Controllable synthesizing method for hydroxy zinc fluoride nanometer materials with different morphologies and environmental photocatalytic application of hydroxy zinc fluoride nanometer materials
A technology of zinc hydroxyfluoride and nanomaterials, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, zinc halides, etc., to achieve mild reaction conditions, rich and diverse morphology, and environmental protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] This embodiment prepares zinc hydroxyfluoride nanomaterials according to the following steps:
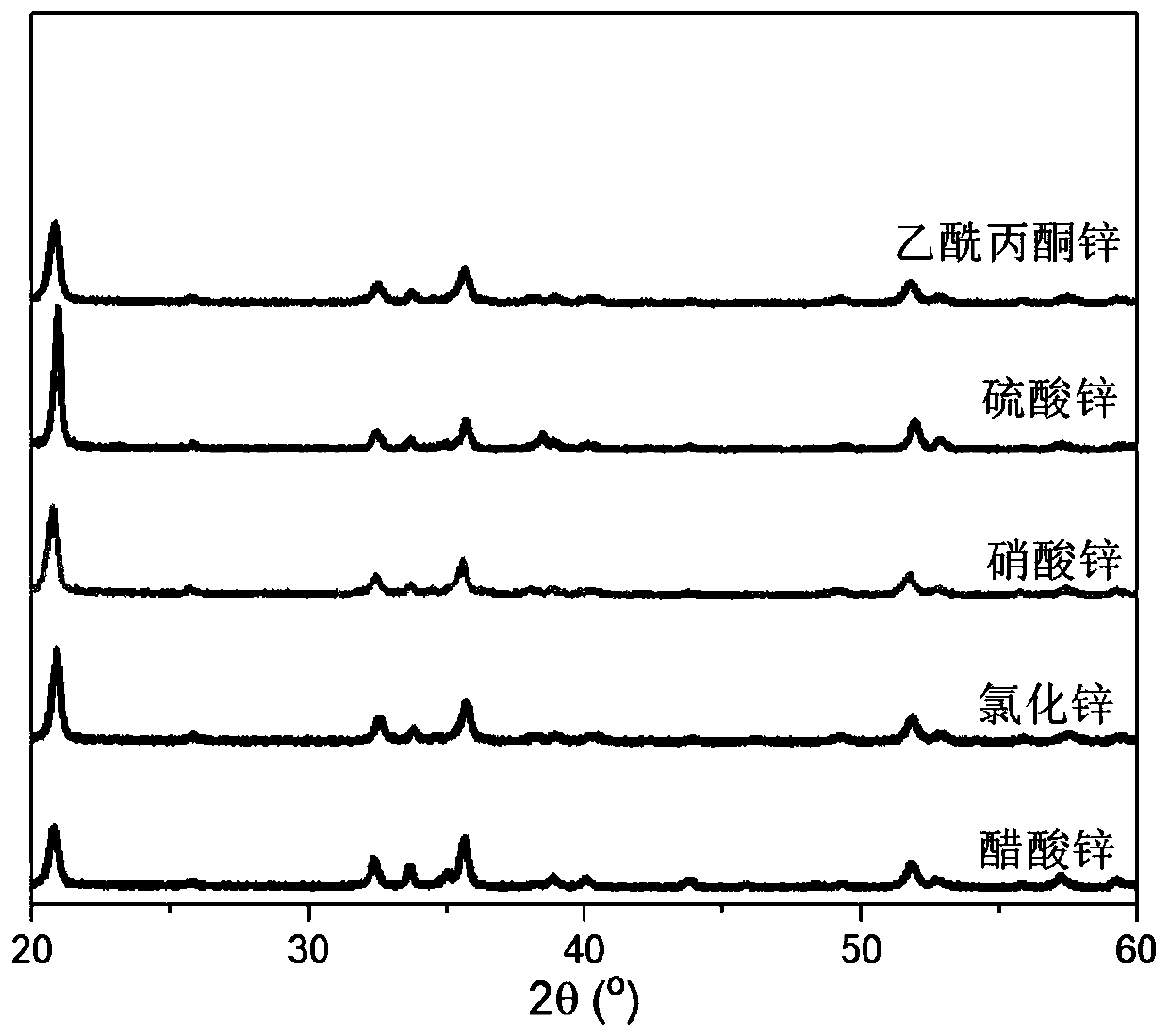
[0033] (1) Weigh 0.83g ammonium fluoride and a certain amount of zinc source (0.49g zinc acetate or 0.31g zinc chloride or 0.64g zinc sulfate heptahydrate or 0.66g zinc nitrate hexahydrate or 0.59g zinc acetylacetonate), in in a plastic beaker;
[0034] (2) Add 82 mL of solvent deionization to the beaker, and stir until the ammonium fluoride and zinc source are completely dissolved;
[0035] (3) Add 0.18 g of alkali source sodium hydroxide to the beaker, stir for 2 hours to obtain a suspension;
[0036] (4) Transfer the suspension to a 100 mL polytetrafluoroethylene liner, seal it, and conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 140° C. for 6 hours. The resulting product is washed and dried to obtain zinc hydroxyfluoride nanomaterials.
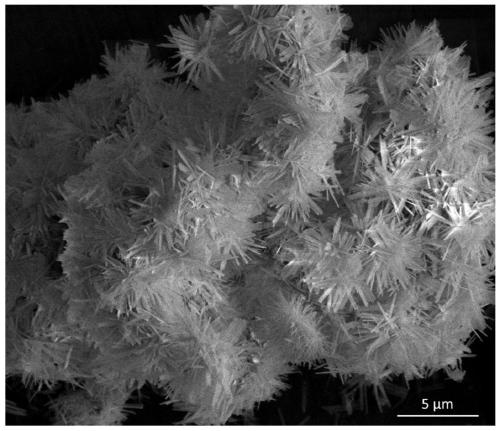
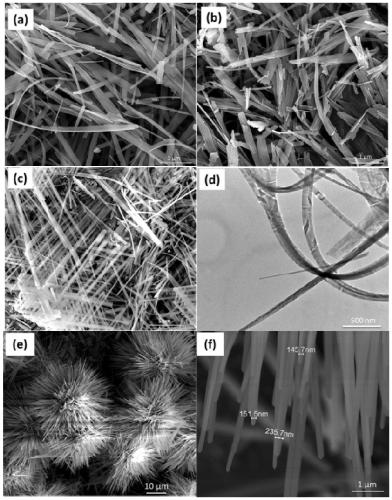
[0037] Characterize the zinc hydroxyfluoride nanomaterial prepared in this example, the results are as follows figure 1 and figure 2 shown. in,...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The method of this embodiment is the same as that of Example 1 (using zinc nitrate as the zinc source), except that the alkali source used in step (3) is tri-n-butylamine.
[0040] Such as image 3 As shown, when other conditions remain unchanged, after replacing sodium hydroxide with tri-n-butylamine, the prepared ZnF(OH) nanomaterial is a flat hat-like hierarchical structure composed of a large number of nanoribbons.
Embodiment 3
[0042] The method of this embodiment is the same as that of Example 1 (using zinc nitrate as the zinc source), except that the alkali source used in step (3) is sodium edetate.
[0043] Such as Figure 4 As shown, when other conditions remain unchanged, after replacing sodium hydroxide with sodium ethylenediamine tetraacetate, a cruciferous ZnF(OH) micro-nano graded material can be obtained.
[0044] Depend on figure 2 d. image 3 and Figure 4 It can be seen that when the alkalis added in step (3) are sodium hydroxide, tri-n-butylamine and sodium edetate, one-dimensional nanobelts, two-dimensional flat hat-like hierarchical structures and three-dimensional cross Flower-like micro-nano hierarchical structure. It can be seen that the morphology of ZnF(OH) materials can also be adjusted by controlling the type of alkali.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com