Method for producing bismuth iron oxide
A bismuth-iron oxide and manufacturing method technology, applied in iron compounds, chemical instruments and methods, iron oxide/iron hydroxide, etc., can solve problems such as easy generation of impurities, less high-purity substances, and difficulty in manufacturing impurity content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
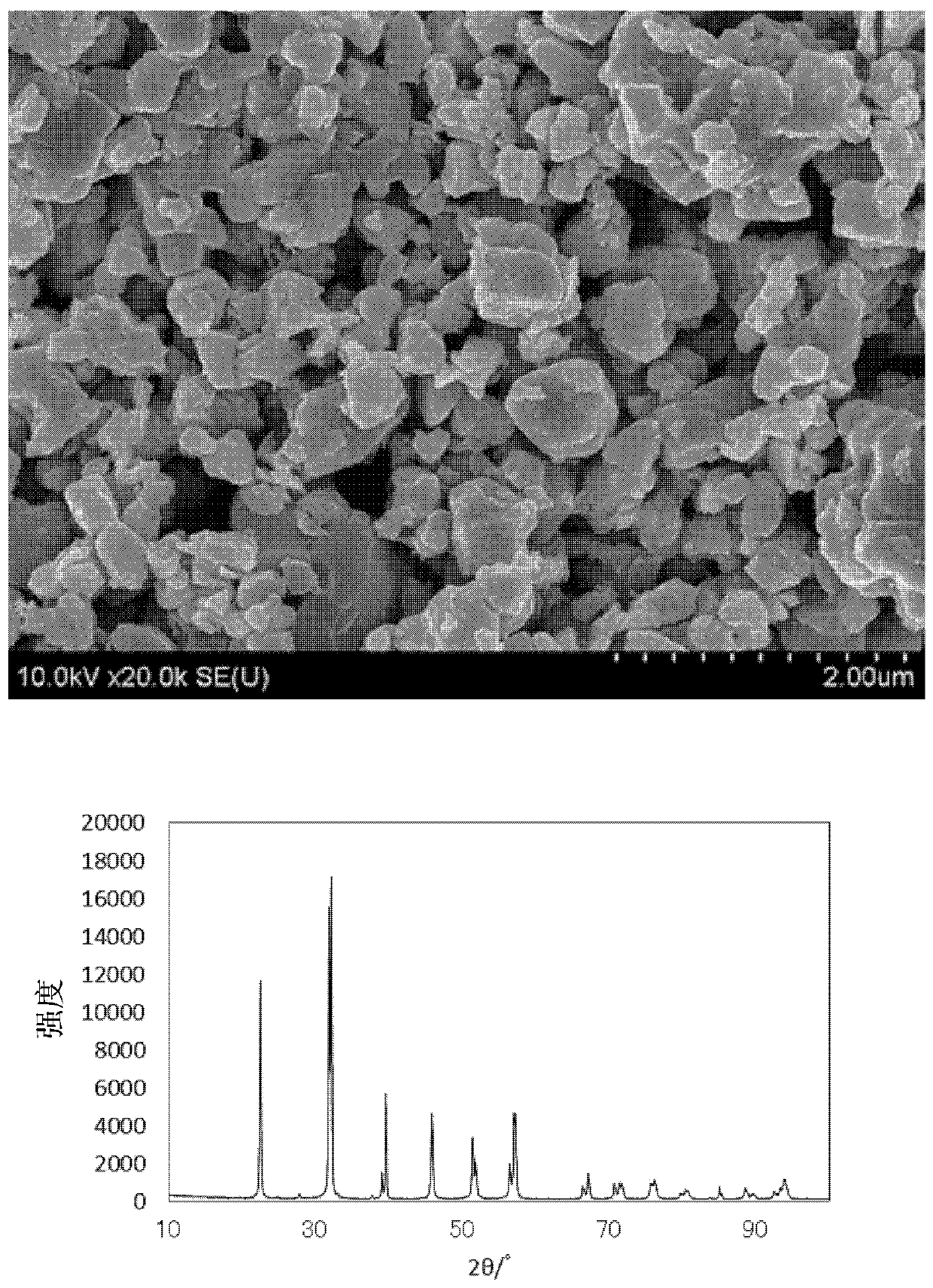
[0064] Add it to a nylon tank with a volume of 700mL ZrO 2 Ball making, weighing and adding 37.1g of bismuth subcarbonate (produced by Nippon Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.), 13.1g of ferric (III) hydroxide (TitanKogyo, Ltd. production), then, add pure water 120g, dispersant (Sannuo Puke Co., Ltd. produced SN5468) 2.0g, and defoamer (SNDEFOAMER produced by San Nopco Co., Ltd.) 0.4g. Next, the nylon tank was sealed, and wet pulverization and mixing were performed at a rotational speed of 120 rpm for 96 hours. Next, the obtained slurry was transferred to a tray, and dried at 120° C. for 24 hours to obtain a raw material pulverized mixed powder. The specific surface area of the raw material crushed and mixed powder is 18.03m 2 / g. In addition, the molar ratio (Bi / Fe) of bismuth to iron was 1.002.
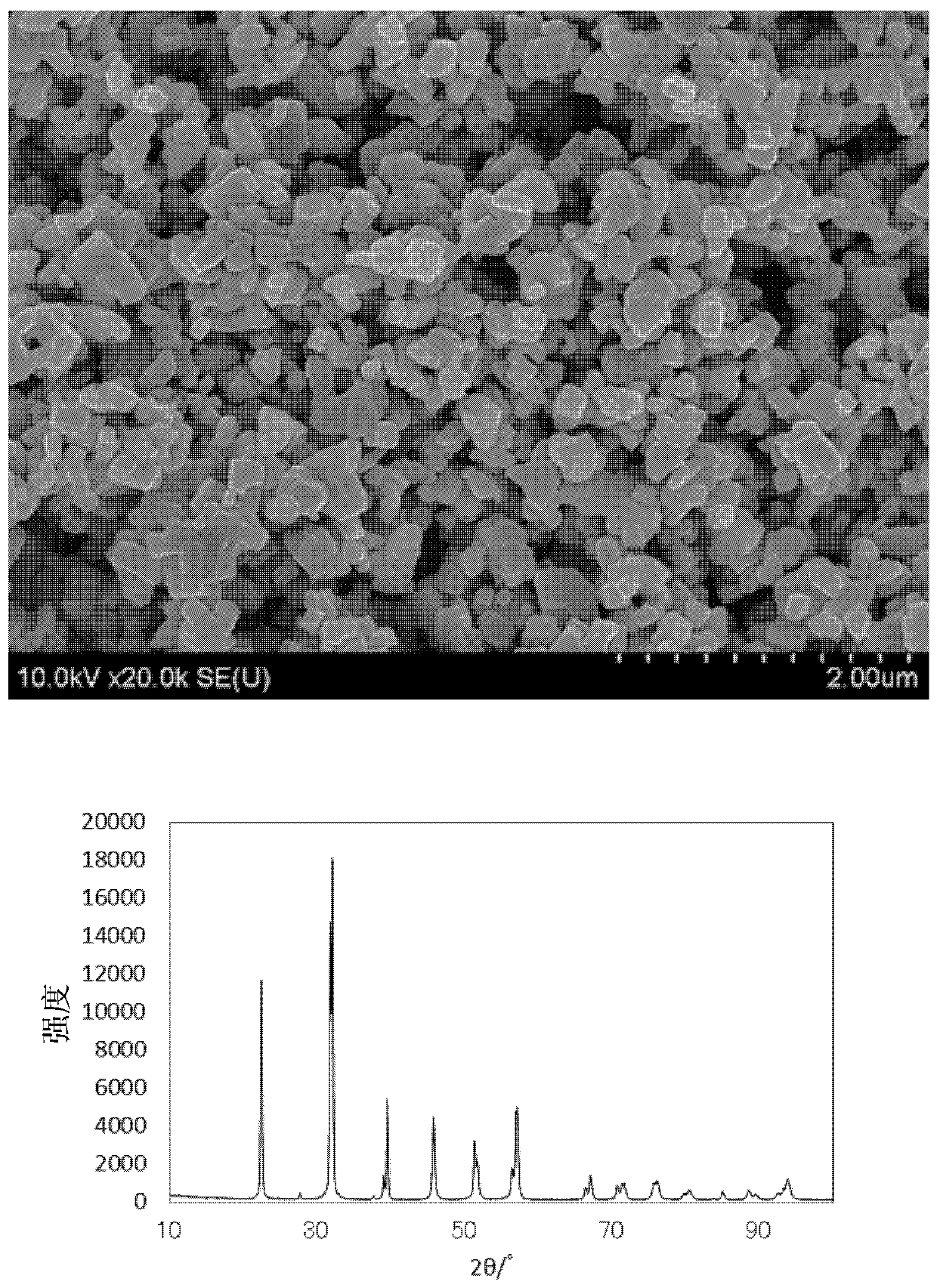
[0065] Next, the raw material pulverized mixed powder was fired at 550° C. in the air atmosphere for 7 hours to obtain a fired product. The obtained fired product was observed by...
Embodiment 2
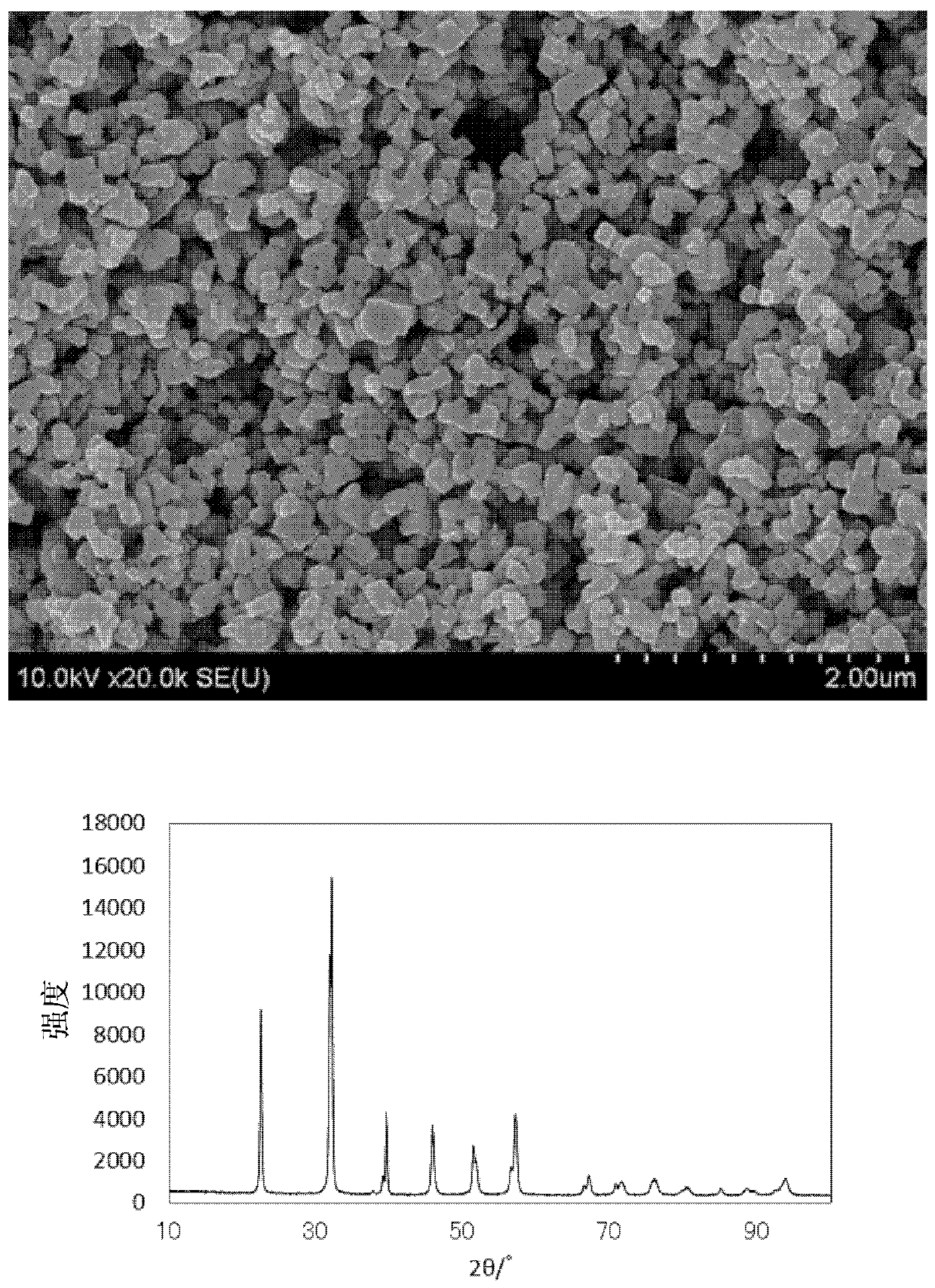
[0067] Except having set the firing temperature to 600° C., it was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1. The SEM image of the obtained fired product is shown in figure 2 . In addition, the obtained fired product was analyzed. The analysis results are shown in Table 1. Further XRD analysis was carried out. The characteristics are shown in Table 2. In addition, the X-ray diffraction pattern is shown in figure 2 .
Embodiment 3
[0069] Add it to a nylon tank with a volume of 700mL ZrO 2 Ball making, weighing and adding 37.0 g of bismuth subcarbonate (produced by Nippon Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.), 11.5 g of iron oxide (III) (produced by Kanto Chemical Co., Ltd.), and then, adding 120 g of pure water, dispersant (San Nopco Co., Ltd. produces SN5468) 2.0g, and defoamer (SNDEFOAMER produced by San Nopco Co., Ltd.) 0.4g. Next, the nylon tank was sealed, and wet pulverization and mixing were performed at a rotational speed of 120 rpm for 96 hours. Next, the obtained slurry was transferred to a tray, and dried at 120° C. for 24 hours to obtain a raw material pulverized mixed powder. The specific surface area of the raw material crushed and mixed powder is 25.57m 2 / g. In addition, the molar ratio (Bi / Fe) of bismuth to iron was 1.000.
[0070] Next, the raw material pulverized mixed powder was fired at 550° C. in the air atmosphere for 7 hours to obtain a fired product. The obtained fired product w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com