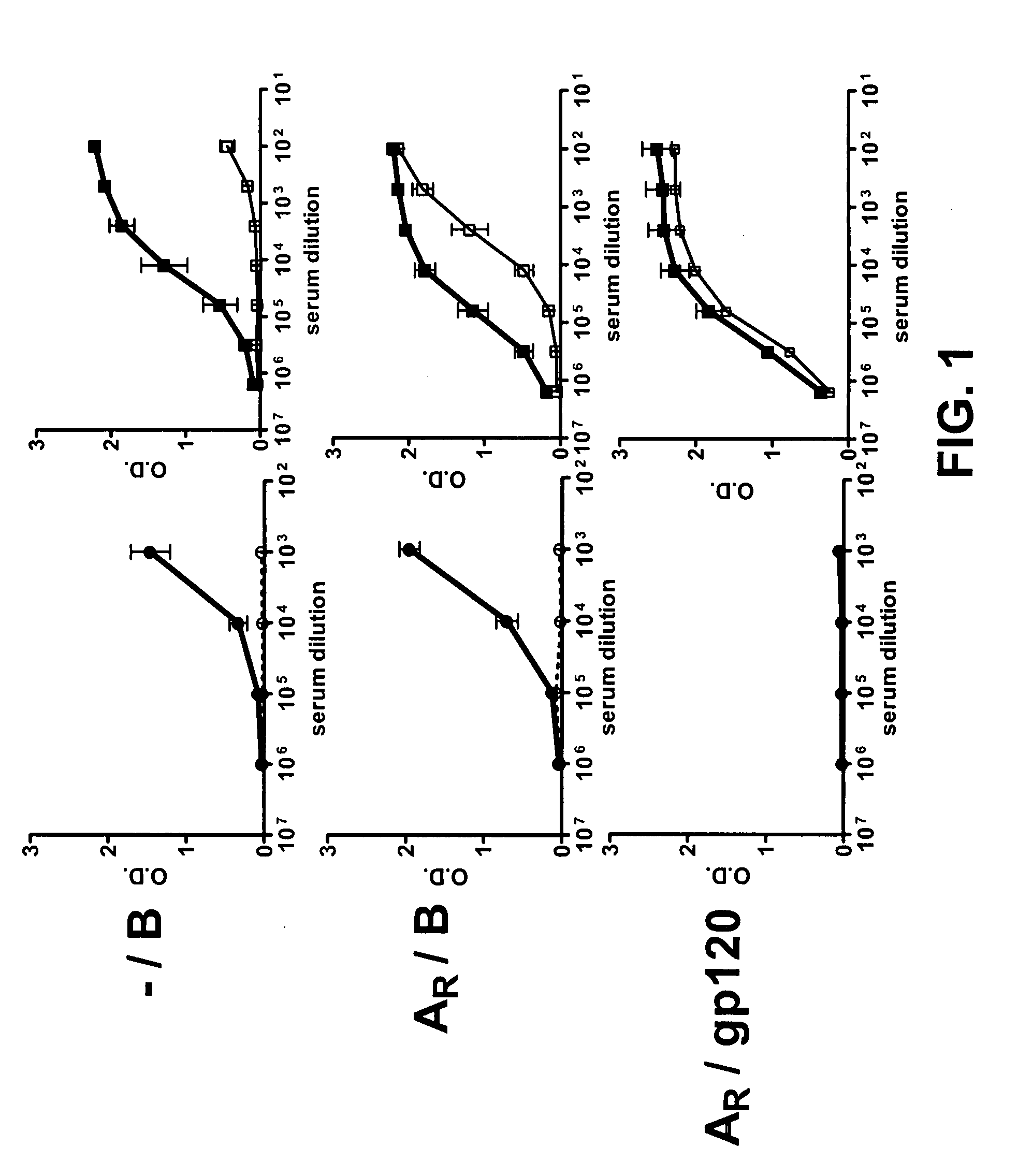
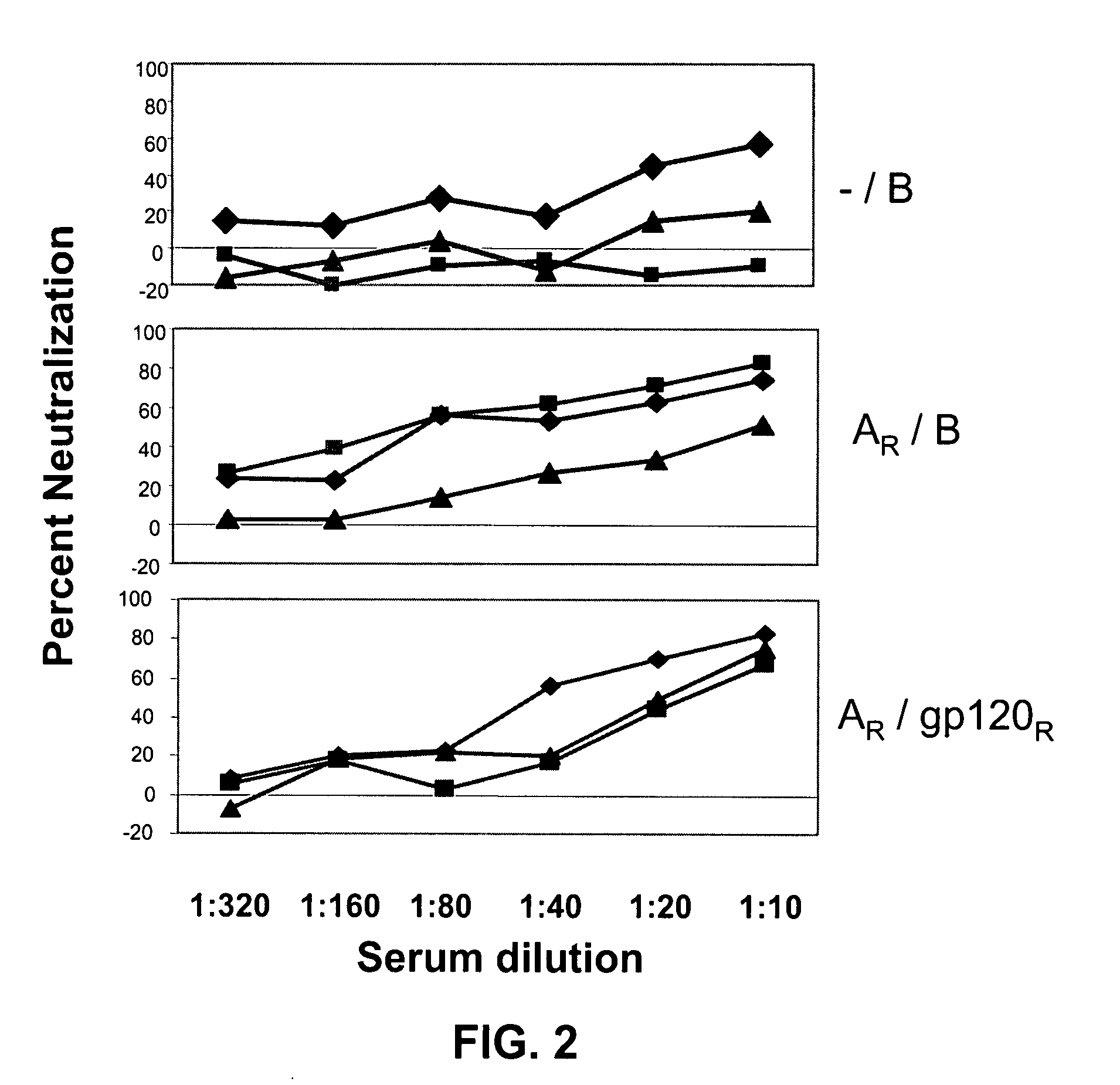
Patents
Literature
371 results about "Antibody response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
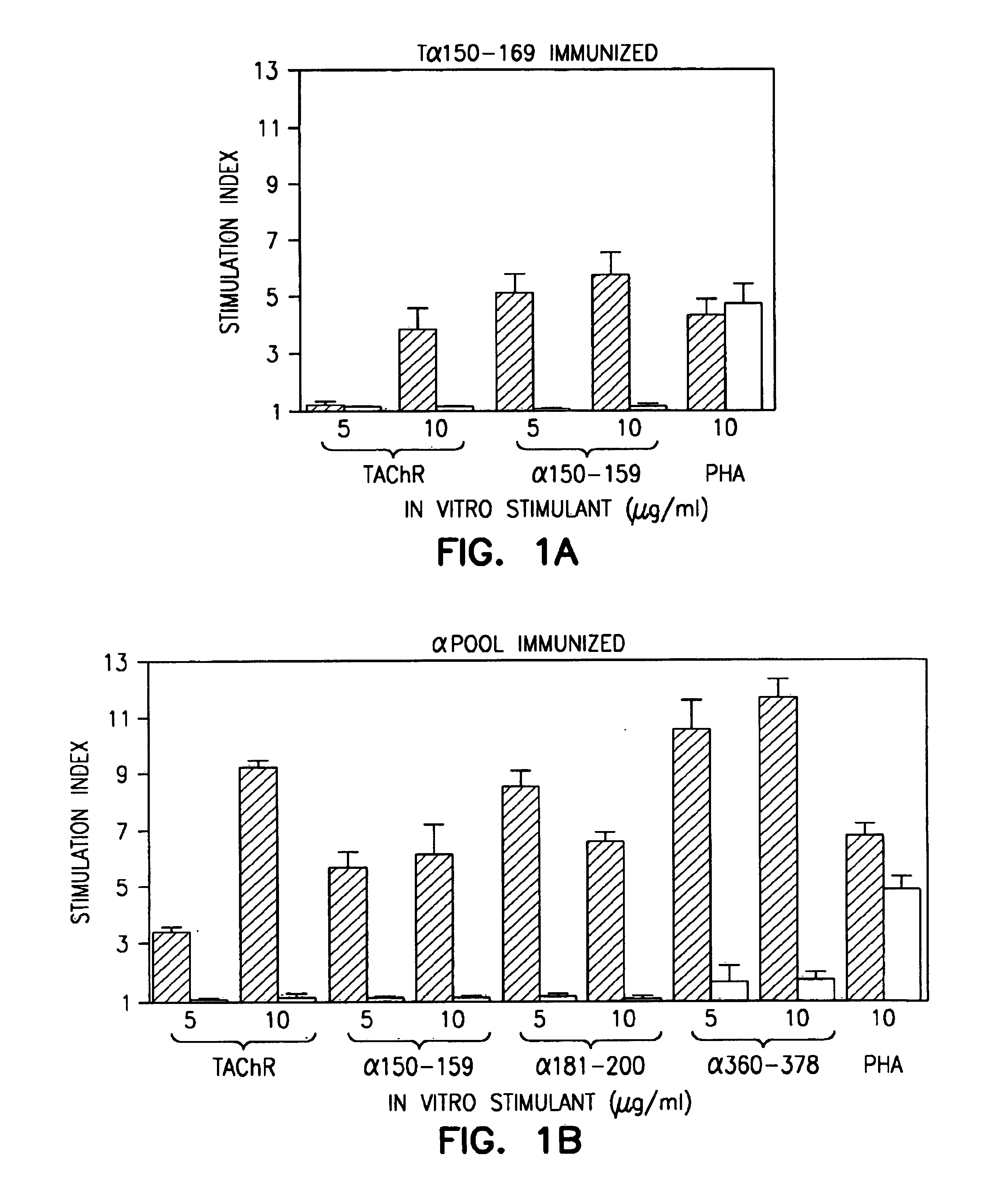
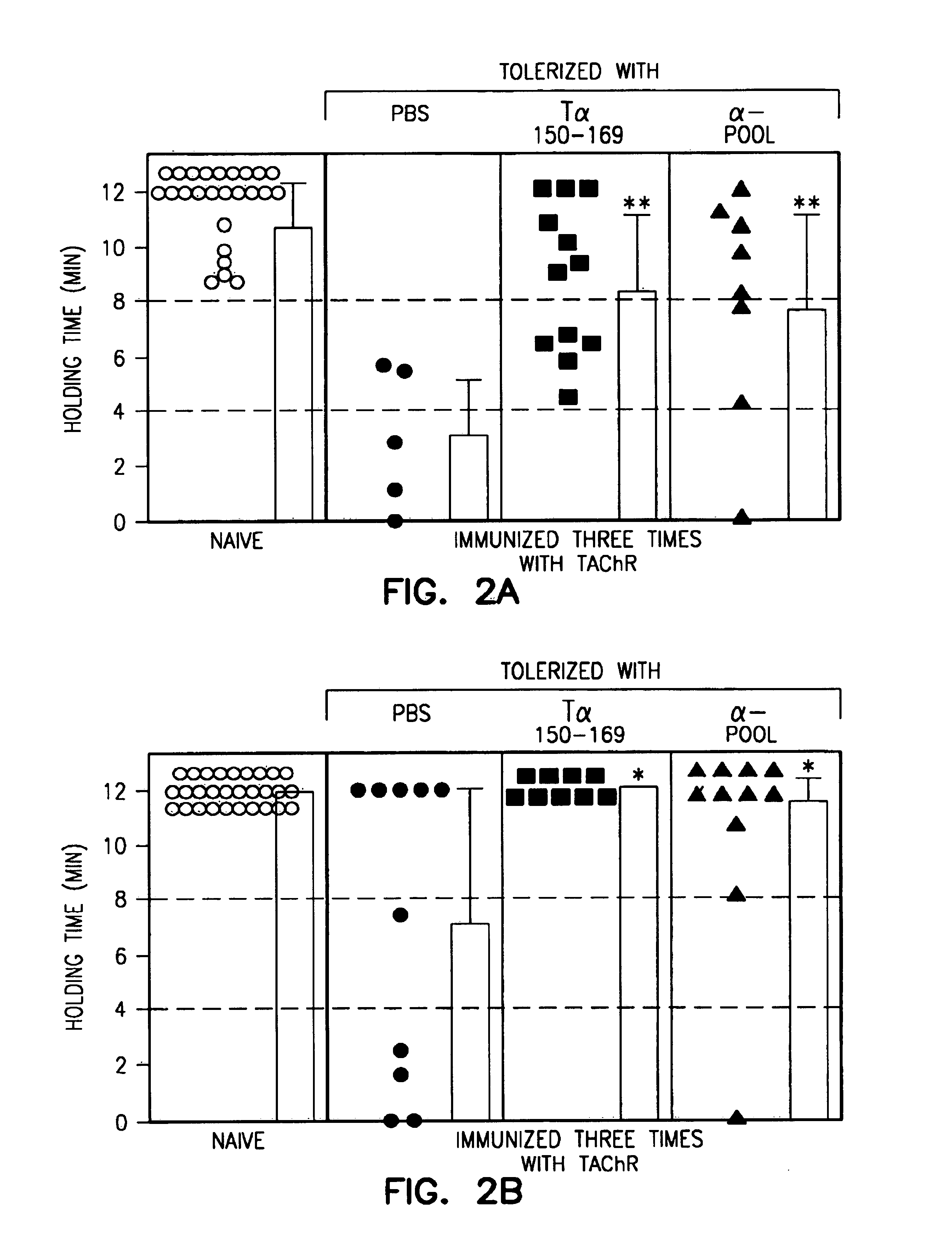
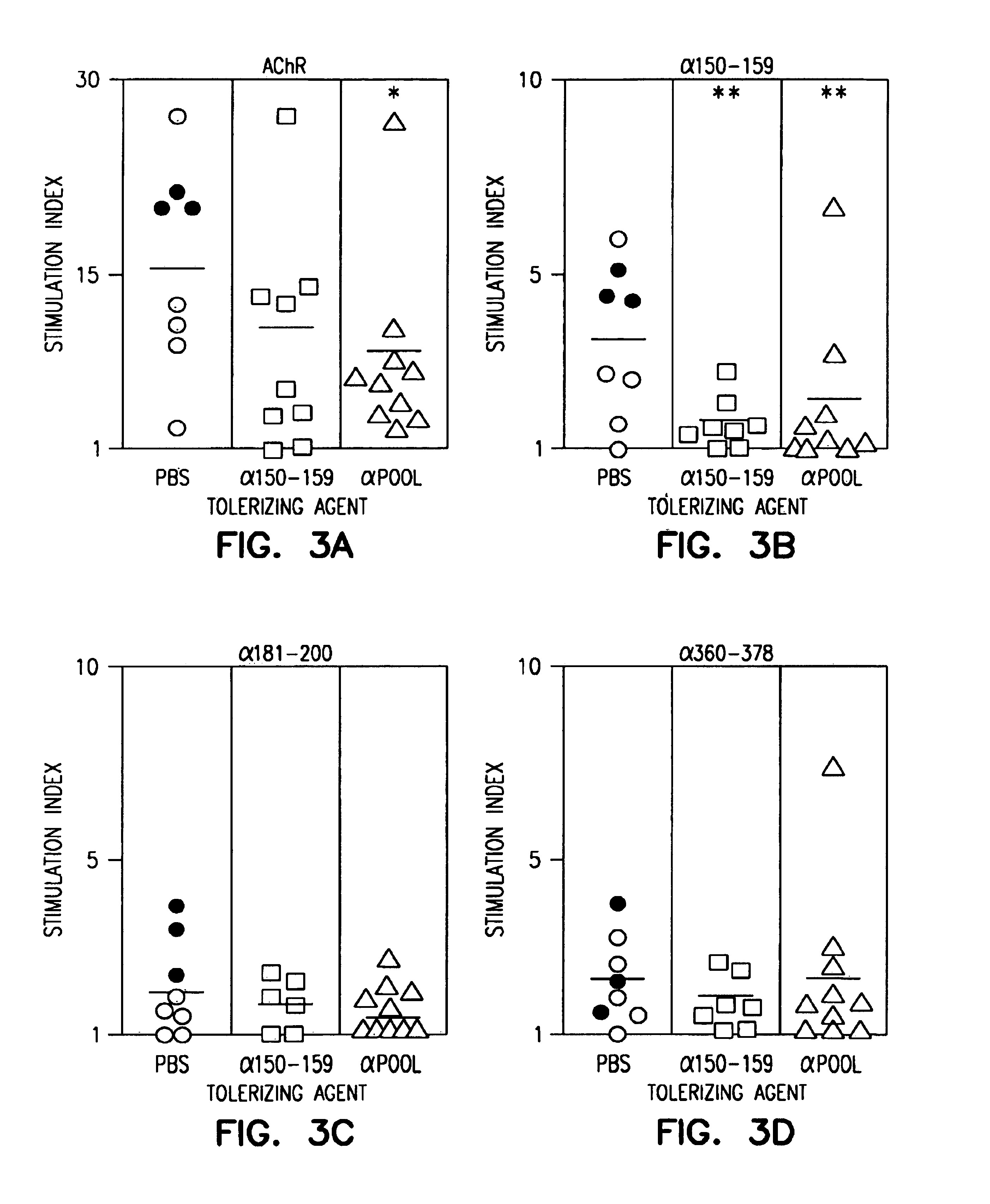
The release of antibodies then results in what is called an antigen -antibody reaction, which eventually leads to the destruction of the invading antigens. Thus, antibody response is one of the important functions of the immune system that helps protect individuals from contracting many diseases.
Polypeptide-vaccines for broad protetion against hypervirulent meningococcal lineages
ActiveUS20060171957A1Improve hydrolysis resistanceAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsSalmonella serotype typhiMeningococcal carriage
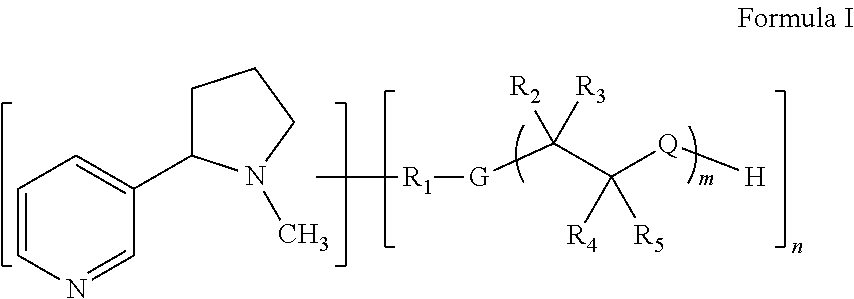
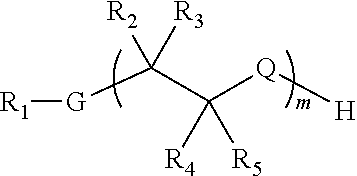
A small number of defined antigens can provide broad protection against meningococcal infection, and the invention provides a composition which, after administration to a subject, is able to induce an antibody response in that subject, wherein the antibody response is bactericidal against two or three of hypervirulent lineages A4, ET 5 and lineage 3 of N. meningitidis serogroup B. Rather than consisting of a single antigen, the composition comprises a mixture of 10 or fewer purified antigens, and should not include complex or undefined mixtures of antigens such as outer membrane vesicles. Five protein antigens are used in particular: (1) a ‘NadA’ protein; (2) a ‘741’ protein; (3) a ‘936’ protein; (4) a ‘953’ protein; and (5) a ‘287’ protein.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
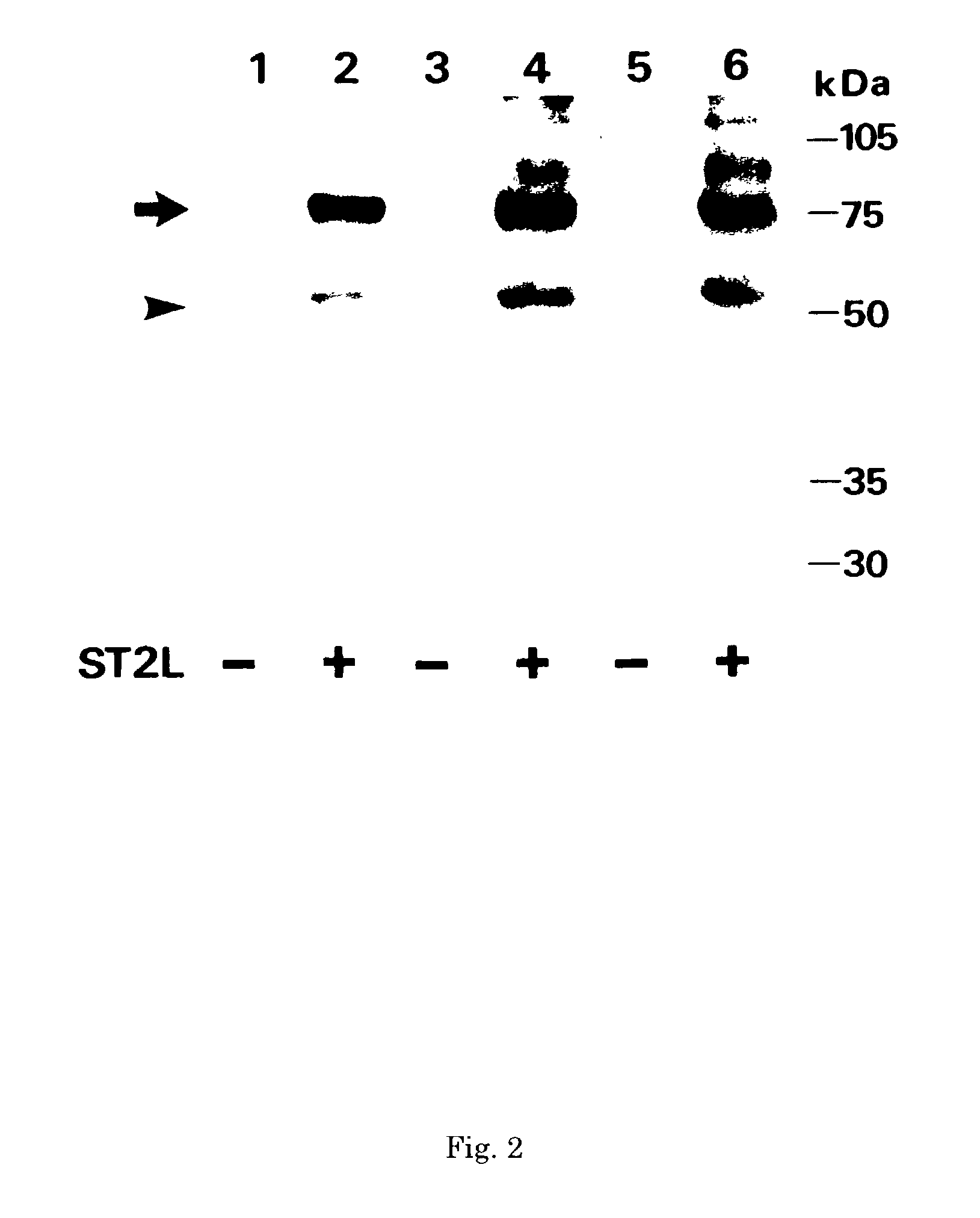
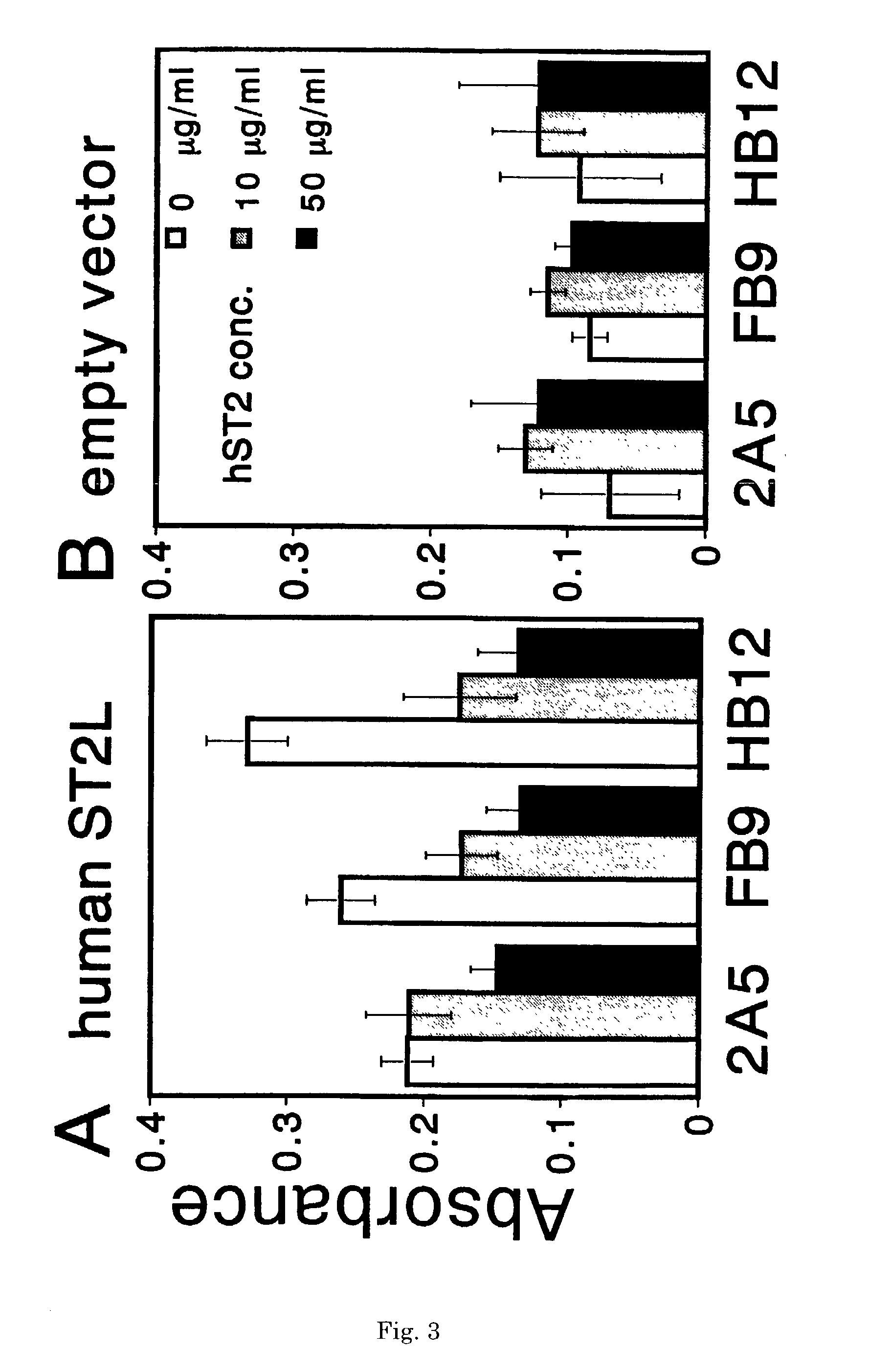
Monoclonal antibody and method and kit for immunoassay of soluble human ST2
InactiveUS7087396B2The process is convenient and fastAnimal cellsEnzymologyImmobilized AntibodiesMonoclonal antibody
A method for determining a soluble human ST2 in a sample conveniently at a high sensitivity and an assay kit are provided. By an immunological method comprising a step for bringing a sample into contact with an immobilized antibody formed by binding to an insoluble support a first anti-human ST2 antibody which binds specifically to a non-denatured human ST2, a step for labelling a first reaction product generated in the previous step by reacting said first reaction product with a second anti-human ST2 antibody which binds specifically to a non-denatured human ST2 by recognizing a site different from the site on ST2 where said first anti-human ST2 antibody binds and which is labelled with a label, and a step for determining the amount of the label on said first reaction product which has been labelled, a soluble human ST2 in a sample is determined. In addition, a recombinant ST2 is employed as a standard to prepare a calibration curve, based on which the ST2 in a sample is quantified.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
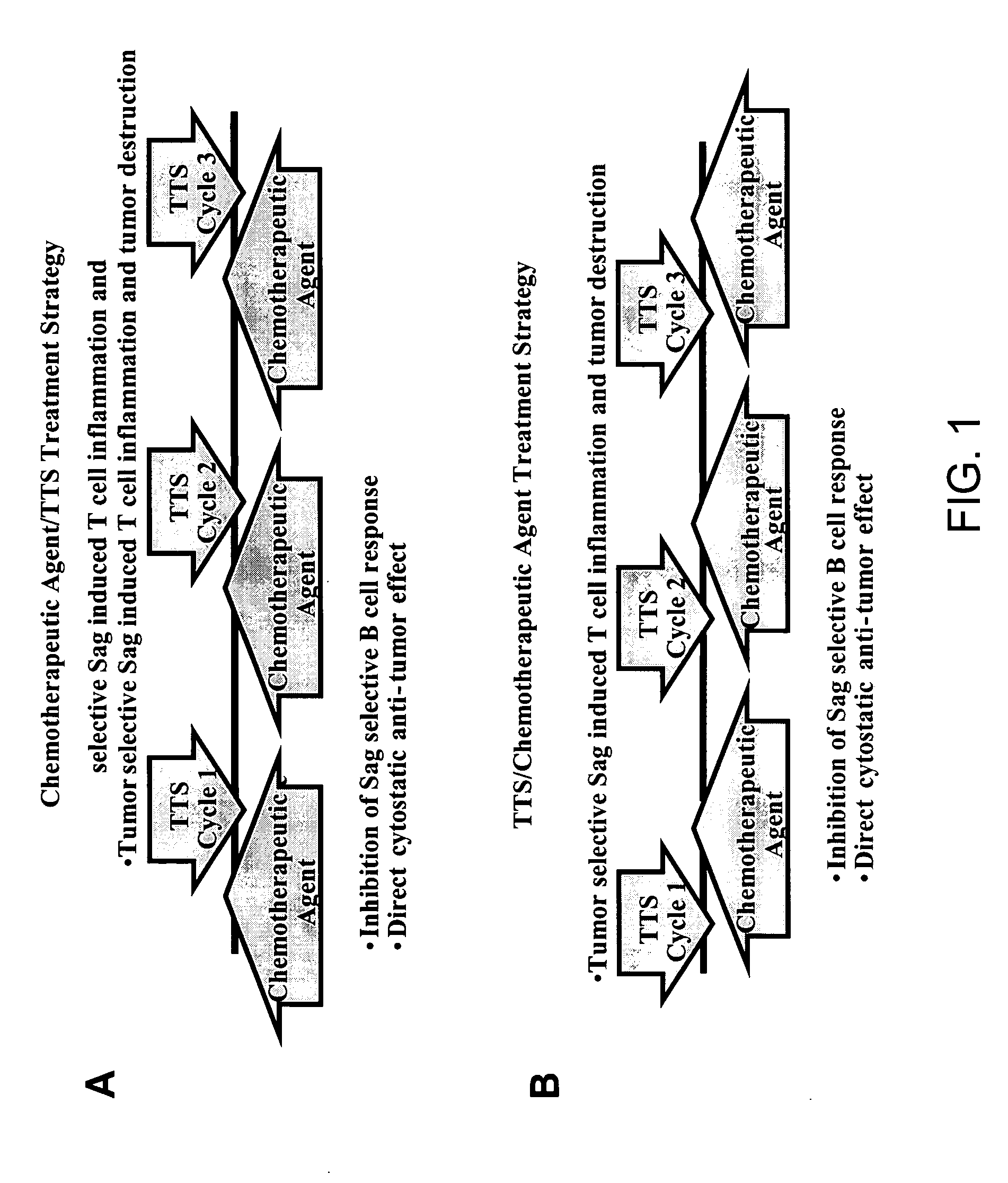
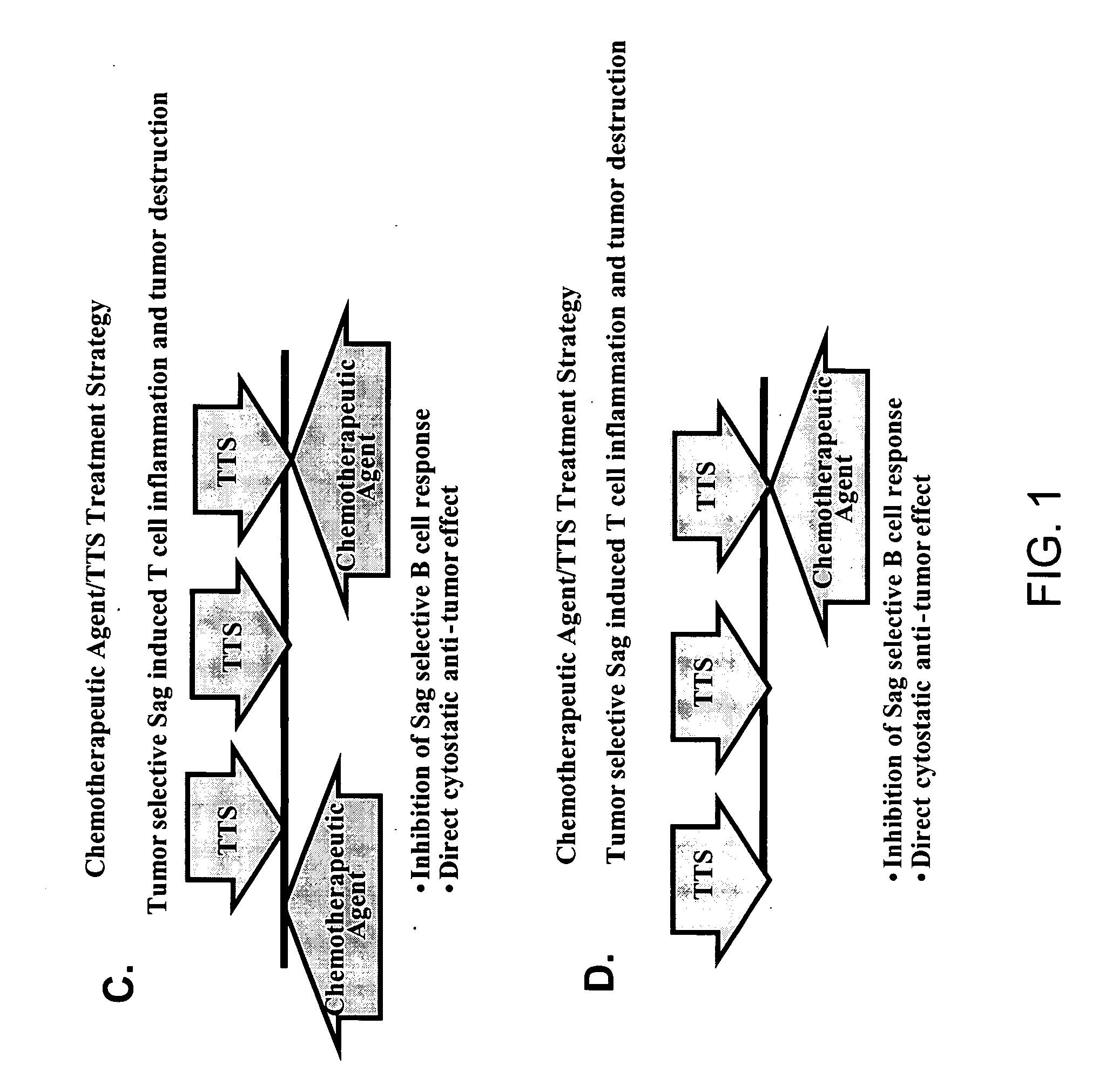
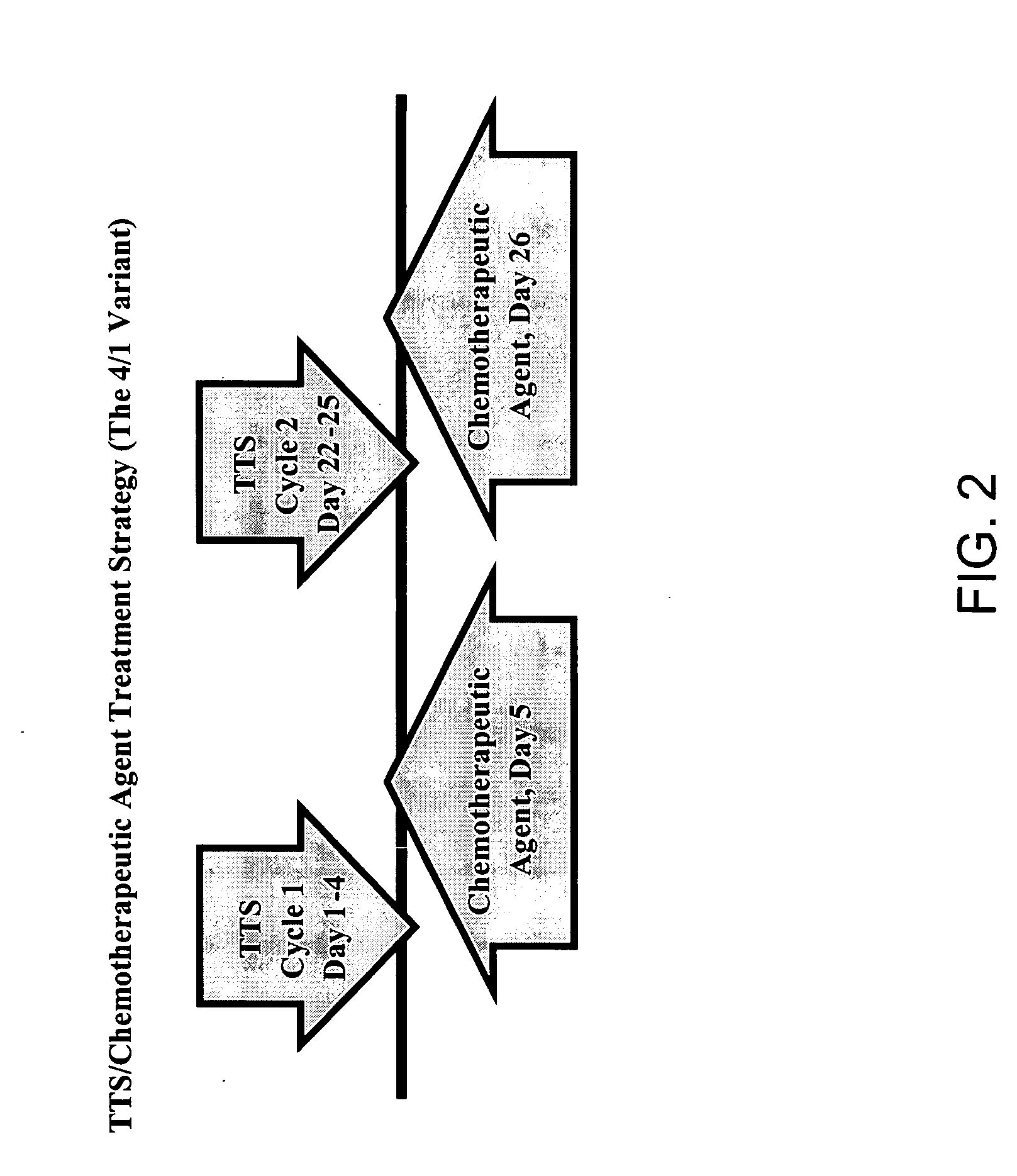
Treatment of hyperproliferative disease with superantigens in combination with another anticancer agent
ActiveUS20060057111A1Reduced antibody productionReduce productionBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsTumor targetDisease
The present invention relates to methods of treating mammals affected by, for example, a hyperproliferative disease such as cancer, by administering a tumor-targeted superantigen and a chemotherapeutic agent, whereby the administration of the tumor-targeted superantigen and chemotherapeutic agent reduce the antibody response and enhance the T cell response. The superantigen, wild-type or modified, is fused to a target-seeking moiety, such as an antibody or an antibody active fragment. The combined administration of a superantigen and a chemotherapeutic agent provides enhanced therapeutic effects in a treated animal.
Owner:ACTIVE BIOTECH AB
Methods to treat undesirable immune responses
InactiveUS6929796B1Reduced activityReduce the amount requiredBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsViral vectorGene replacement therapy
Owner:MINNESOTA RGT UNIV OF A CORP OF MN
Methods and reagents to detect and characterize norwalk and related viruses
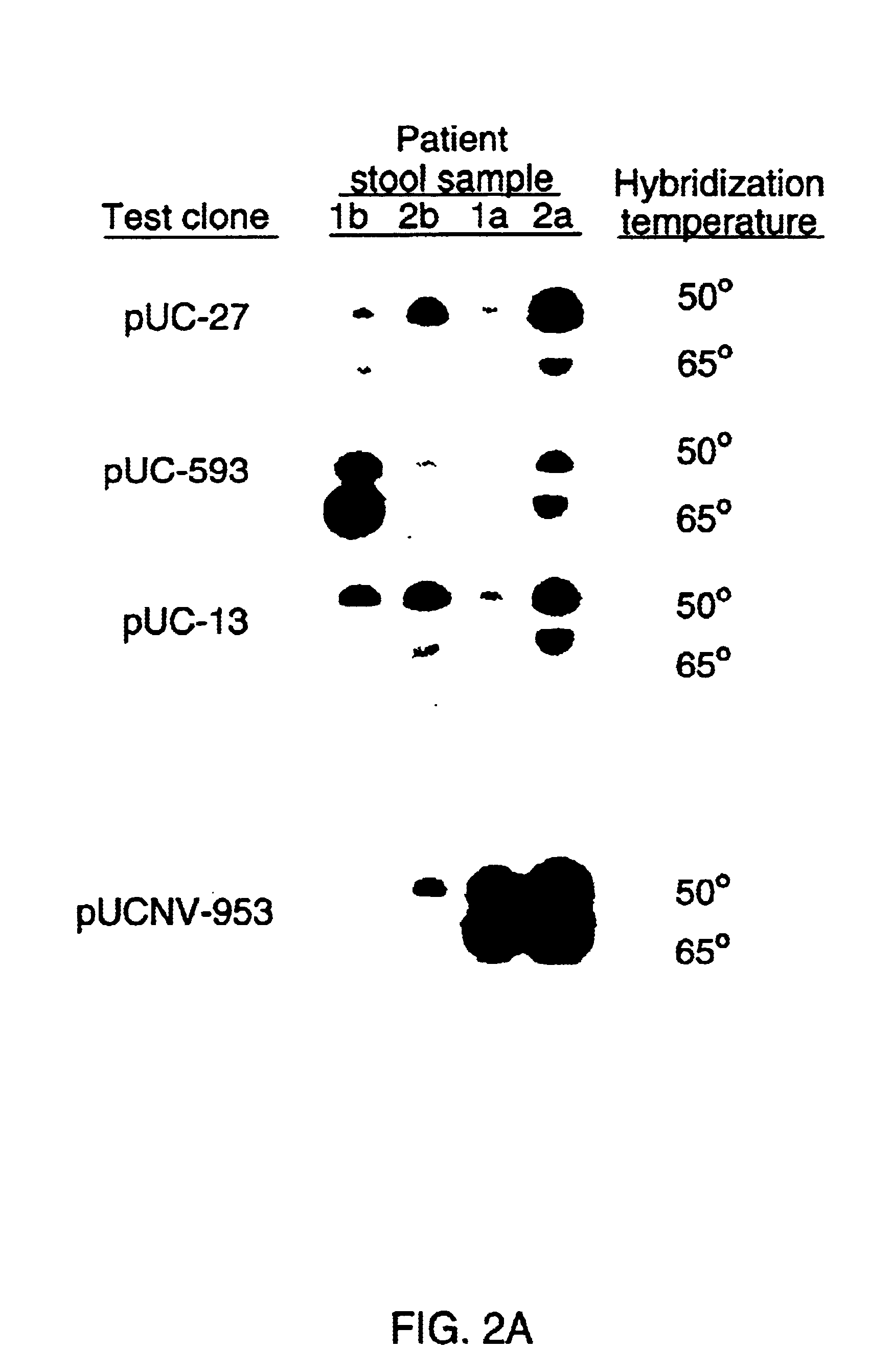
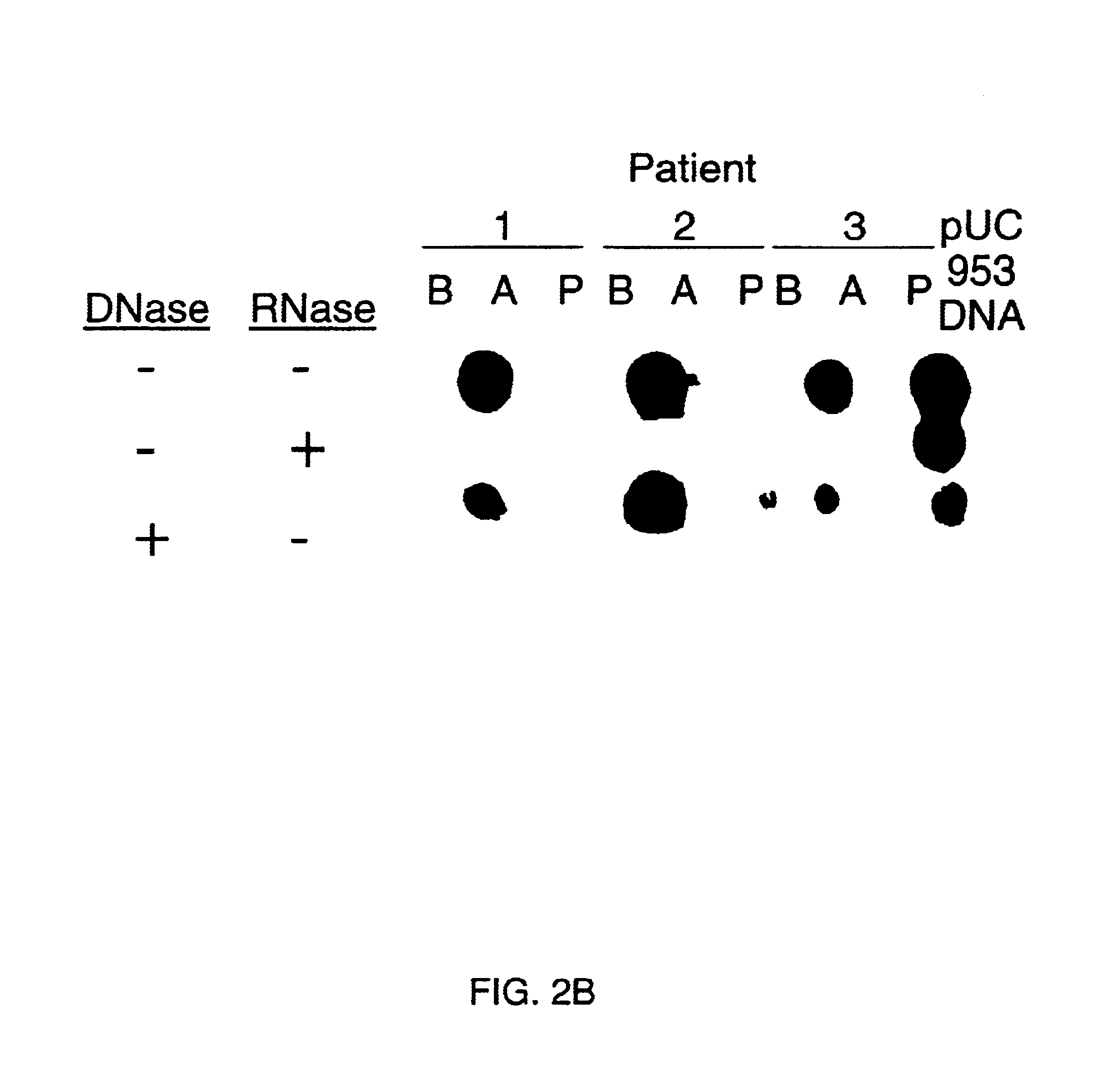
Double-stranded cDNA was synthesized from nucleic acid extracted from Norwalk virus purified from stool specimens of volunteers. One clone was isolated from a cDNA library constructed in a pUC-13 vector after amplification of the cDNA. The specificity of this cDNA (pUCNV-953) was shown by hybridization assays. The cDNA reacted with post (but not pre-) infection stool samples from Norwalk volunteers and with highly purified Norwalk virus, but not with other common enteric viruses such as hepatitis A virus and rotavirus. Finally, the probe detected virus in the same fractions of CsCl gradients in which viral antigen was detected using a specific Norwalk virus radioimmunoassay, and particles were detected by immune electron microscopy. Single-stranded RNA probes derived from the DNA clone after subcloning into an in vitro transcription vector were also used to show that the Norwalk virus contains a ssRNA genome of about 8 kb in size. The original clone was also used to detect additional cDNAs which represent at least 7 kb of nucleic acid of the Norwalk genome. The availability of a Norwalk-specific cDNA and the first partial genome sequence information allow rapid cloning of the entire genome and of establishment of sensitive diagnostic assays. Such assays can be based on detection of Norwalk virus nucleic acid or Norwalk viral antigen using polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to proteins expressed from the cDNA or to synthetic peptides made based on the knowledge of the genome sequence. Assays using proteins deduced from the Norwlk virus genome and produced in expression systmes can measure antibody responses. Vaccines made by recombinant DNA technology are now feasible.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
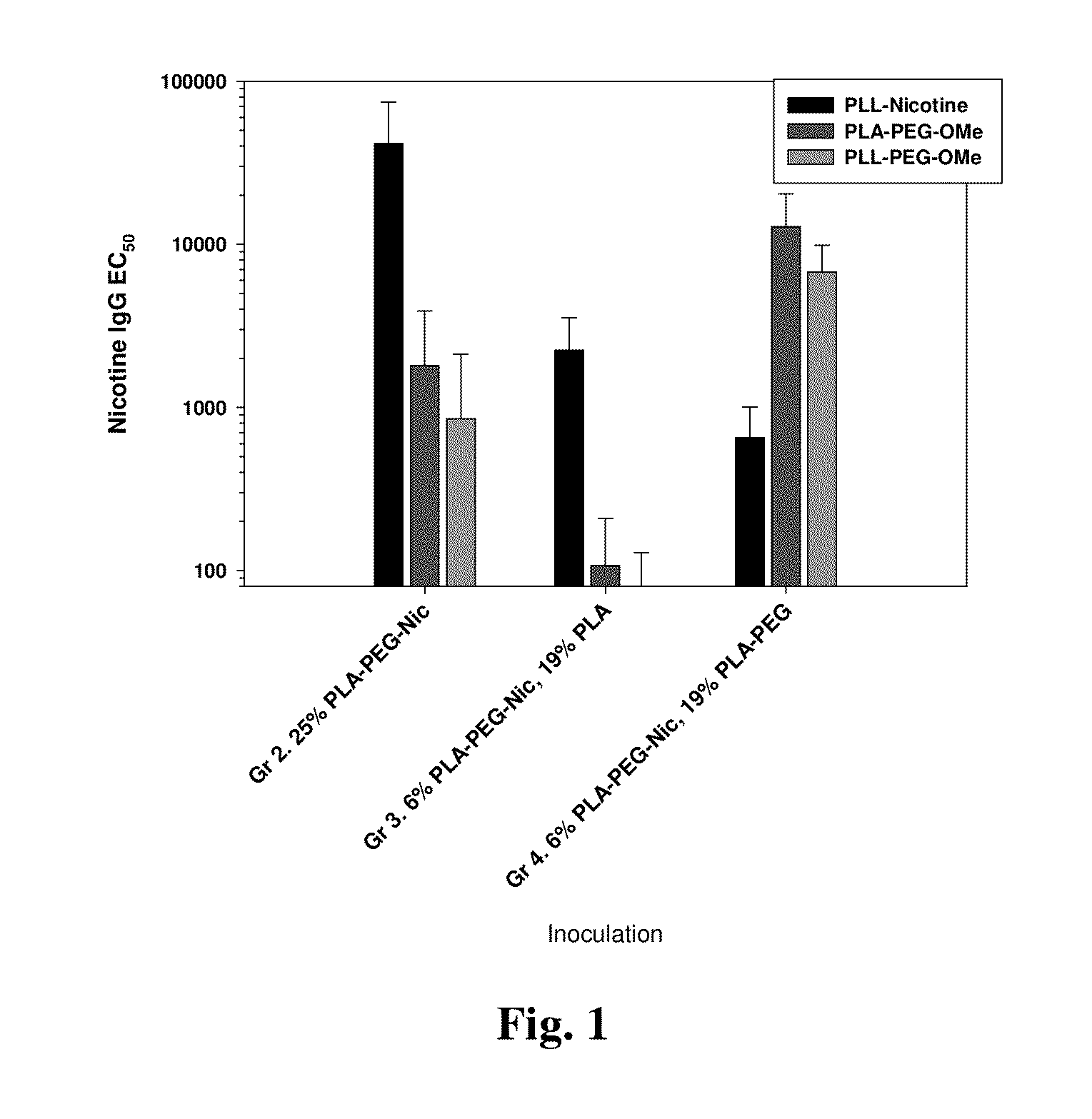
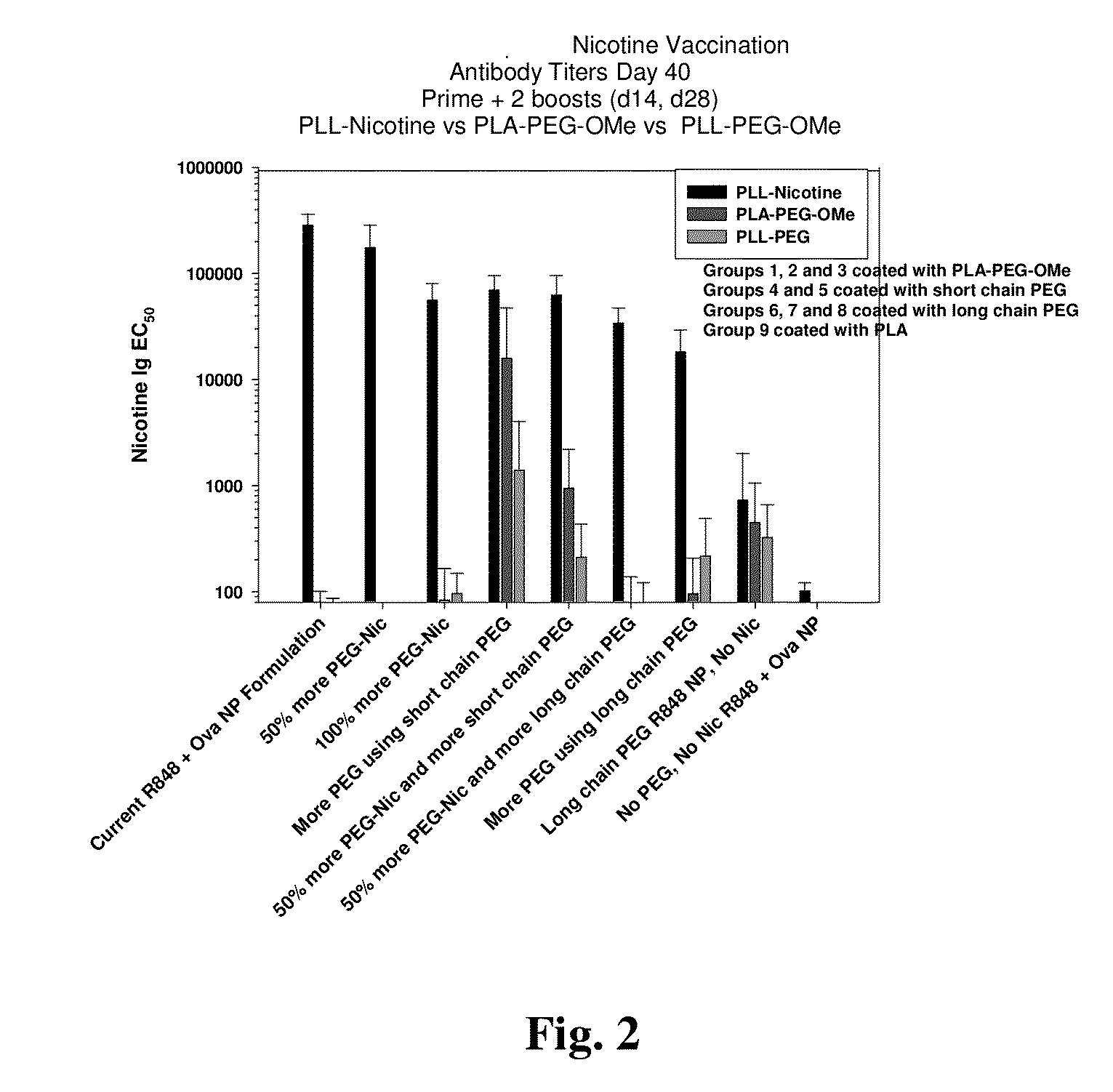
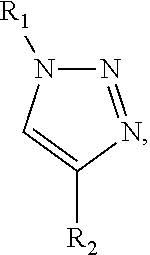
Modified nicotinic compounds and related methods
Provided herein are compounds and related composition and methods that may be used to raise an antibody response to nicotinic compounds, in some embodiments.
Owner:SELECTA BIOSCI
Polysaccharide-staphylococcal surface adhesin carrier protein conjugates for immunization against nosocomial infections
ActiveUS20070141077A1Prevention and reduction of severityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCarrier proteinImmunogenicity
Immunogenic polysaccharide-protein conjugates having a polysaccharide antigen (or its oligosaccharide fragment representing one or more antigenic epitopes) derived from a nosocomial pathogen conjugated to a staphylococcal surface adhesin carrier protein are used in immunogenic compositions to elicit antibody responses to both the polysaccharide antigen and the staphylococcal surface adhesin carrier protein. Such immunogenic compositions are used to immunize against diseases caused by Staphylococcal aureus, Staphylococcal epidermidis or other nosocomial pathogens.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS CORP
Control of antibody responses to synthetic nanocarriers
Disclosed are synthetic nanocarrier compositions that comprise B cell antigen for desired antibody production and an off-target response attenuating polymeric coating as well as related methods.
Owner:SELECTA BIOSCI
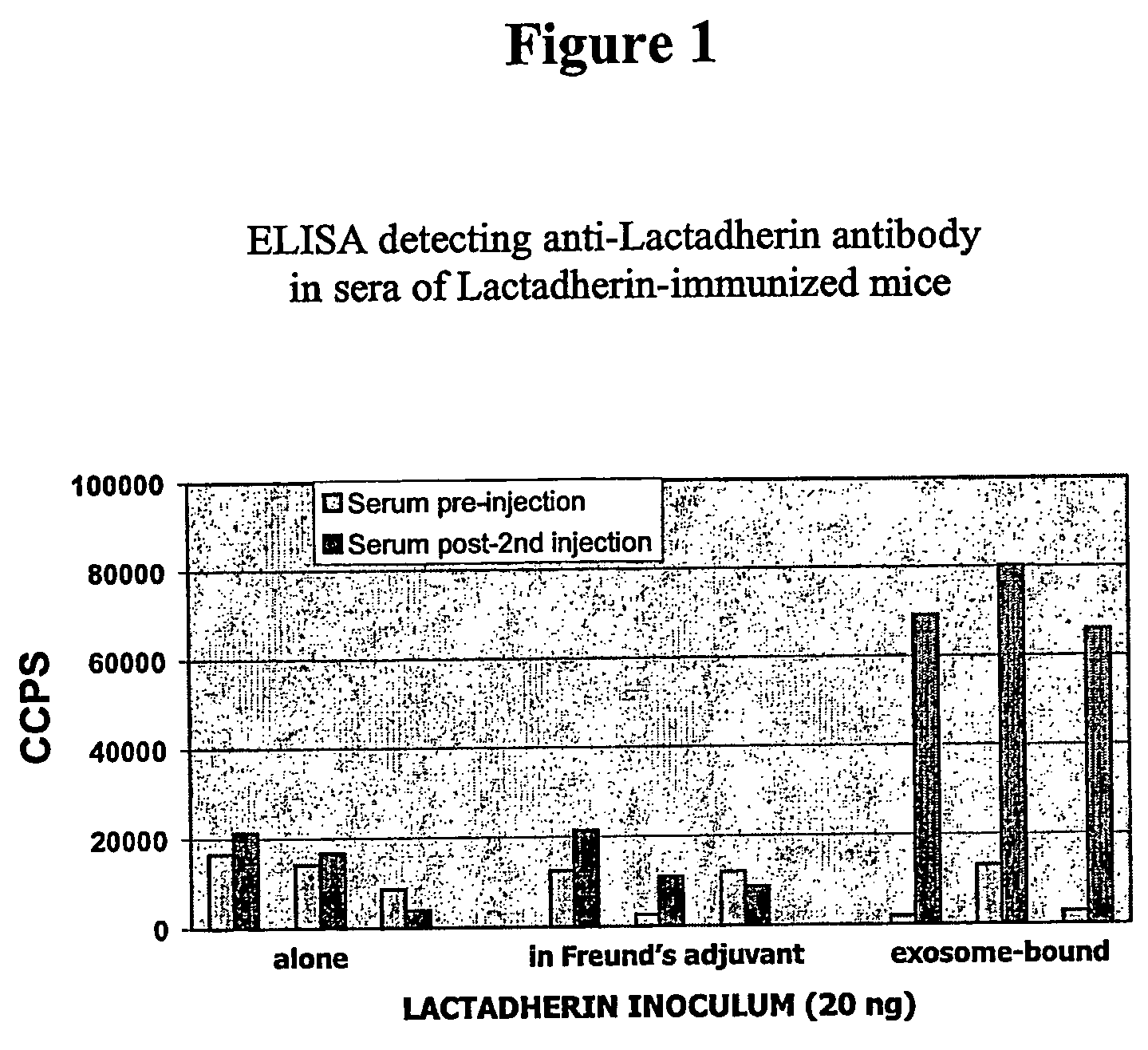
Methods and compounds for raising antibodies and for screening antibody repertoires
InactiveUS20060222654A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansSnake antigen ingredientsAntibody-Producing CellsImmunogenicity
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for raising antibodies generally comprising 1) providing highly immunogenic vesicles bearing at least one target antigen and 2) immunizing animals with the said antigen-bearing vesicles to induce antigen-specific antibody responses. The invention also relates to methods of screening antibody repertoires comprising 1) providing vesicles bearing at least one target antigen and one marker and 2) isolating antibody-producing cells or particles with defined antigen specificity using the said antigen- and marker-bearing vesicles. Antibodies with defined antigen specificity can then be prepared from isolated antibody-producing cells using known methods of the art. This invention can be used in experimental, research, therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic areas.
Owner:EXOTHERA
INDUCTION OF BROADLY REACTIVE NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODIES BY FOCUSING THE IMMUNE RESPONSE ON V3 EPITOPES OF THE HIV-1 gp120 ENVELOPE
InactiveUS20080279879A1Vigorous Ab responseViral antigen ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousNeutralizing antibody
Compositions, kits and methods for boosting, or for priming and boosting, high titer broadly neutralizing cross-clade antibody responses focused on single HIV-1 neutralizing epitopes are disclosed. gp120 DNA plasmids comprising HIV env genes are used to prime the antibody response. Primed subjects are immunized with recombinant fusion proteins that comprise a “carrier” protein fusion partner, preferably a truncated form of the MuLV gp70 Env protein, and a desired HIV neutralizing epitopes. Preferred epitopes are epitopes of V3 from one or more HIV clades. Immune sera from such immunized subjects neutralized primary isolates from virus strains heterologous to those from which the immunogens were constructed. Neutralizing activity was primarily due to V3-specific antibodies and cross-clade neutralizing Abs were present. This approach results in more potent and broader neutralizing antibody levels, a result of “immunofocusing” the humoral immune response on neutralizing epitopes such as V3.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
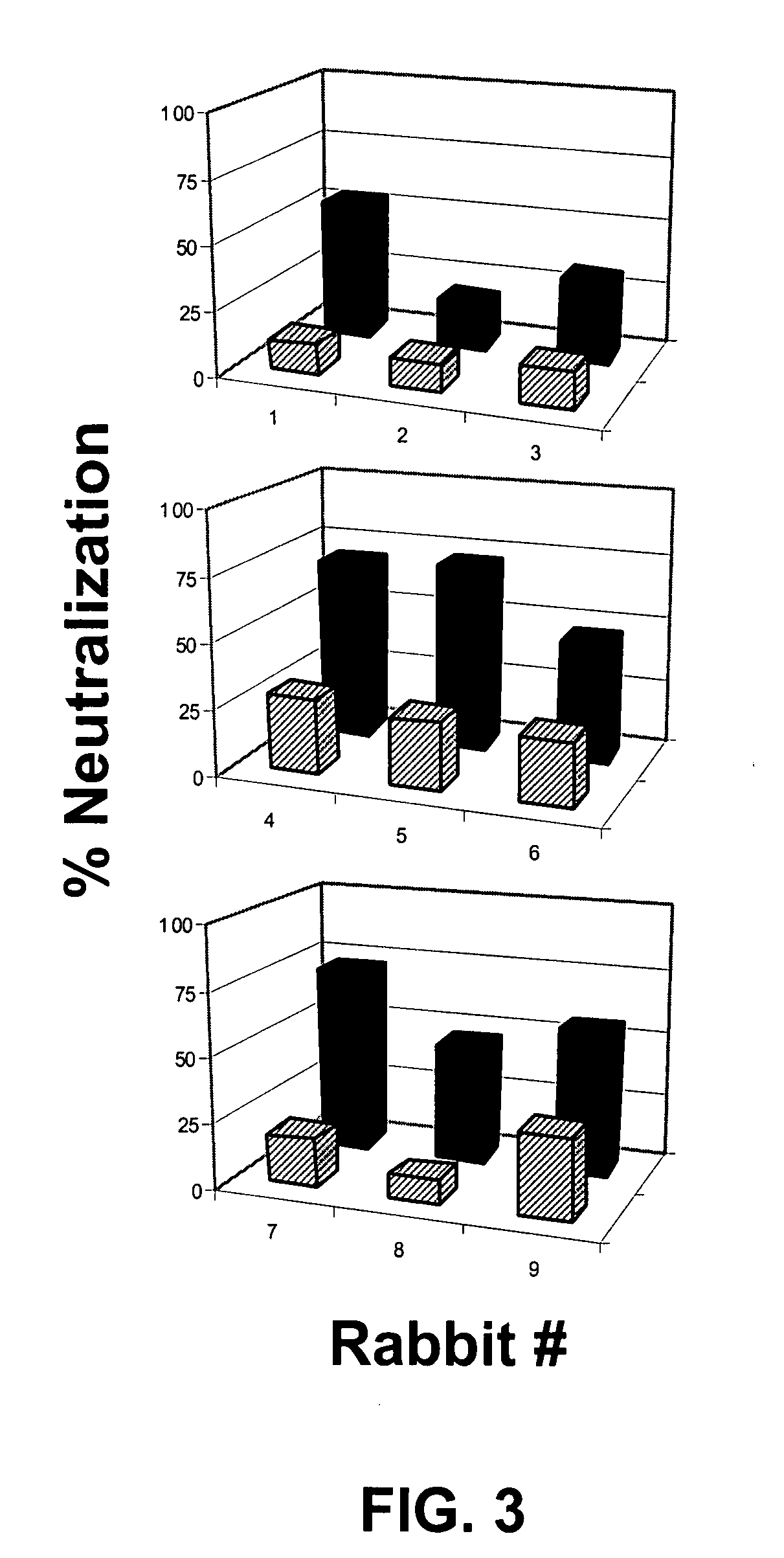
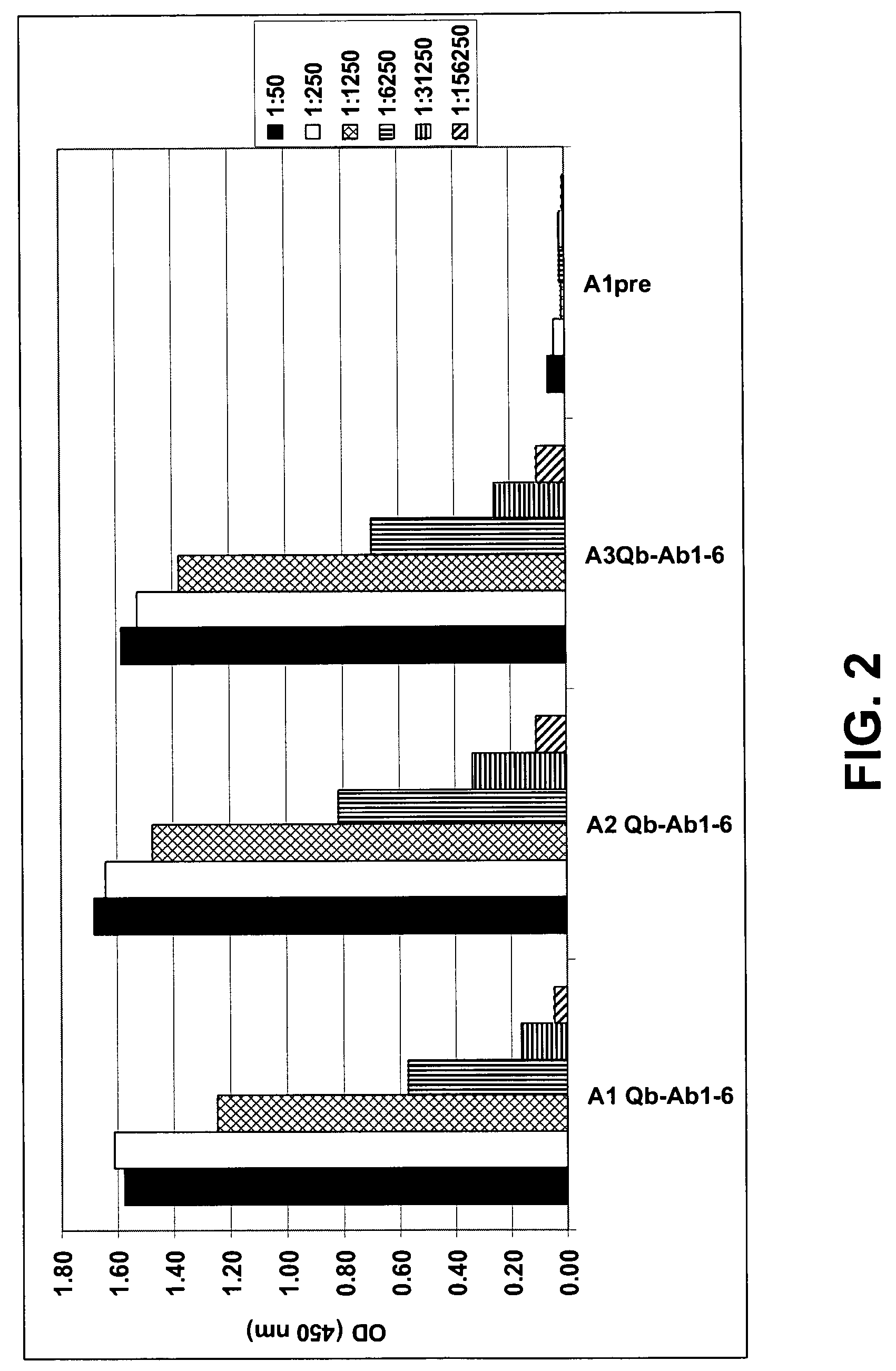
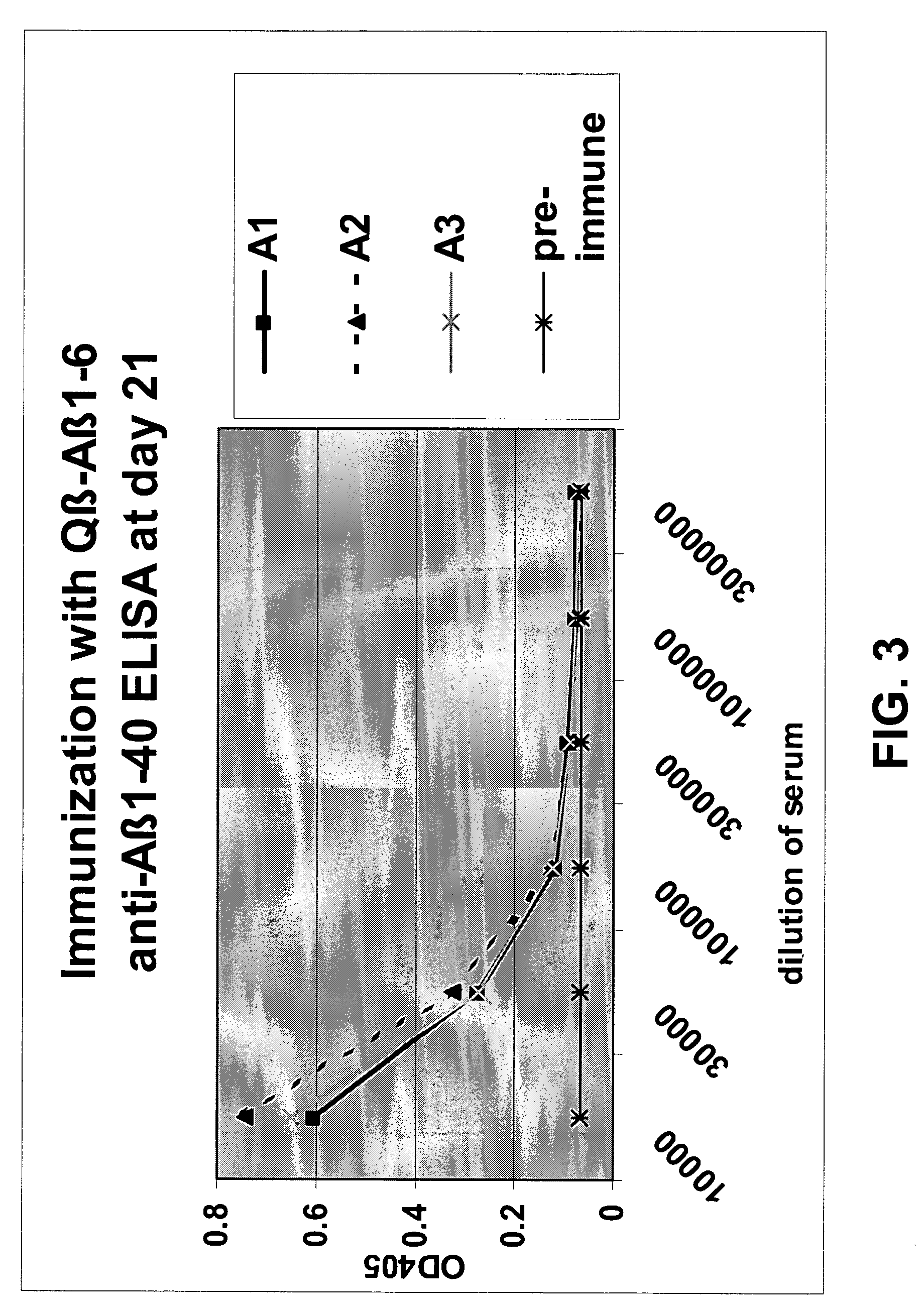
Amyloid β1-6 antigen arrays
InactiveUS7279165B2High potencyEfficient inductionNervous disorderVirus peptidesVirus-like particleSpecific immunity
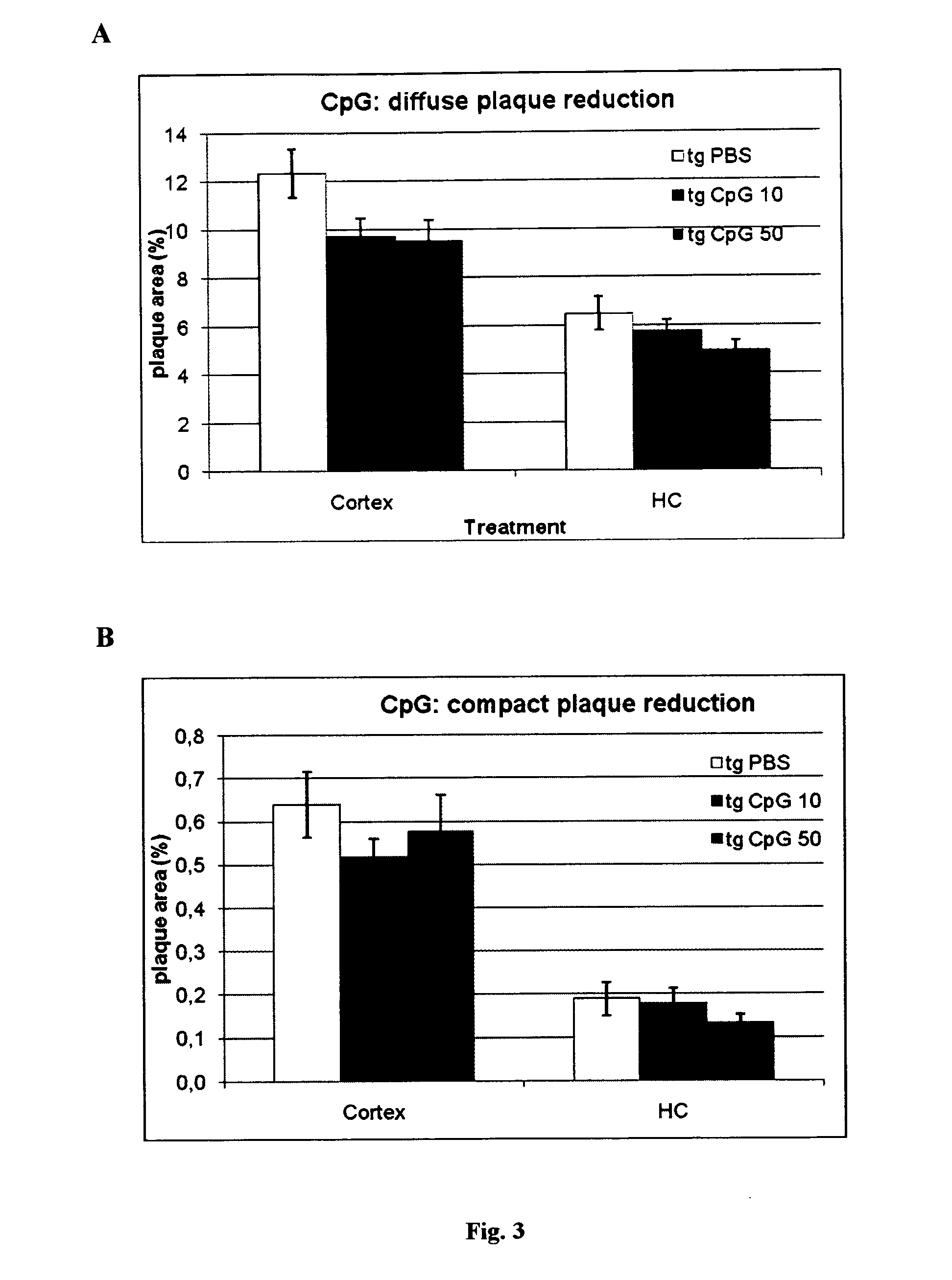
The present invention is related to the fields of molecular biology, virology, immunology and medicine. The invention provides a composition comprising an ordered and repetitive antigen or antigenic determinant array, and in particular an Aβ1-6 peptide-VLP-composition. More specifically, the invention provides a composition comprising a virus-like particle and at least one Aβ1-6 peptide bound thereto. The invention also provides a process for producing the conjugates and the ordered and repetitive arrays, respectively. The compositions of the invention are useful in the production of vaccines for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and as a pharmaccine to prevent or cure Alzheimer's disease and to efficiently induce immune responses, in particular antibody responses. Furthermore, the compositions of the invention are particularly useful to efficiently induce self-specific immune responses within the indicated context.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method for a fully automated monoclonal antibody-based extended differential
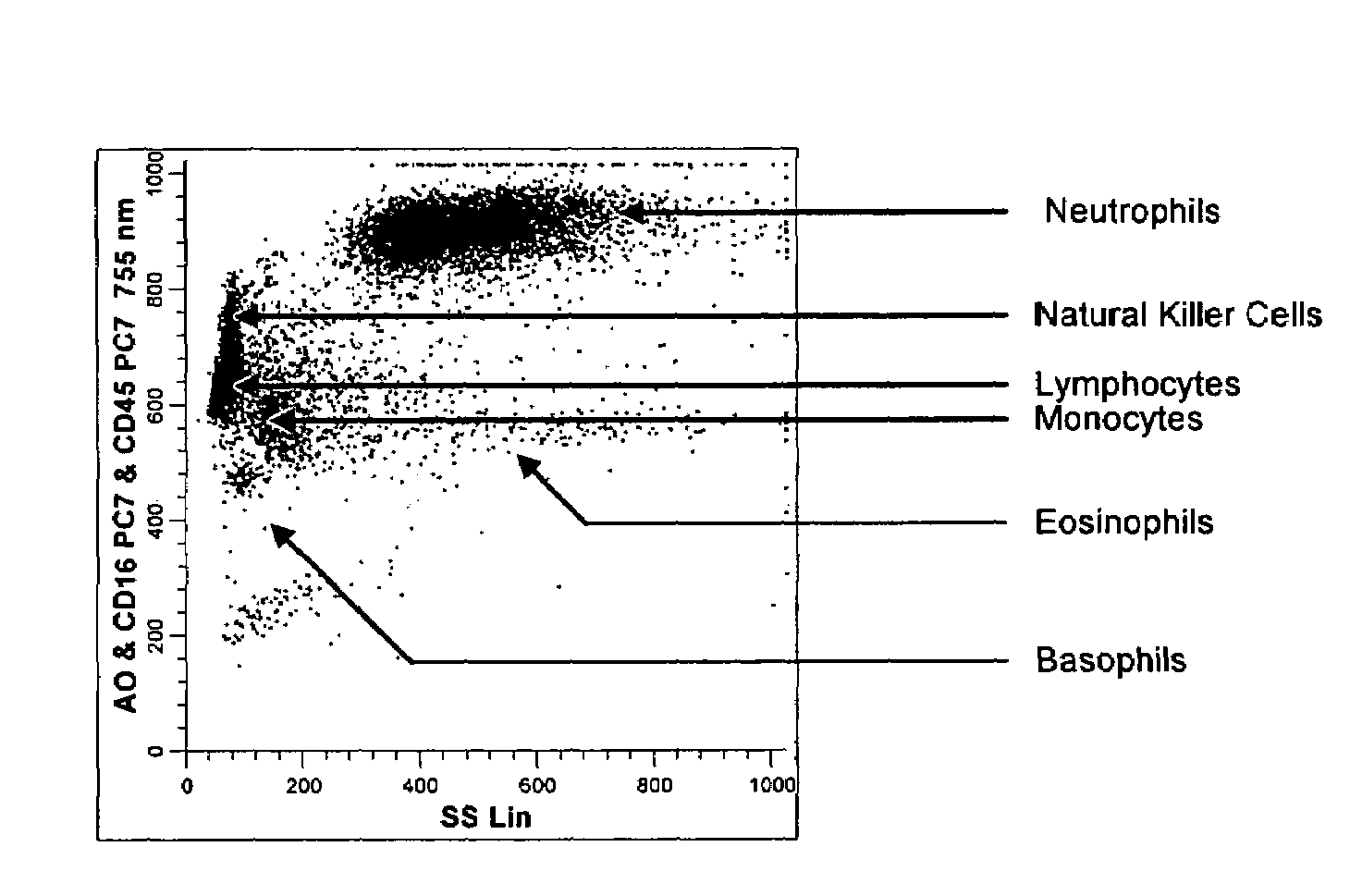
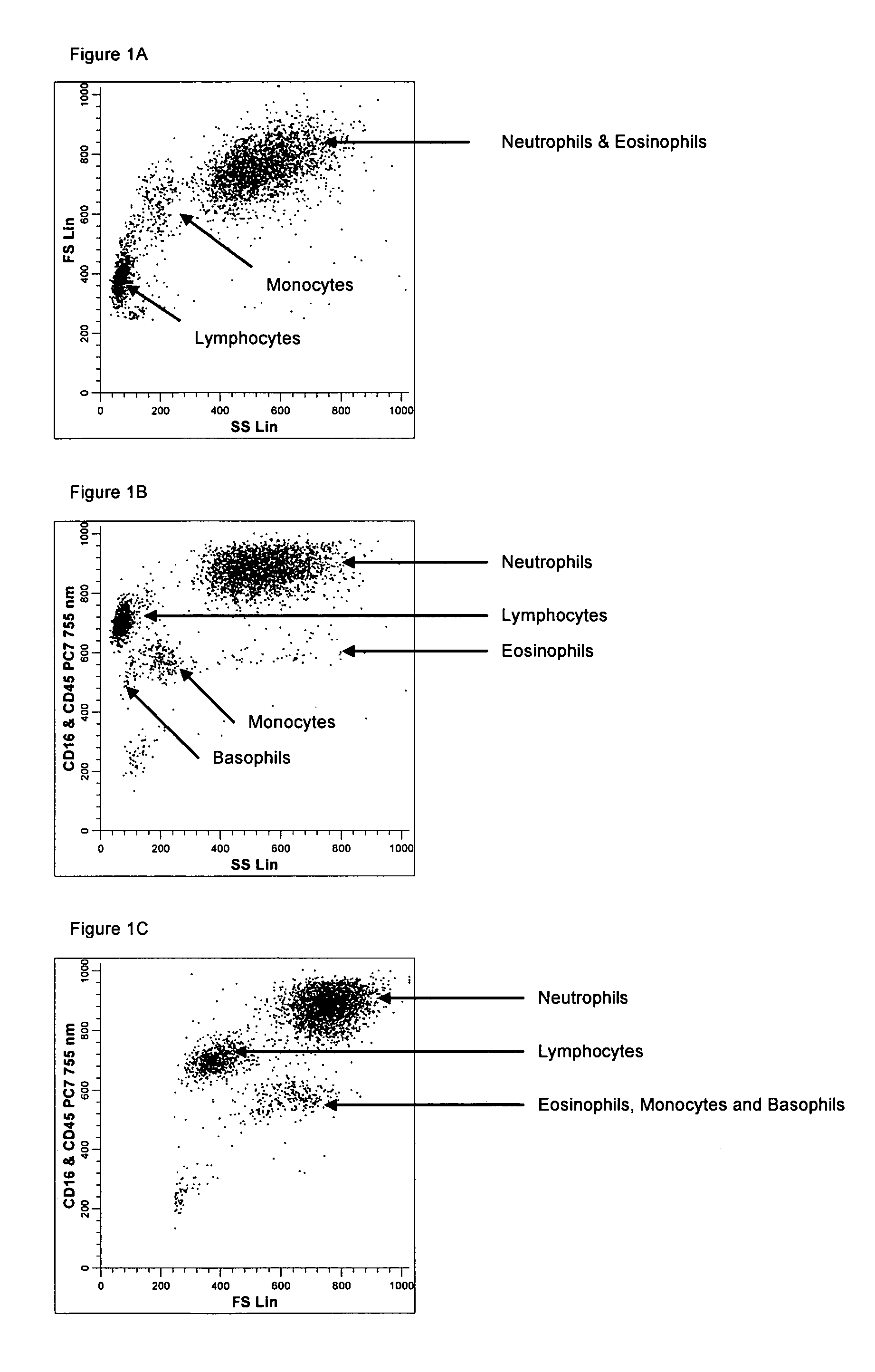
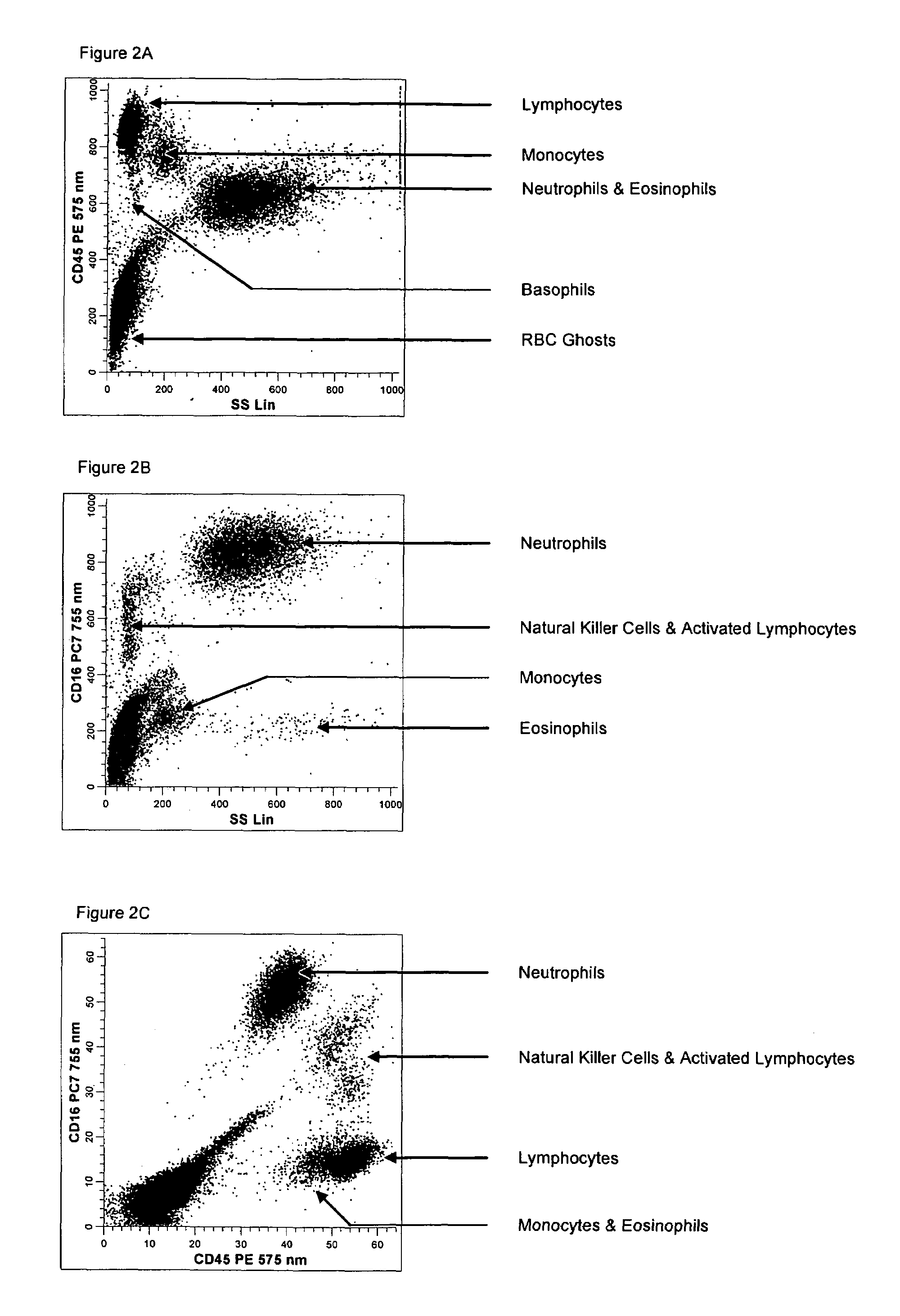
ActiveUS7625712B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceWhite blood cell
A method useful for the enumeration of cell populations in a biological sample includes the steps of reacting in a single reaction mixture a sample, a first antibody labeled with a fluorochrome having a first emission spectrum and an additional antibody. The first antibody binds to an antigenic determinant differentially expressed on leukocytes and non-leukocytes. The additional antibody binds to an antigenic determinant differentially expressed on mature and immature granulocytes or myeloid cells, and is labeled either with the first fluorochrome or an additional fluorochrome having an emission spectrum distinguishable from the first emission spectrum. The reaction mixture can be mixed with a nucleic acid dye having an emission spectrum that overlaps with one of the first or additional emission spectra. The reaction mixture may be treated with a lytic system that differentially lyses non-nucleated red blood cells and conserves leukocytes. Populations of hematological cells are detected and enumerated using at least two parameters (fluorescence, optical, and electrical) for each population.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Molecular antigen array
InactiveUS7264810B2Efficient inductionHighly ordered and repetitive antigenVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsSpecific immunityAllergy
The present invention is related to the fields of molecular biology, virology, immunology and medicine. The invention provides a composition comprising an ordered and repetitive antigen or antigenic determinant array. The invention also provides a process for producing an antigen or antigenic determinant in an ordered and repetitive array. The ordered and repetitive antigen or antigenic determinant is useful in the production of vaccines for the treatment of infectious diseases, the treatment of allergies and as a pharmaccine to prevent or cure cancer and to efficiently induce self-specific immune responses, in particular antibody responses.
Owner:KUROS BIOSCIENCES AG
Antigen arrays for treatment of bone disease
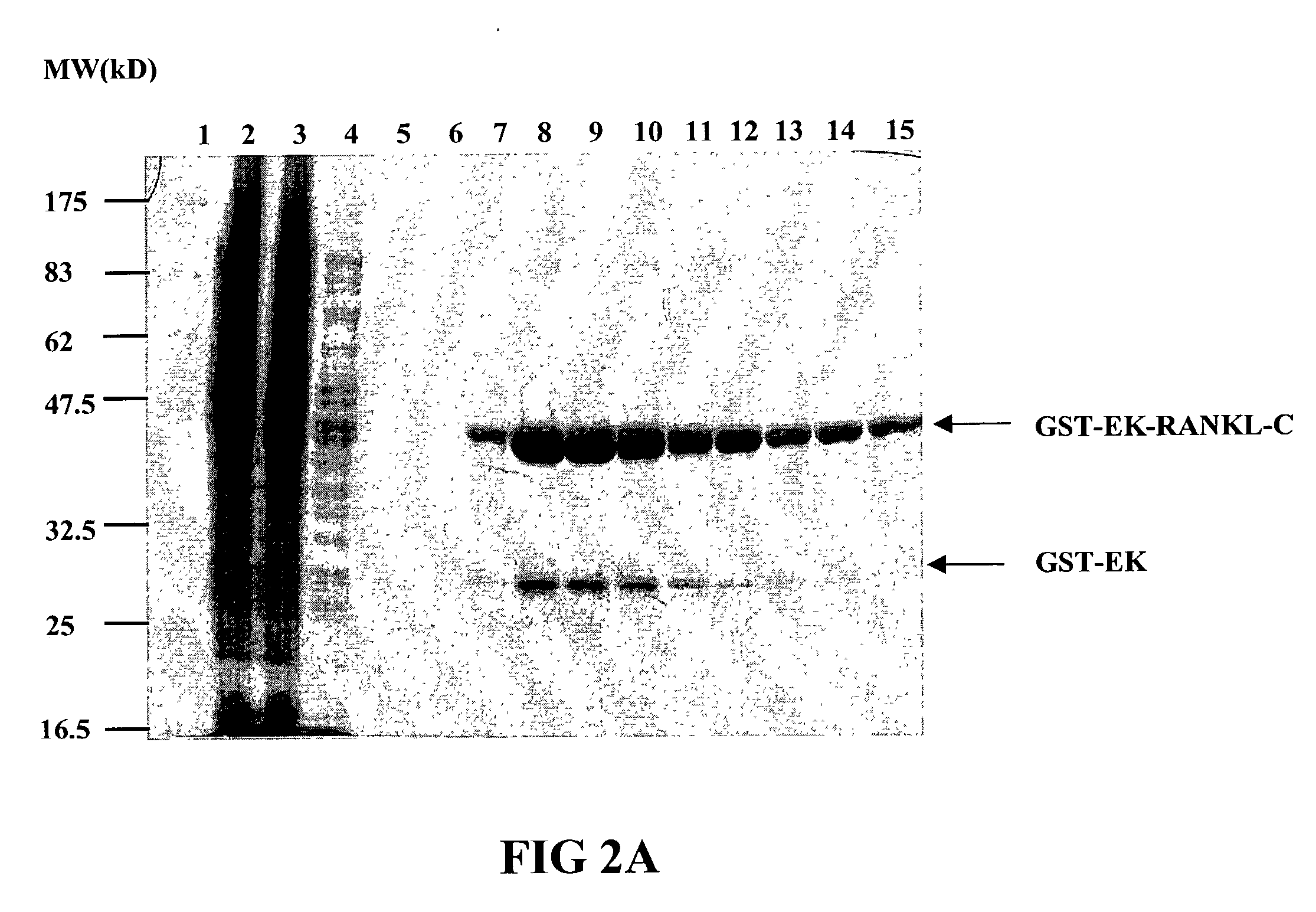
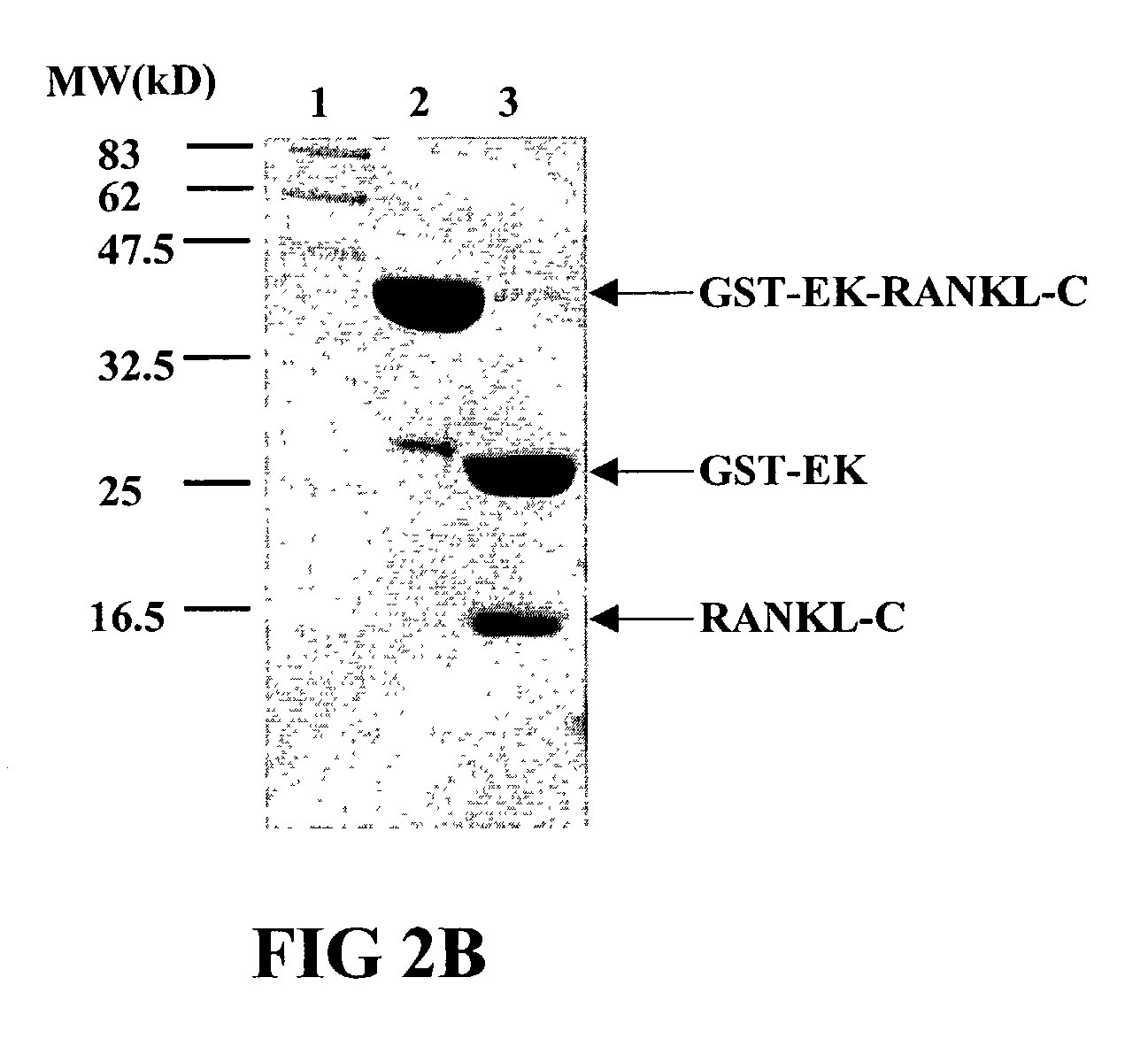
InactiveUS7128911B2Induce high titer of anti-RANKLEfficient inductionVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseRANKL Protein
The present invention is related to the fields of molecular biology, virology, immunology and medicine. The invention provides a composition comprising an ordered and repetitive antigen or antigenic determinant array, and in particular a RANKL protein, RANKL fragment or RANKL peptide-VLP-array. More specifically, the invention provides a composition comprising a virus-like particle and at least one RANKL protein, RANKL fragment or RANKL peptide bound thereto. The invention also provides a process for producing the conjugates and the ordered and repetitive arrays, respectively. The compositions of the invention are useful in the production of vaccines for the treatment of bone diseases and as a pharmaccine to prevent or cure bone diseases and to efficiently induce immune responses, in particular antibody responses. Furthermore, the compositions of the invention are particularly useful to efficiently induce self-specific immune responses within the indicated context.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
Antigen arrays for treatment of allergic eosinophilic diseases
InactiveUS7094409B2Inhibit eosinophiliaInduce high titersVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsSpecific immunityEosinophilic cell
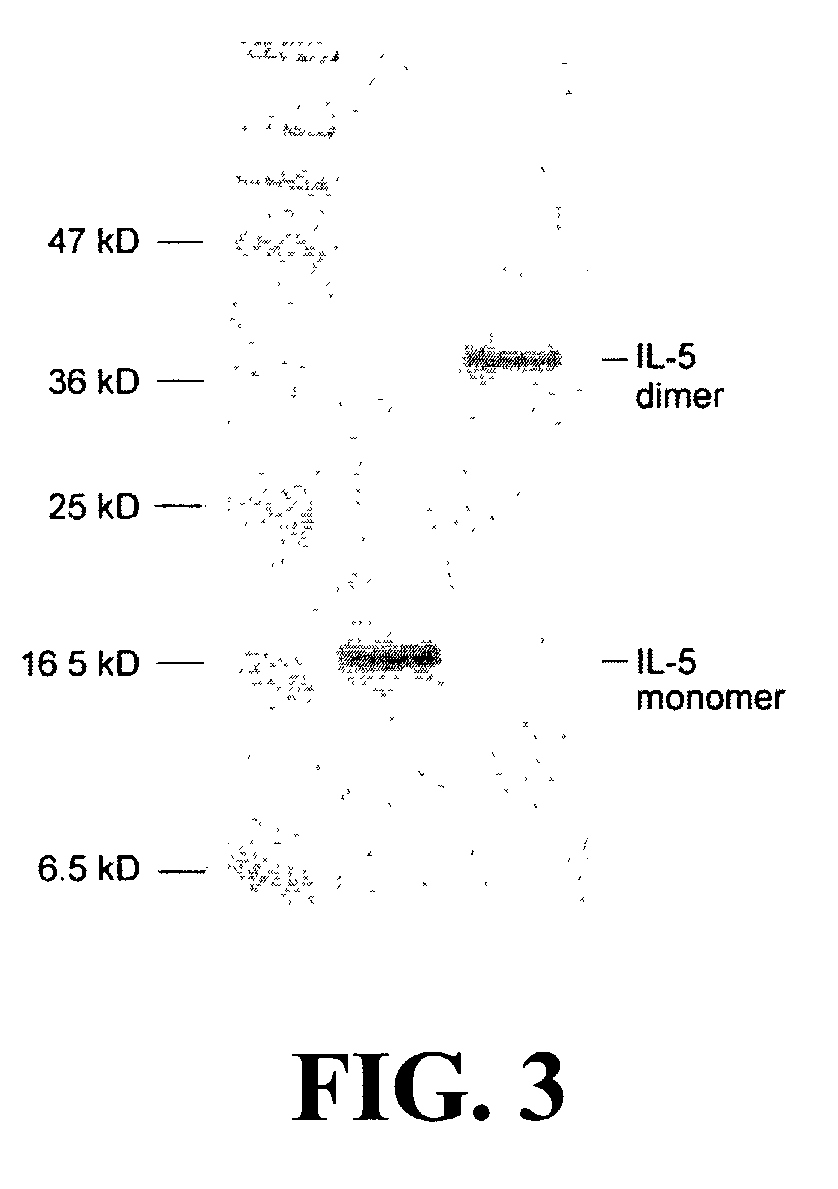
The present invention is related to the fields of molecular biology, virology, immunology and medicine. The invention provides a composition comprising an ordered and repetitive antigen or antigenic determinant array, and in particular an array comprising a protein or peptide of IL-5, IL-13 or eotaxin. More specifically, the invention provides a composition comprising a virus-like particle and at least one protein, or peptide of IL-5, IL-13 and / or eotaxin bound thereto. The invention also provides a process for producing the conjugates and the ordered and repetitive arrays, respectively. The compositions of the invention are useful in the production of vaccines for the treatment of allergic diseases with an eosinophilic component and as a pharmaccine to prevent or cure allergic diseases with an eosinophilic component and to efficiently induce immune responses, in particular antibody responses. Furthermore, the compositions of the invention are particularly useful to efficiently induce self-specific immune responses within the indicated context.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
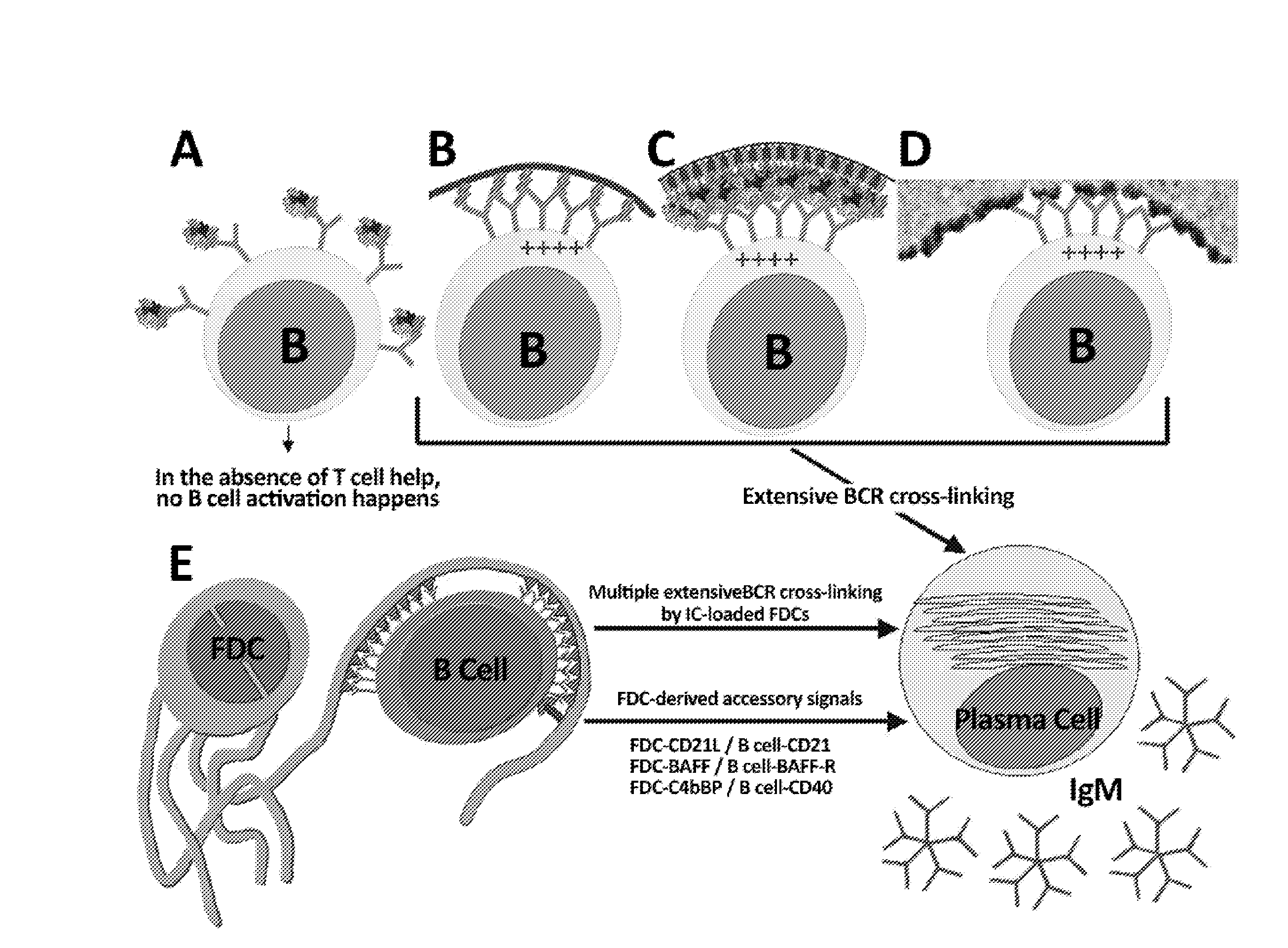
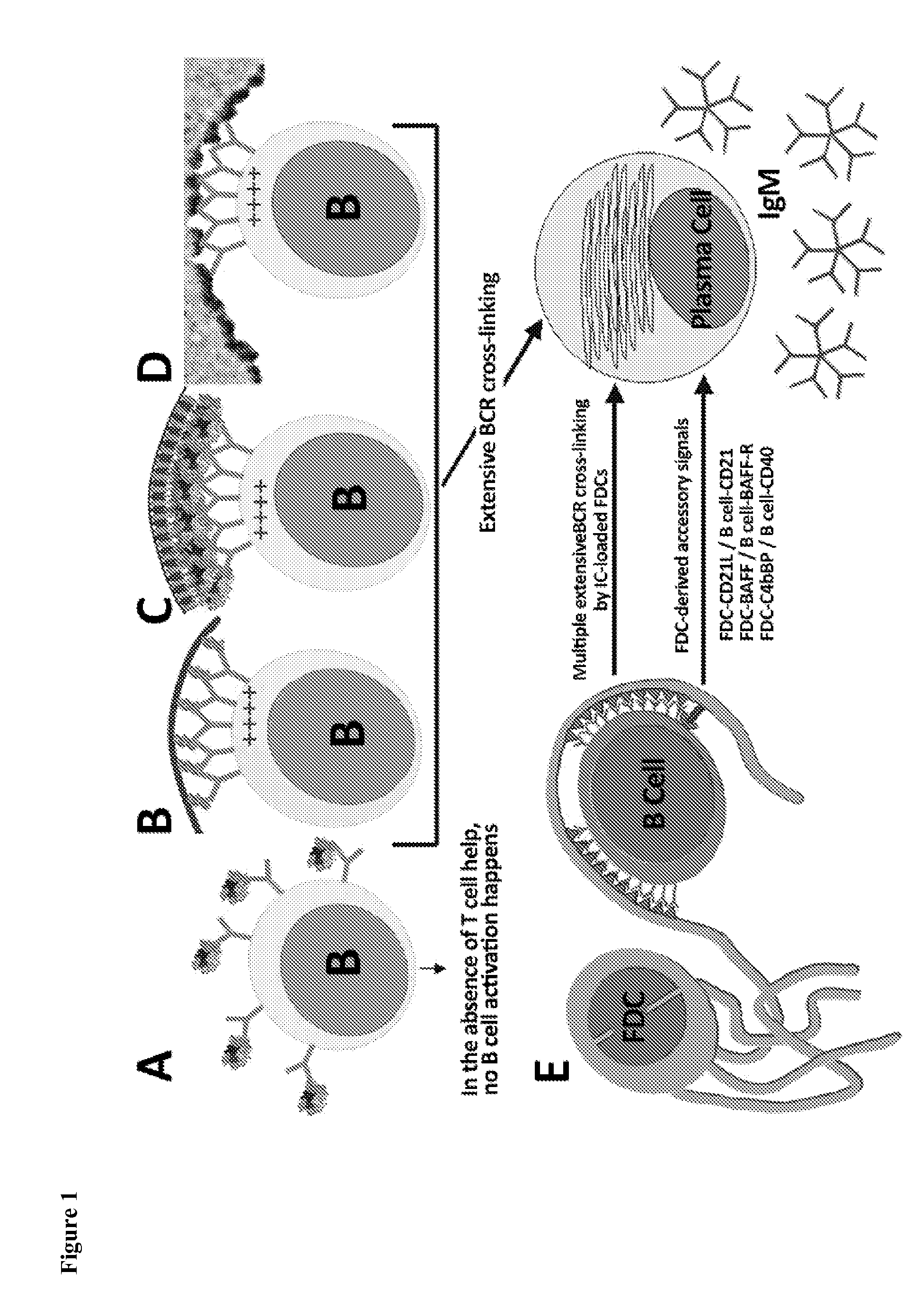
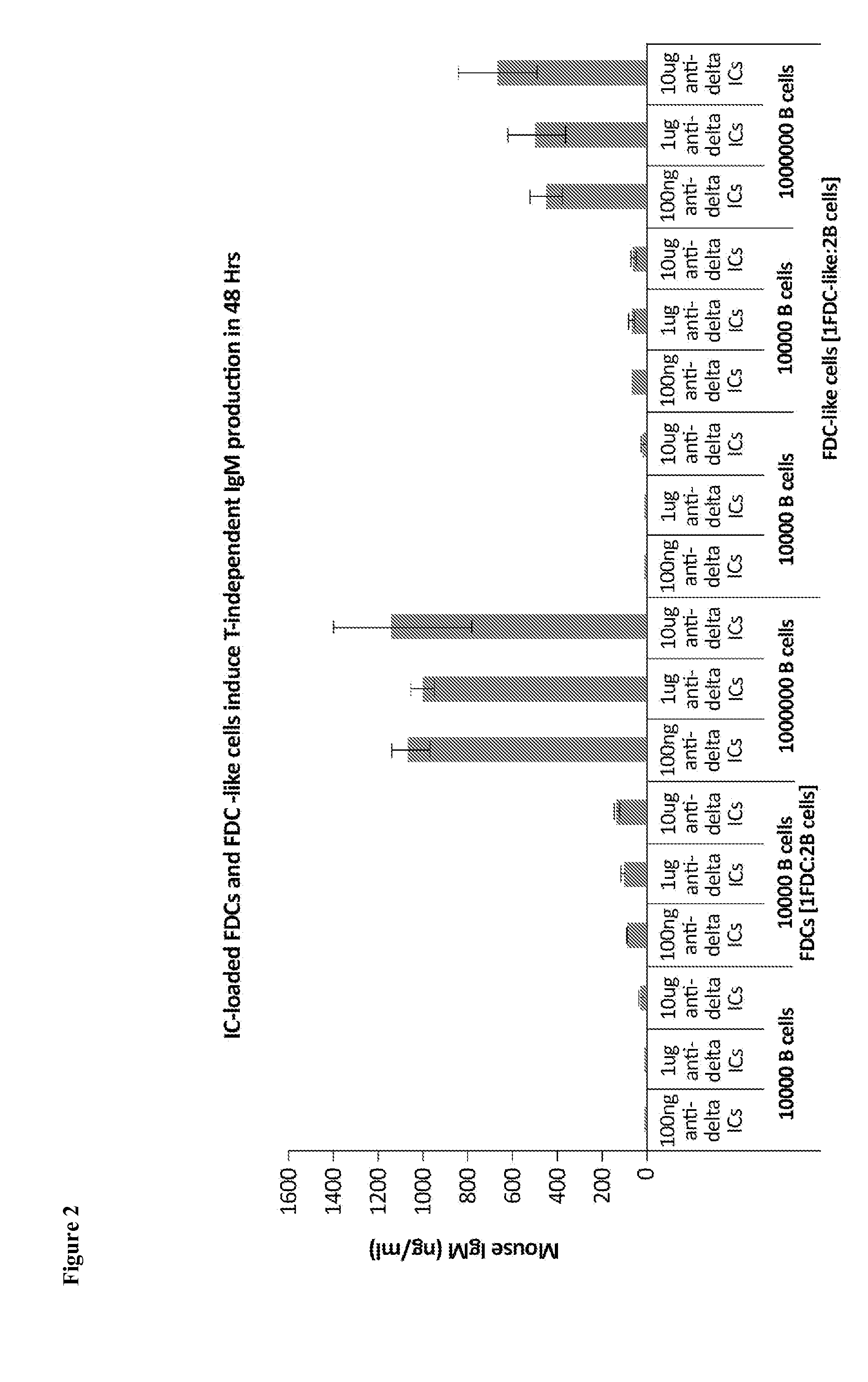
Rapid generation of t cell-independent antibody responses to t cell-dependent antigens
InactiveUS20090104221A1Easy to demonstrateLess immunogenicMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug screeningEndemic diseasesGerminal center
The present invention comprises the use of follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) or FDC-like cells to generate FDC-dependent, but T cell-independent, B cell responses to T cell-dependent antigens, with antigen-specific and polyclonal antibody production in ˜48 h. In another embodiment, a germinal center (GC) lymphoid tissue equivalent (LTE) was used to generate antigen-specific IgM, followed by switching to IgG. The GC LTE model can be used in vaccine assessment. Dual forms of immunogen were used in the GC LTE and in vivo. Dual immunogens resulted in rapid, specific IgM responses and enhanced IgG responses. This vaccine design approach can be used, for example, to provide rapid IgM protection (˜24-48 h) and high-affinity IgG more quickly in people moving to areas with endemic disease, or in people with T cell insufficiencies, who can be immunized to rapidly generate protective IgM.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR VAX DESIGN +1
Polypeptide-vaccines for broad protection against hypervirulent meningococcal lineages
ActiveUS8663656B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsSalmonella serotype typhiMeningococcal carriage
A small number of defined antigens can provide broad protection against meningococcal infection, and the invention provides a composition which, after administration to a subject, is able to induce an antibody response in that subject, wherein the antibody response is bactericidal against two or three of hypervirulent lineages A4, ET 5 and lineage 3 of N. meningitidis serogroup B. Rather than consisting of a single antigen, the composition comprises a mixture of 10 or fewer purified antigens, and should not include complex or undefined mixtures of antigens such as outer membrane vesicles. Five protein antigens are used in particular: (1) a ‘NadA’ protein; (2) a ‘741’ protein; (3) a ‘936’ protein; (4) a ‘953’ protein; and (5) a ‘287’ protein.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Immunomodulating polymers
InactiveUS7083777B1Suppressing antibody responseConducive to survivalAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNeutral Amino AcidsDisease
A pharmaceutical composition consisting of identical repeating units, each unit having a charge motif composed of a positively charged free amino moiety and a negatively charged moiety, wherein the positively charged free amino moiety and the negatively charged moiety of each charge motif are separated by at least one neutral amino acid, and wherein the positively charged free amino moiety of one of the charge motifs is separated by a distance of at least 8 amino acids from the positively charged amino moiety of another charge motif, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. Said pharmaceutical composition is useful for inducing IL-2, activating T cells to produce a T helper 1 cytokine profile, suppressing IgG antibody response to specific antigen, promoting allograft survival, reducing postoperative surgical adhesion formation, and / or protecting against abscess formation associated with surgery, trauma or diseases that predispose the host to abscess formation.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Method of providing patient specific immune response in amyloidoses and protein aggregation disorders
ActiveUS20100297108A1Increase heightFavor selective antibody responseOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell AggregationsSpecific immunity
A novel treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other disorders involving protein misfolding or aggregation is provided by enhancing or sustaining an antibody response against predominantly directed against pathological protein aggregates or neo-epitopes present on pathogenic forms of said protein or protein complex. Furthermore, therapeutic methods are also described, wherein ex vivo stimulated antigen-selected peripheral blood lymphocytes are regrafted into the cognate donor.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome vaccine, based on isolate JA-142
InactiveUS6641819B2Improve efficiencyShorten the timeSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsPhysiologyVirus strain
Substantially avirulent forms of atypical porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus and corresponding vaccines are provided which result from cell culture passaging of virulent forms of PRRS. The resultant avirulent atypical PRRS virus is useful as a vaccine in that PRRS specific antibody response is elicited by inoculation of host animals, thereby conferring effective immunity against both previously known strains of PRRS virus and newly isolated atypical PRRS virus strains. The preferred passaging technique ensures that the virus remains in a logarithmic growth phase substantially throughout the process, which minimizes the time required to achieve attenuation. The present invention also provides diagnostic testing methods which can differentiate between animals infected with field strains and attenuated strains of PRRSV.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
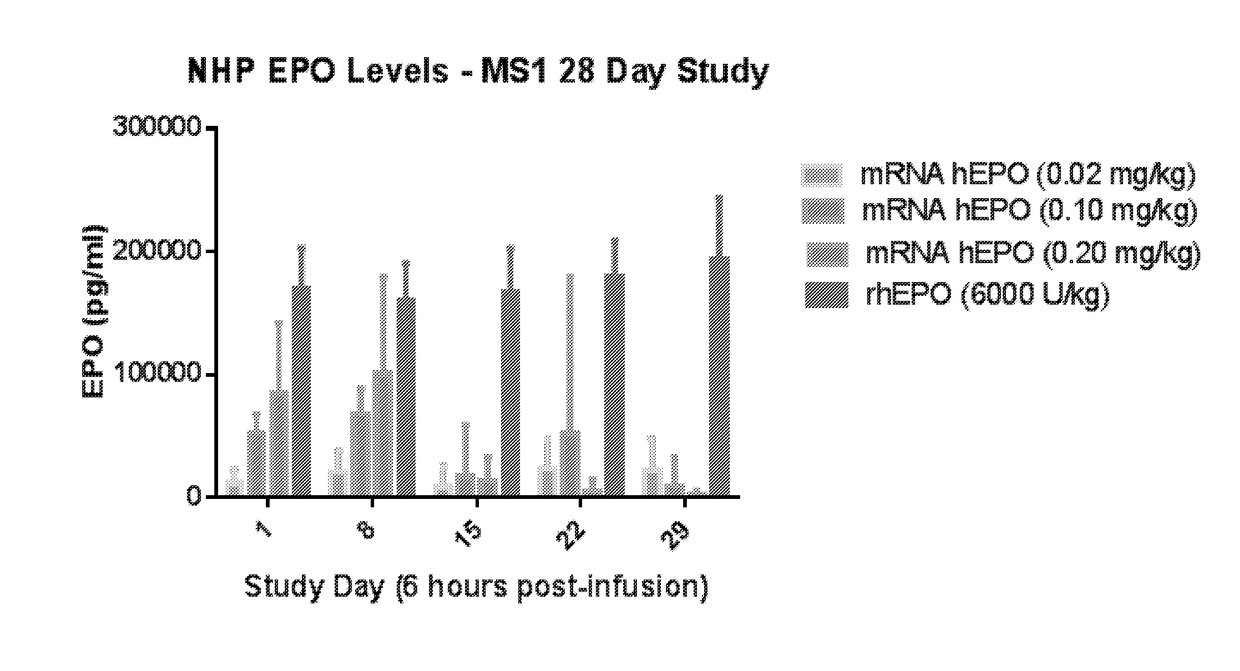
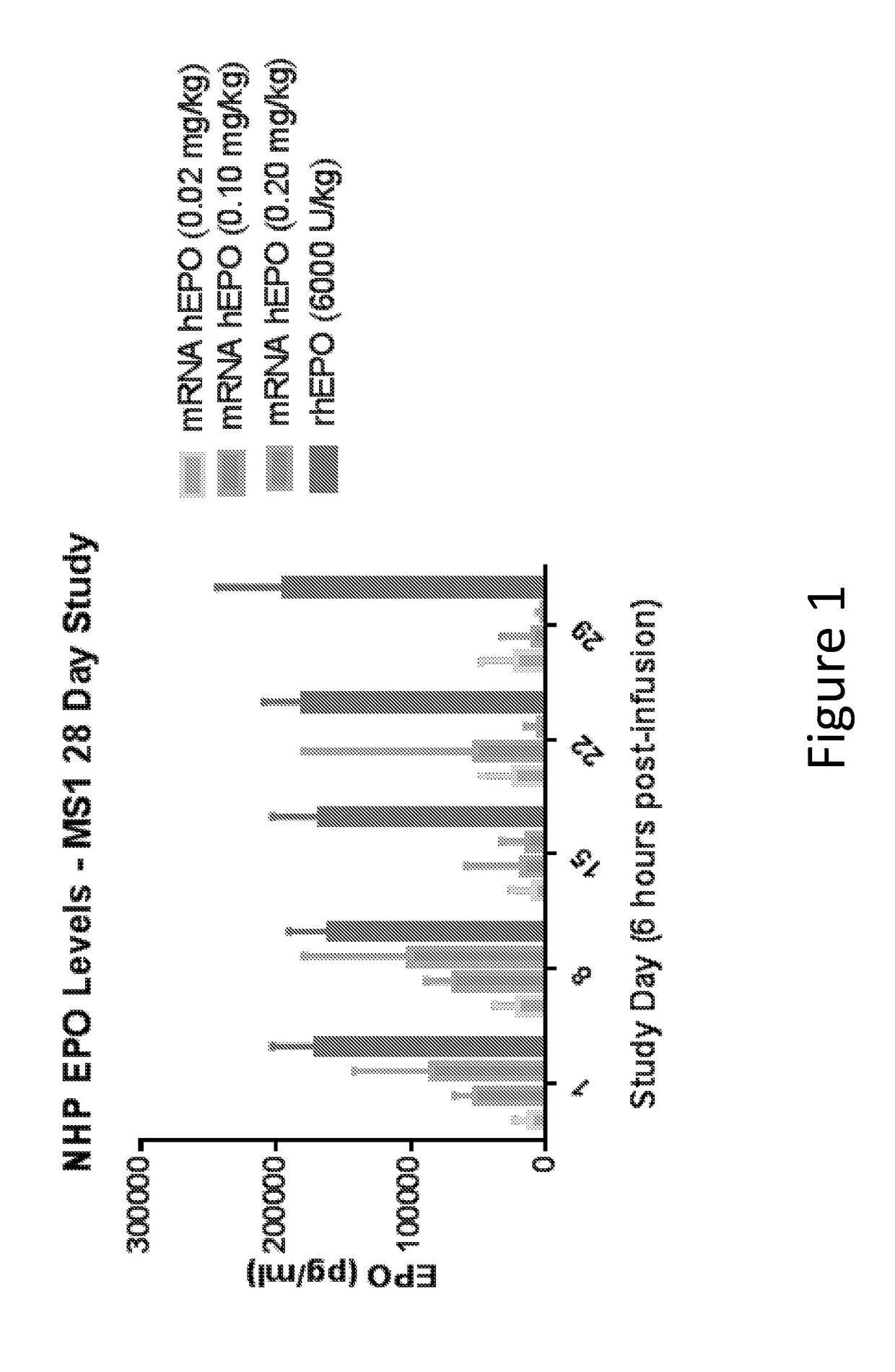
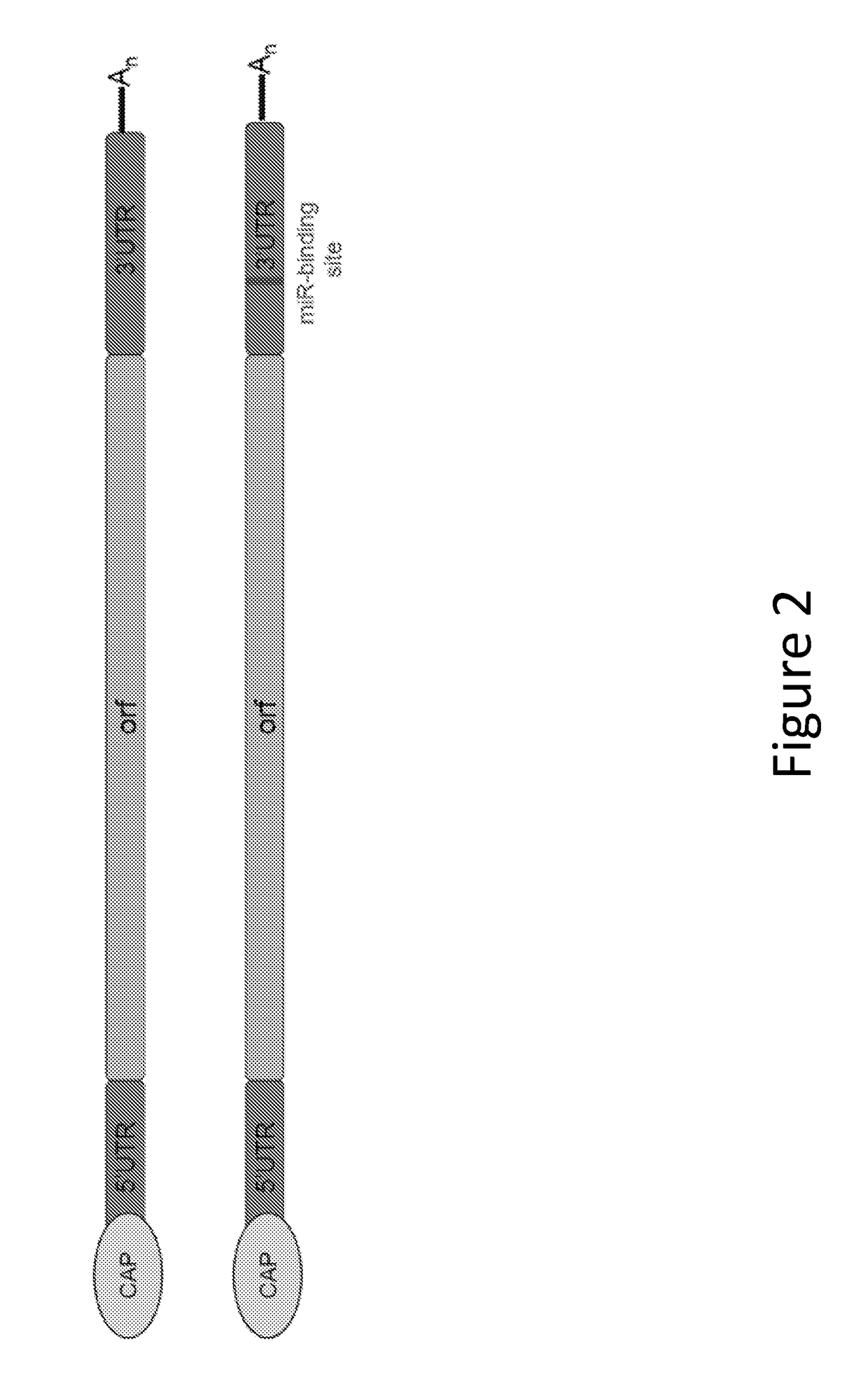
Methods for therapeutic administration of messenger ribonucleic acid drugs
ActiveUS20180256628A1Reducing and inhibiting accelerated blood clearanceBlood clearance is reduced and inhibitedOrganic active ingredientsNucleic acid vectorAntiendomysial antibodiesBinding site
The disclosure features methods of reducing or inhibiting an anti-drug antibody response in a subject, as well as methods of reducing or inhibiting unwanted immune cell activation in a subject to be treated with a messenger RNA (mRNA), comprising administering to the subject a mRNA, e.g., a chemically modified messenger RNA (mmRNA), encoding a polypeptide of interest, wherein the mRNA comprises at least one microRNA (miR) binding site for a miR expressed in immune cells, such as miR-126 binding site and / or miR-142 binding site, such that an anti-drug antibody response to the polypeptide or interest, or unwanted immune cell activation (e.g., B cell activation, cytokine secretion), is reduced or inhibited in the subject. The disclosure further provides therapeutic treatment regimens designed to reduce or inhibit AD A or unwanted immune cell activation (e.g., B cell activation, cytokine secretion) in a subject being treated with mRNA-based therapeutics.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Immunomodulating polymers
InactiveUS7026285B2Suppressing antibody responseConducive to survivalOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseT cell
Methods and products for inducing IL-2 secretion, inducing IL-10 secretion, activating T cells, suppressing IgG antibody response to specific antigen, promoting allograft survival, reducing postoperative surgical adhesion formation, and protecting against abscess formation associated with surgery, trauma or diseases that predispose the host to abscess formation are provided. The methods of the invention are accomplished using an immunomodulator which is a polymer having at least two repeating charge motifs separated by at least a certain minimum distance.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Immuno-Oncolytic Therapies
ActiveUS20160235793A1Reduced responseImprove immunityViral antigen ingredientsUnknown materialsAbnormal tissue growthInterleukin-18 binding protein
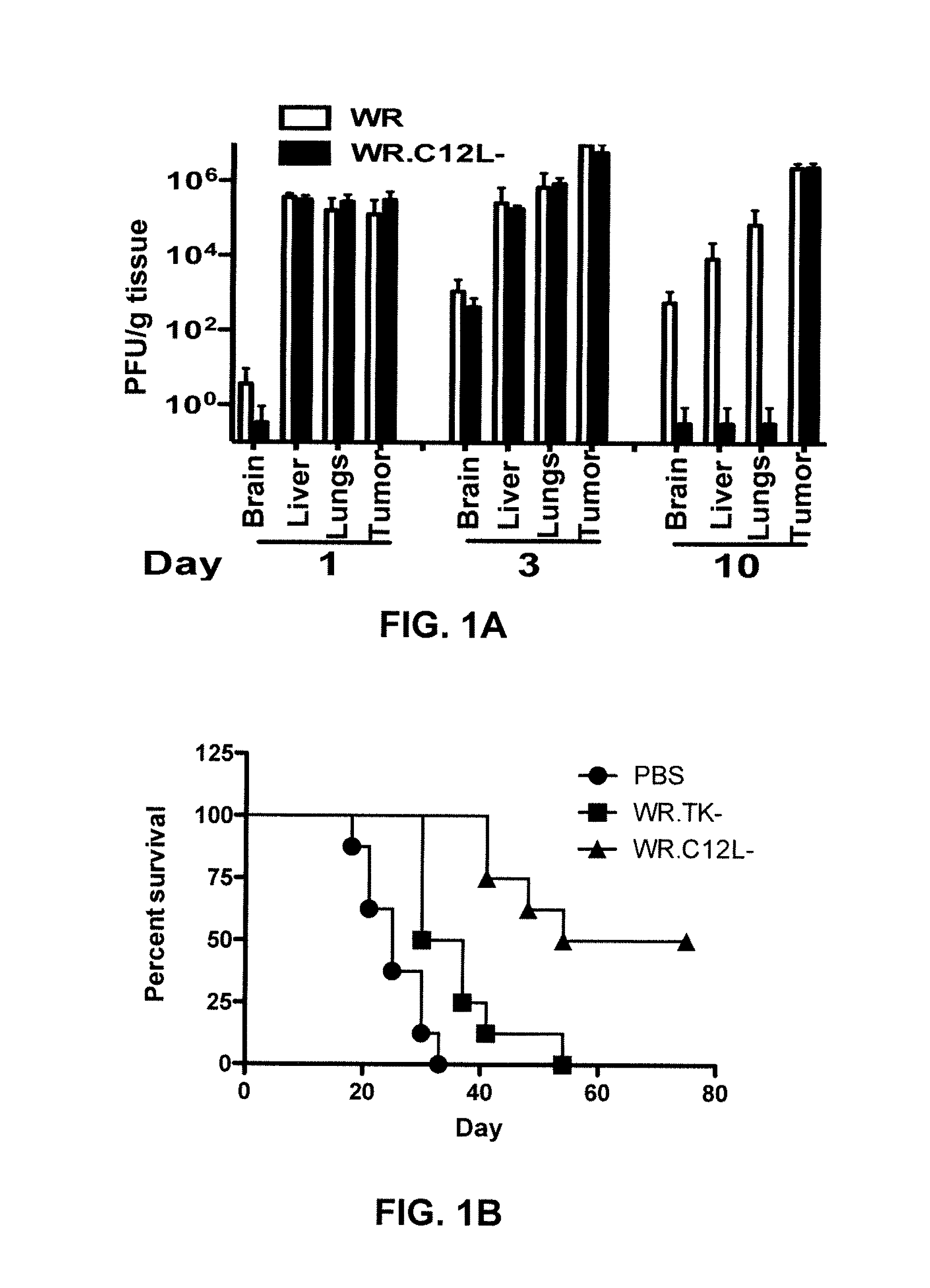
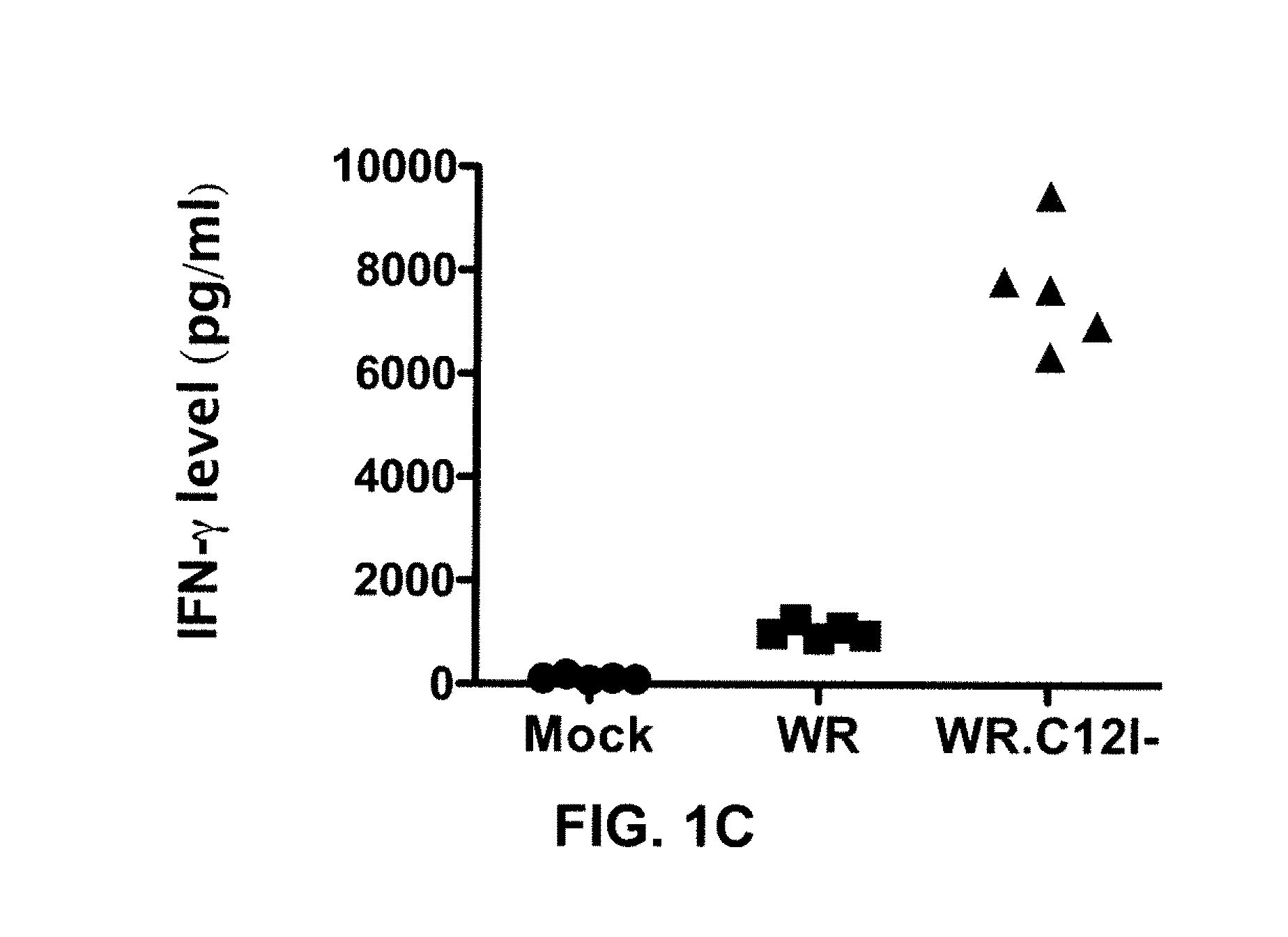
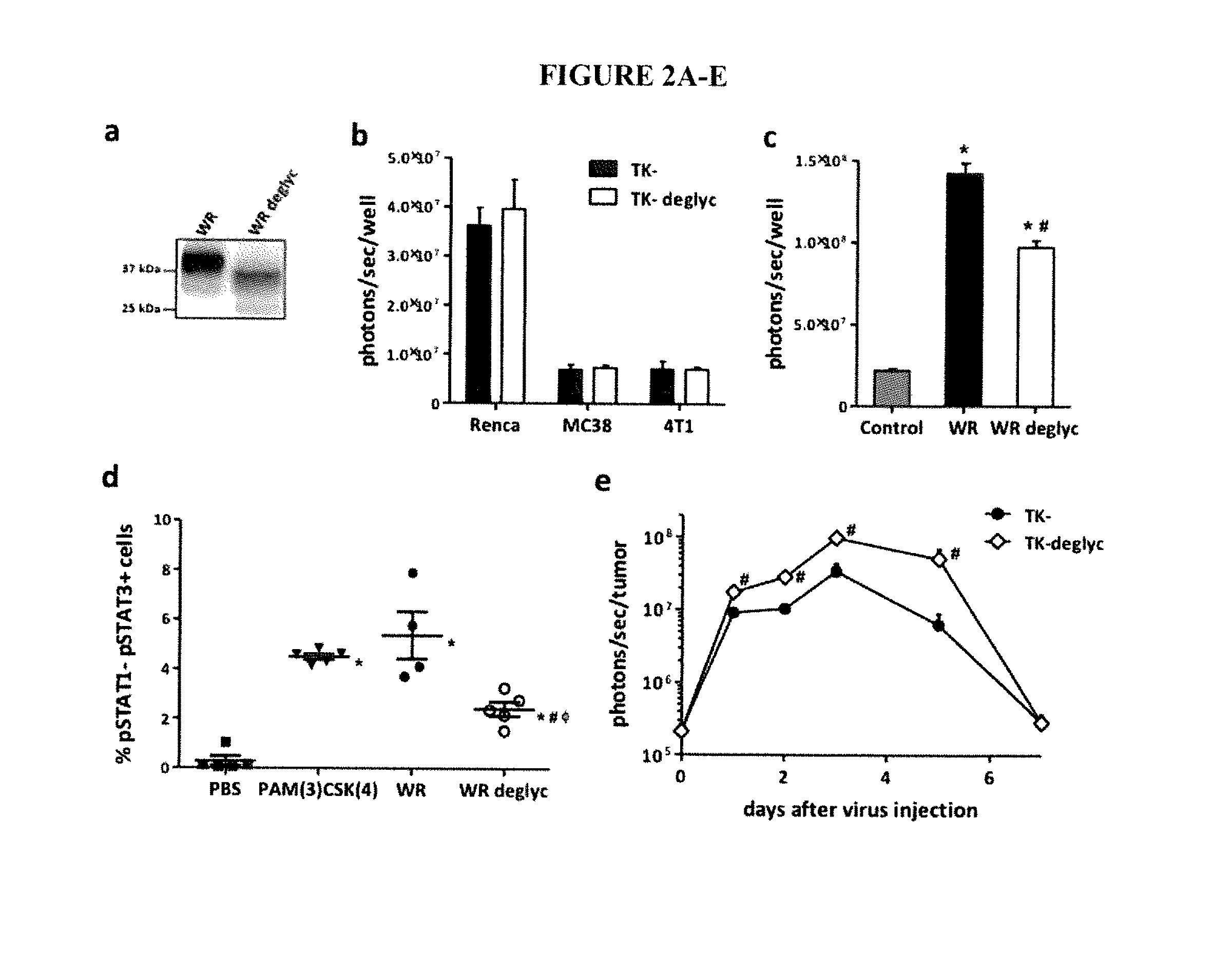
The present invention relates to oncolytic vaccinia viruses which have been modified to promote anti-tumor immunity and / or reduce host immunity and / or antibody response against the virus. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that oncolytic vaccinia virus (i) bearing a genome deletion of a gene that reduces T cell immunity (interleukin-18 binding protein); (ii) treated with a sialidase enzyme which is believed to reduce TLR2 activation and therefore the antibody response; (iii) carrying a gene that enhances cytotoxic T lymphocyte induction (e.g., TRIF) and / or (iv) reduces tumor myeloid-derived suppressor cells by reducing prostaglandin E2 reduces tumor growth. Accordingly, the present invention provides for immunooncolytic vaccinia viruses and methods of using them in the treatment of cancers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Compositions and methods for modified dendrimer nanoparticle delivery
ActiveUS20170079916A1Efficiently drive proliferationEnhance antibody responseAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryDendrimerDiagnostic agent
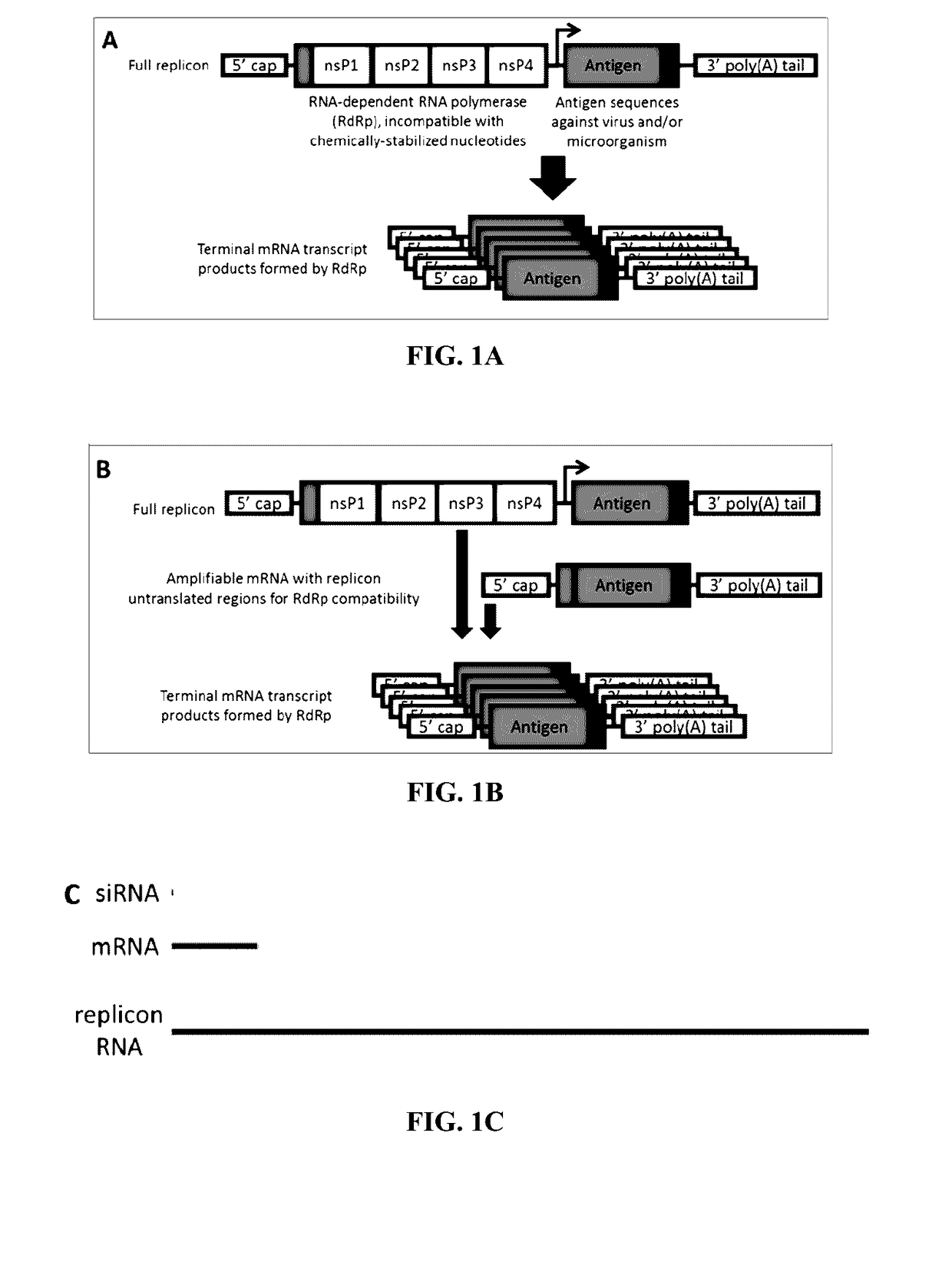
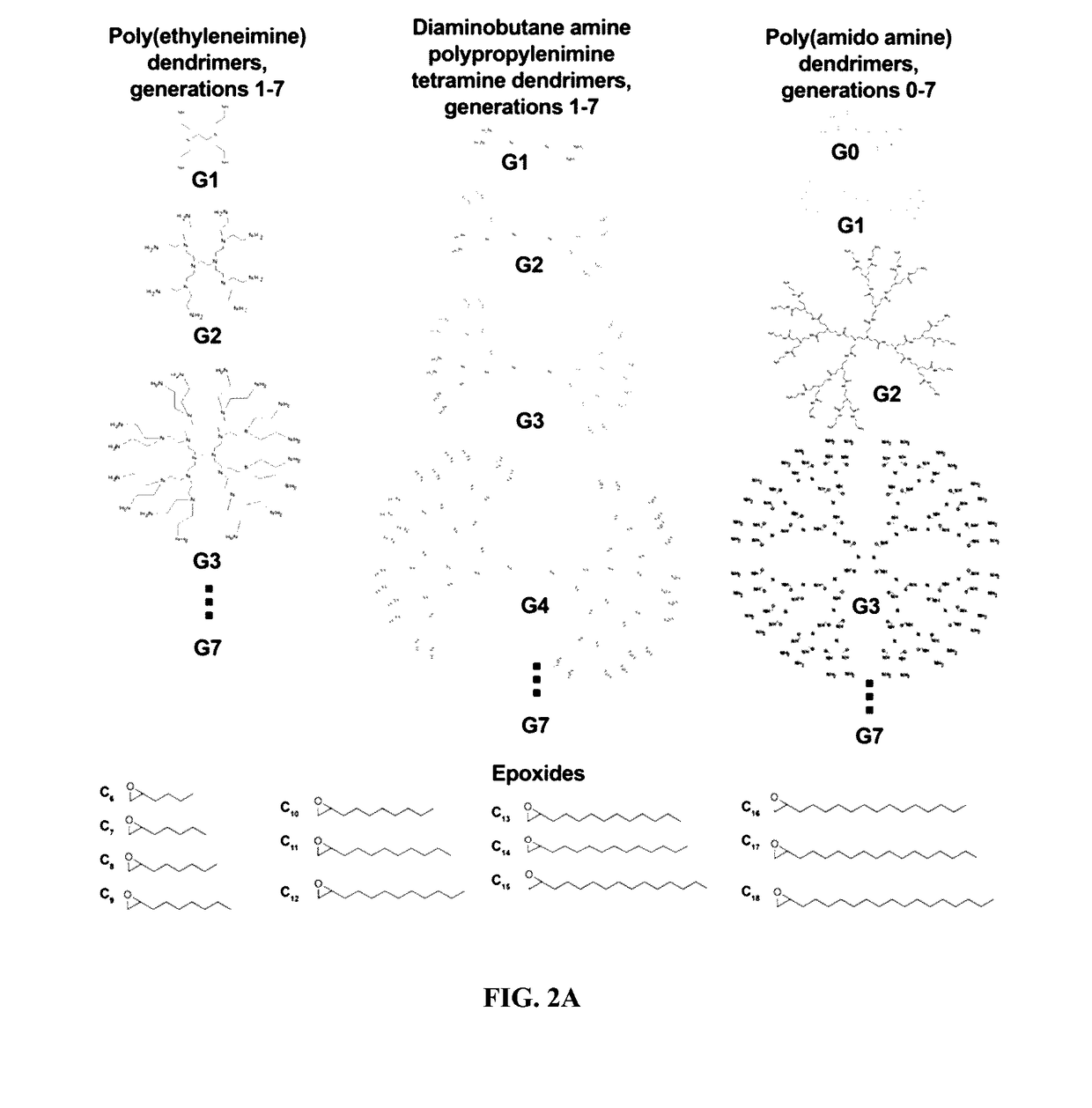
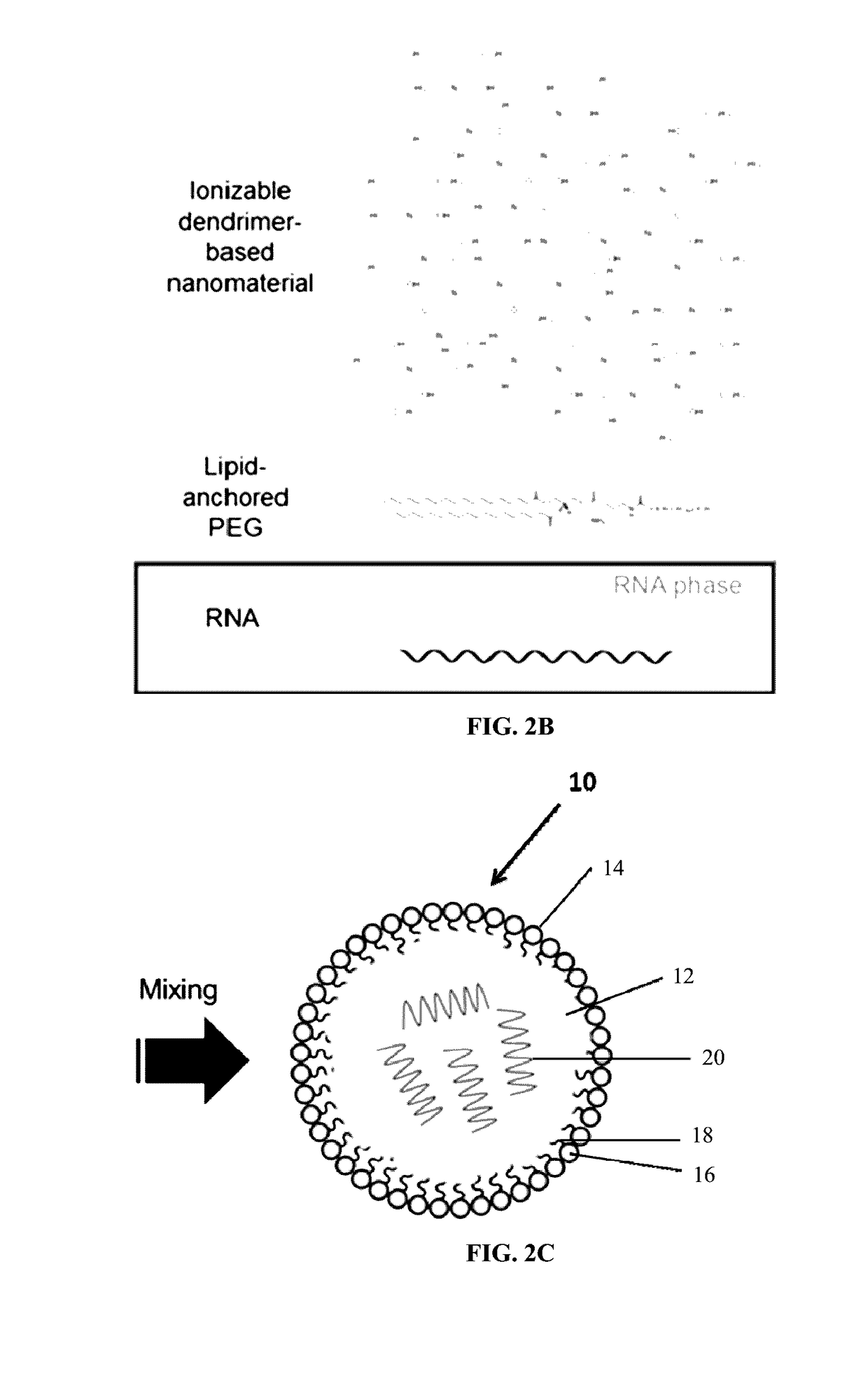
Compositions and methods for modified dendrimer nanoparticle (“MDNP”) delivery of therapeutic, prophylactic and / or diagnostic agent such as large repRNA molecules to the cells of a subject have been developed. MDNPs efficiently drive proliferation of antigen-specific T cells against intracellular antigen, and potentiate antigen-specific antibody responses. MDNPs can be multiplexed to deliver two or more different repRNAs to modify expression kinetics of encoded antigens and to simultaneous deliver repRNAs and mRNAs including the same UTR elements that promote expression of encoded antigens.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
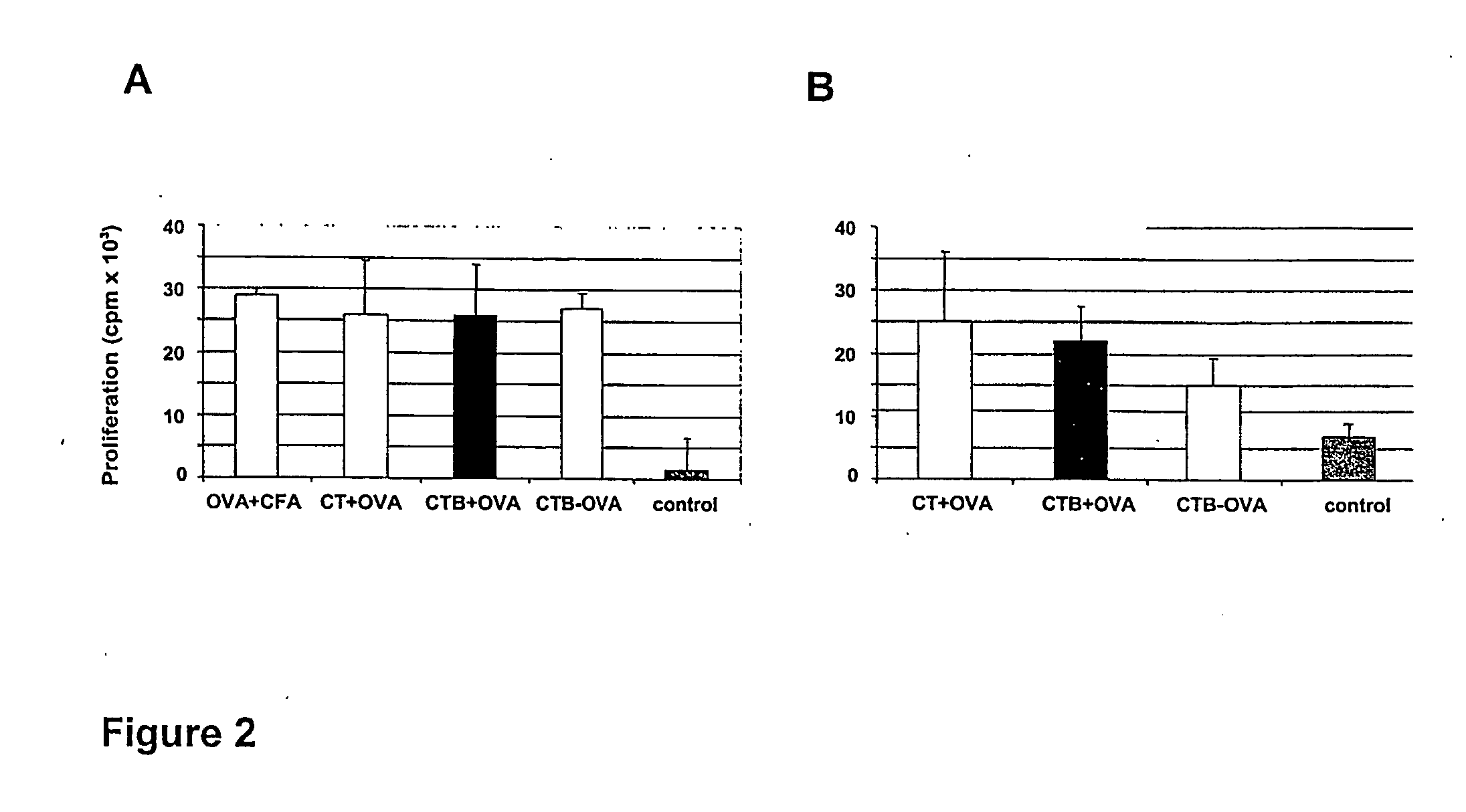
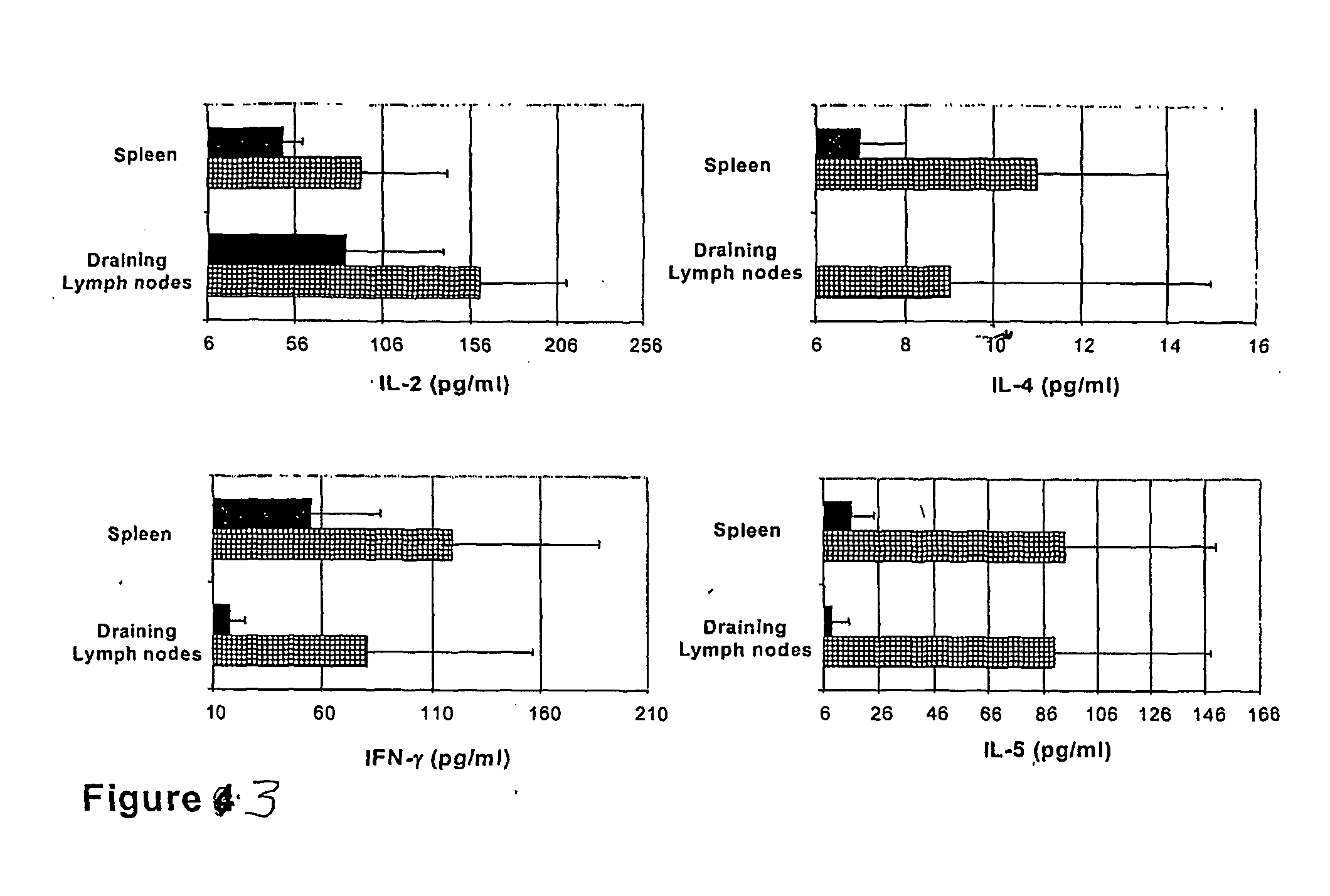
Supression of allergic reactions by transdermal administration of allergens conjugated to cholera toxin or fragments thereof
InactiveUS20050074462A1Suppress allergic reactionsBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAdjuvantCo administration
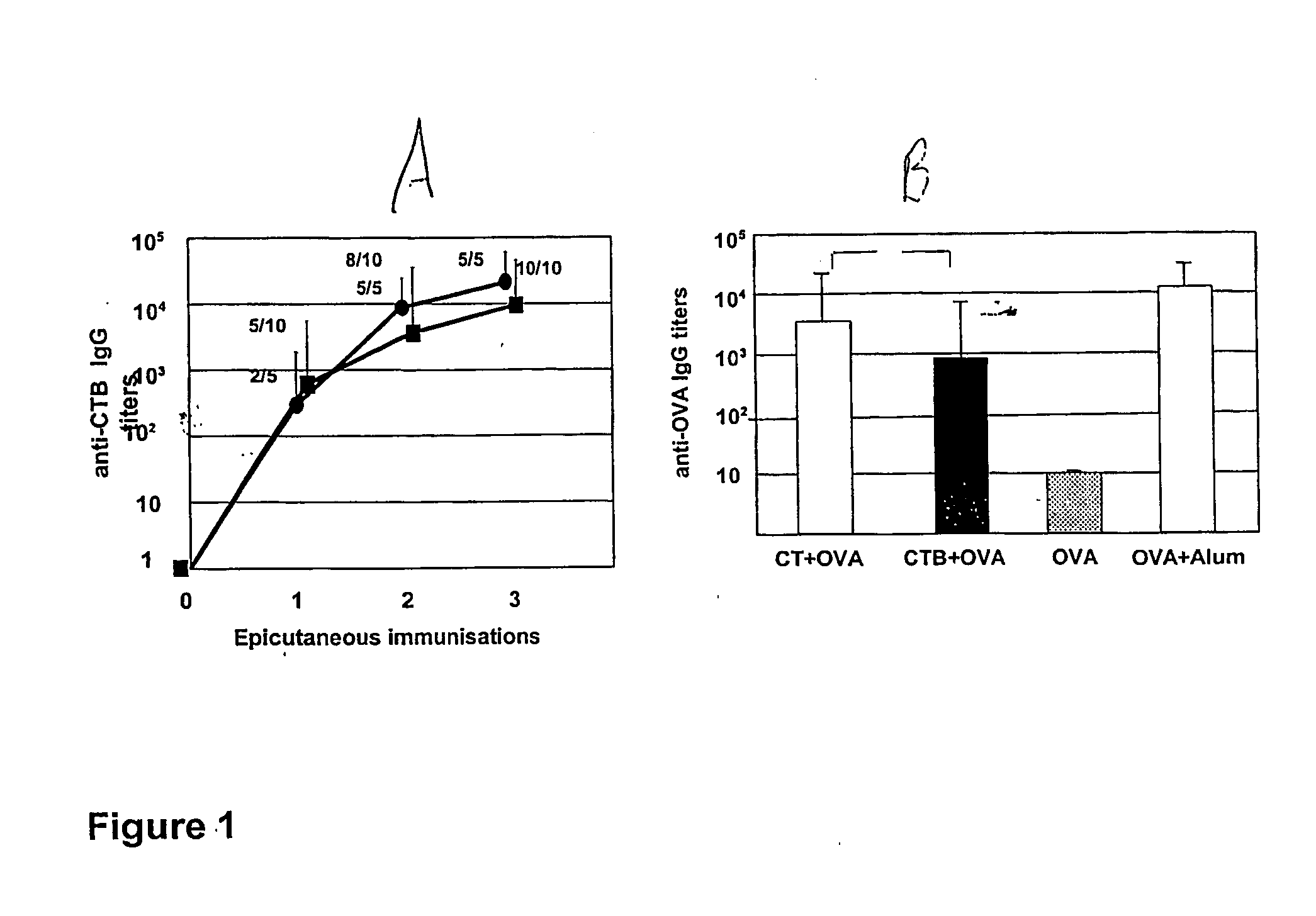
The present invention discloses the use of the non-toxic cell-binding B subunit of CT (CTB), and holotoxin CT that is devoid of ADP-ribosylating activity, as adjuvants for enhancing transcutaneous immune response to a co-administered protein allergen. It was found that topical administration of CTB to mice induced serum antibody response against itself comparable to those evoked by CT, but was inefficient at promoting systemic antibody responses against an admixed prototype protein allergen. To the contrary co-administration of either CT or CTB with allergen led to vigorous antigen-specific T cell proliferative responses in lymph nodes draining the cutaneous site of administration and at distant systemic sites. Consistent with these observations, it was found that CTB selectively potentiated Th1-driven responses without affecting Th2-dependent responses. Cutaneously applied CT enhanced serum IgE responses to a co-administered allergen, while CTB partially suppressed epicutaneously induced IgE responses to the same allergen.
Owner:DUOTOL
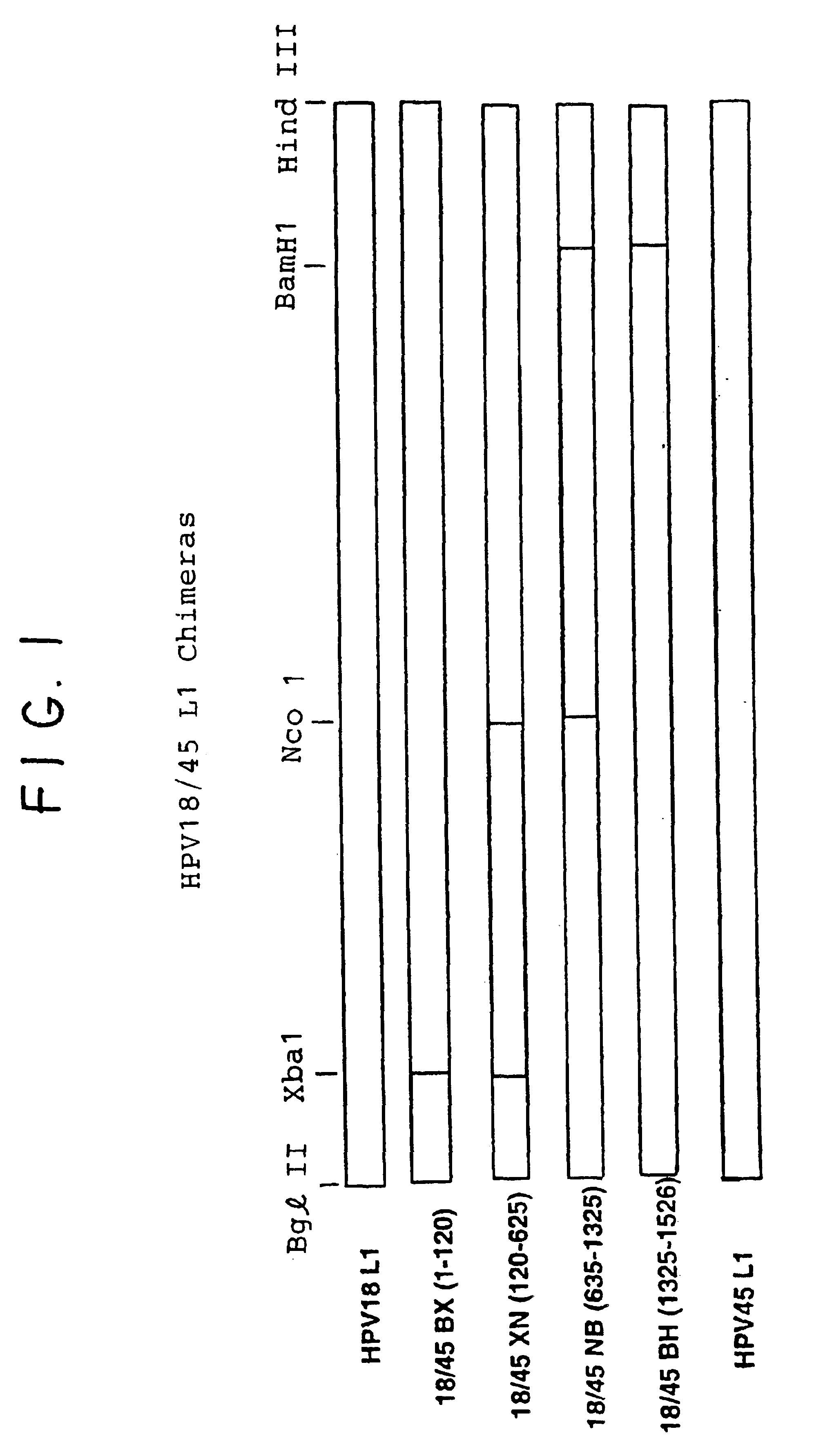
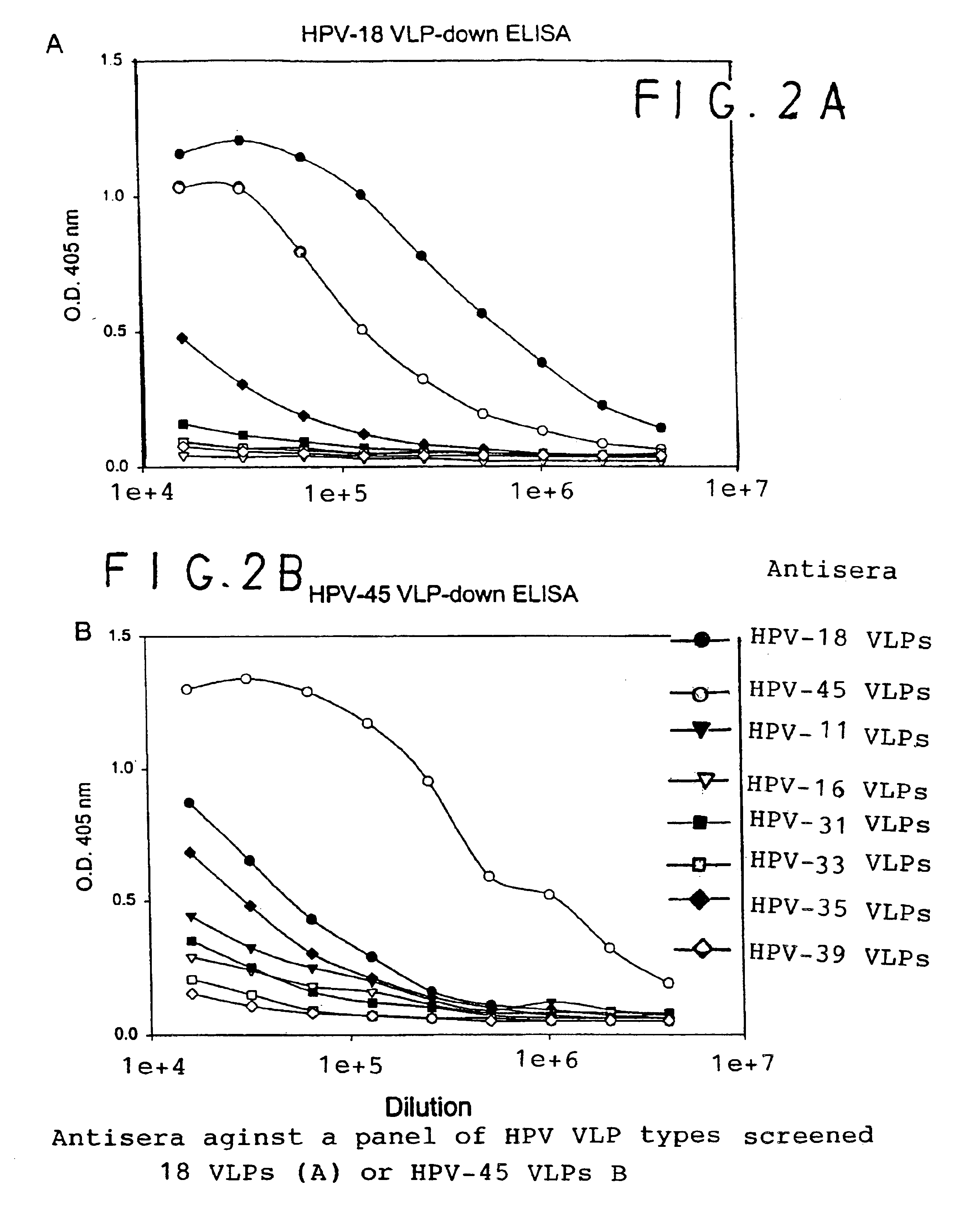
Chimeric human papillomavirus (HPV) L1 molecules and uses therefor
InactiveUS6908613B2Need can be quite largeLevel of protectionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman papillomavirusVirus-like particle
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Method for designing vaccines against constantly mutating pathogens
InactiveUS20090162383A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic antibodyImmunodominant Epitopes
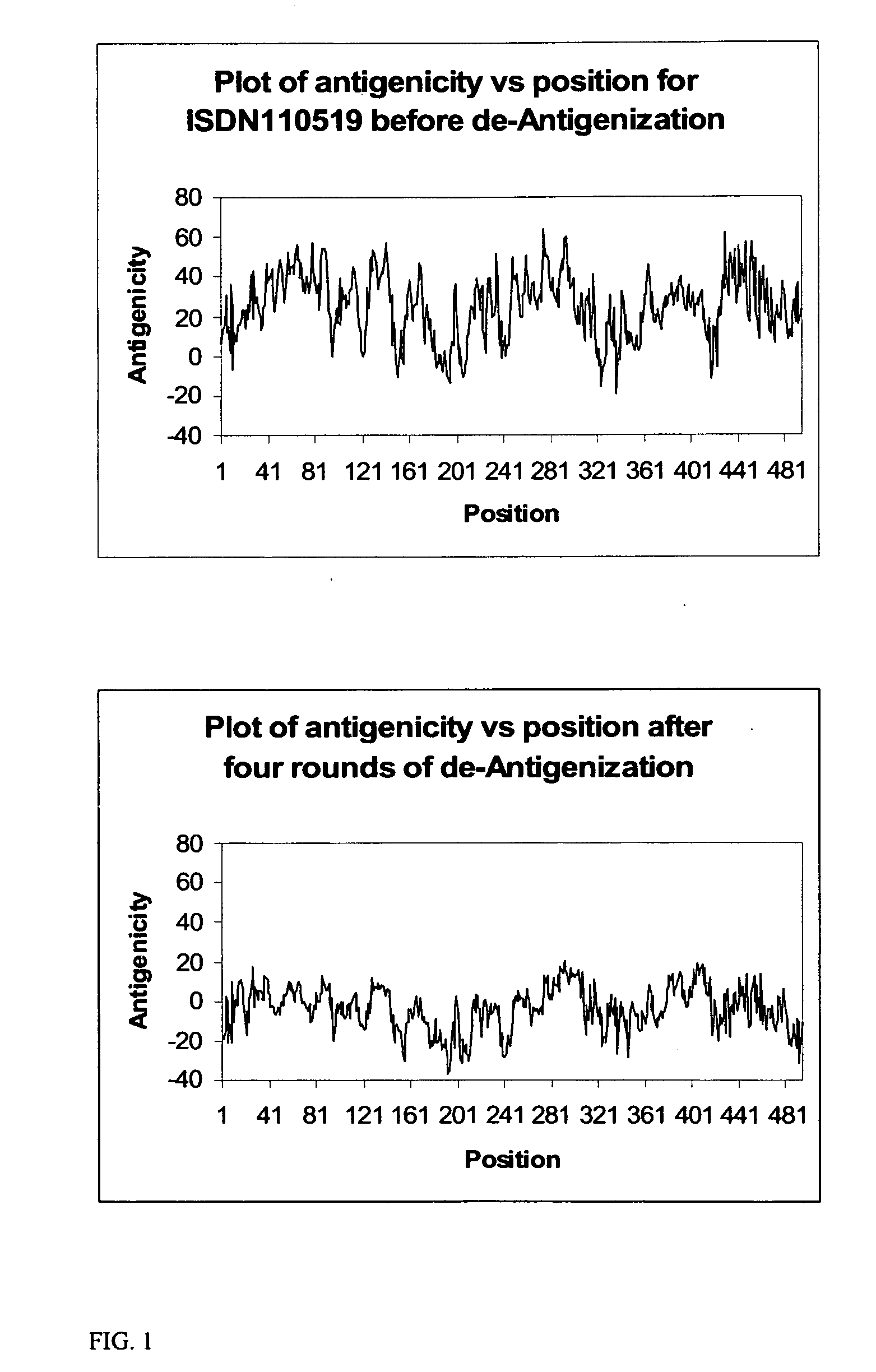
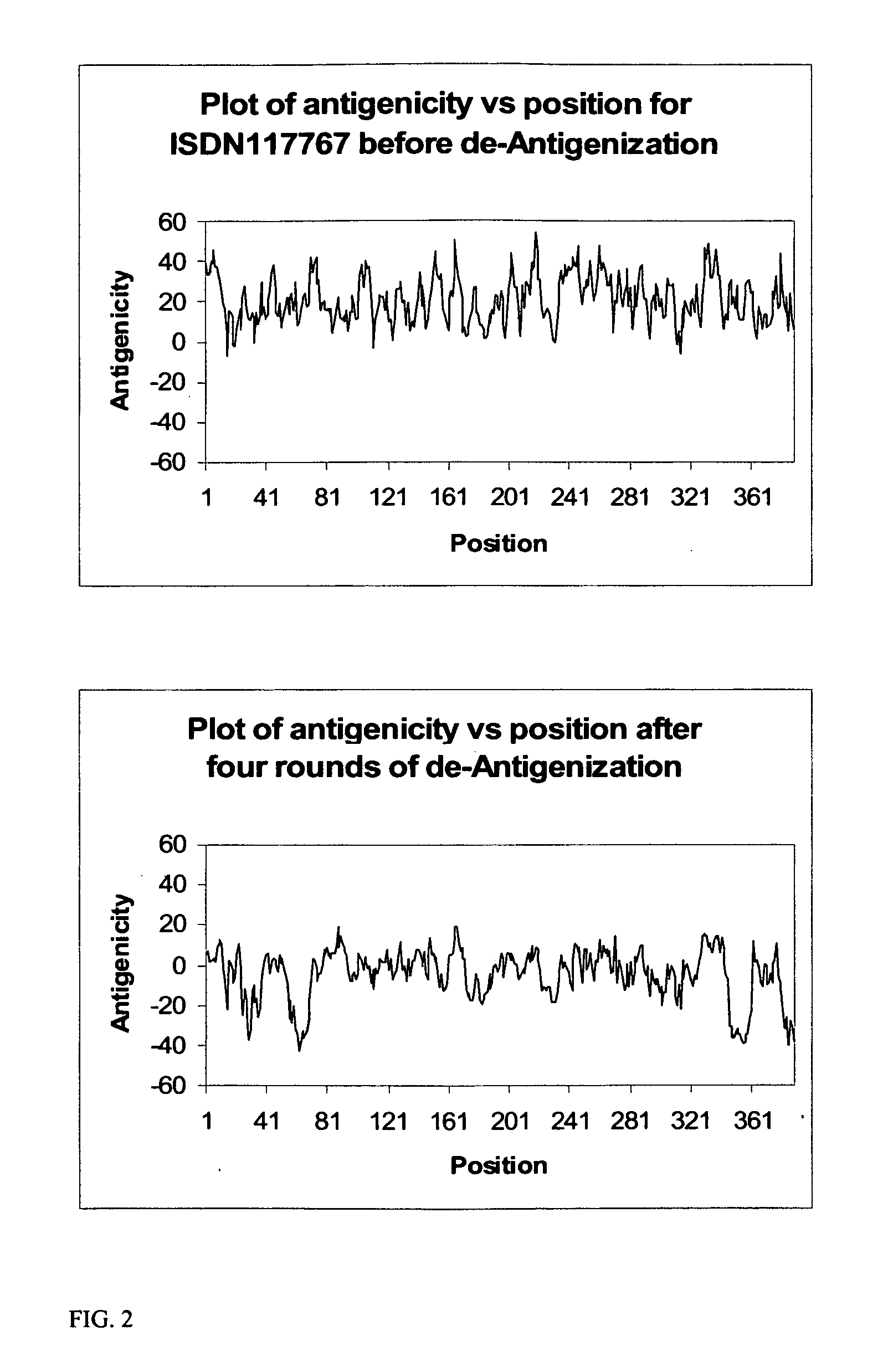
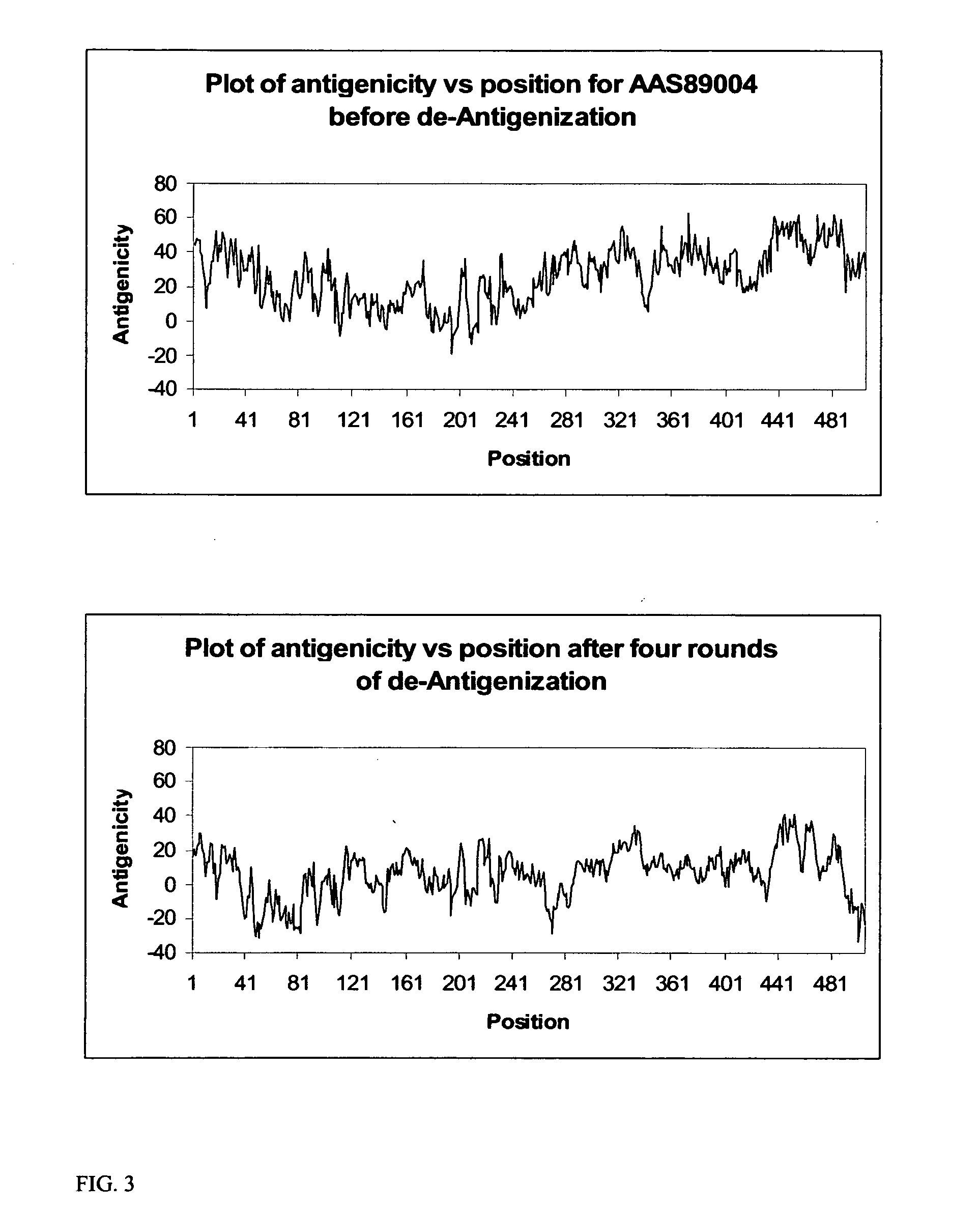
A unique method is disclosed for identifying and replacing surface amino acid residues of a protein antigen that reduces the antigenicity of the putative immunodominant epitopes of the antigen and makes all the accessible regions of the molecule essentially antigenically equivalent, so that the antibody response will be directed against more parts of the molecule and not mainly against the erstwhile immunodominant epitopes. The method will simultaneously change the antigenicity of the molecule and preserve its structure. The method is useful in the design of molecules useful for immunization, for example, as vaccines, or for the generation of therapeutic antibodies, against constantly mutating pathogens. It is also useful in the design of molecules useful for immunization against pathogens that had been intentionally mutated so as to render those pathogens able to infect erstwhile immune individuals.
Owner:PADLAN EDUARDO A
Influenza Virus Vaccines
InactiveUS20080254065A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsFowlInfluenza virus vaccine
The invention provides a vaccine for protecting a human patient against infection by a human influenza virus strain, wherein the vaccine comprises an antigen from an avian influenza virus strain that can cause highly pathogenic avian influenza. The antigen can invoke an antibody response in the patient that is capable of neutralising said human influenza virus strain. Whereas the prior art used known non-pathogenic avian strains to generate antibodies in humans against known pathogenic avian strains, the invention uses known pathogenic avian strains to protect against emerging pathogenic human strains. Furthermore, whereas the prior art focused on achieving a close antigenic match between the vaccine strain and the target strain, the invention selects vaccine strains based on their pathogenicity, regardless of any perceived close antigenic relationship to the target strain. As the invention does not require detailed knowledge of an emerging strain, a vaccine can be provided further in advance to reduce the risk and potential effects of a human pandemic outbreak.
Owner:SEQIRUS UK LTD
Molecular antigen arrays
The present invention provides a composition comprising an AP205 virus like particle (VLP) and an antigen. The invention also provides a process for producing an antigen or antigenic determinant bound to AP205 VLP. AP205 VLP bound to an antigen is useful in the production of compositions for inducing immune responses that are useful for the prevention or treatment of diseases, disorders or conditions including infectious diseases, allergies, cancer, drug addiction, poisoning and to efficiently induce self-specific immune responses, in particular antibody responses.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
Canine vaccine for protection against ehrlichiosis
ActiveUS20060188524A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAdjuvantCell mediated immunity
The present invention provides a safe and effective vaccine composition which comprises: an effective immunizing amount of an inactivated Ehrlichia canis bacterin; a pharmacologically acceptable carrier; and an immunogenically stimulating amount of an adjuvant system consisting essentially of an antibody response inducing agent and a cell-mediated immunity response inducing agent. The present invention also provides a method for the prevention or amelioration of canine ehrlichiosis in dogs.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com