Use of sabina plant polysaccharides in preparation of medicines for preventing and treating viral acute lung injury
A technology of acute lung injury and plant polysaccharides, which is applied in the preparation of drugs for the prevention and treatment of viral acute lung injury, and new drug application fields of plant polysaccharides of the genus Juniperaceae, to reduce inflammatory immune damage, reduce permeability, and inhibit replication Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Take 100 g of cedar cedar, crush it, extract it by cold soaking with 95% ethanol for 3 times, place the medicinal residues in a ventilated place at room temperature to dry, then extract with hot water 3 times, filter, combine the extracts, concentrate, add ethanol to the alcohol content The total polysaccharide was obtained by dialysis of the supernatant with water for 3 days, concentration of the dialysate, and freeze-drying. The sugar content of cedar polysaccharide was measured by the sulfuric acid-phenol method to be 81.2%; the uronic acid content of cedar polysaccharide was measured by the m-hydroxybiphenyl method; the protein content of cedar polysaccharide was measured by the Coomassie brilliant blue method of 1.1% %.
Embodiment 2
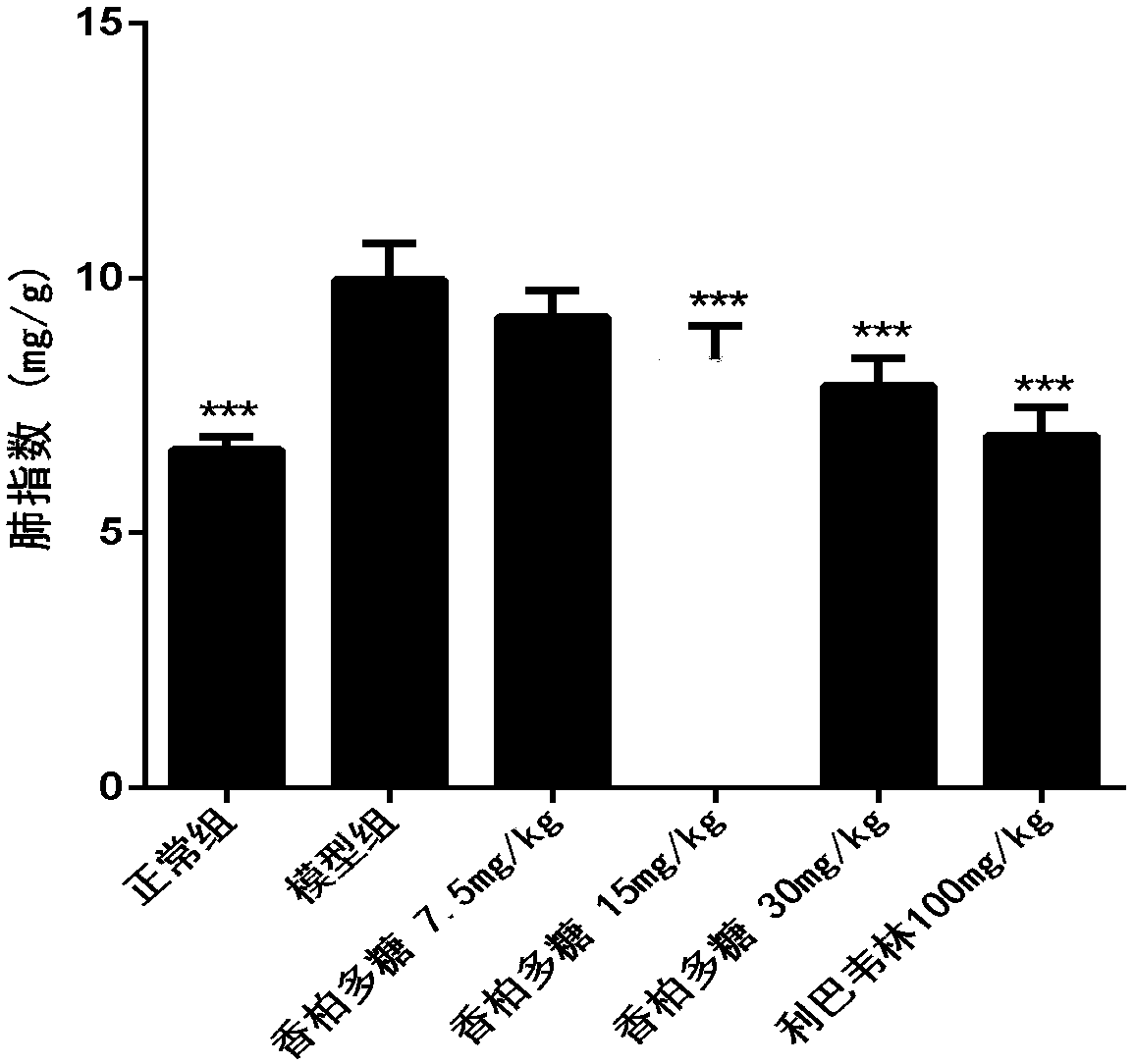
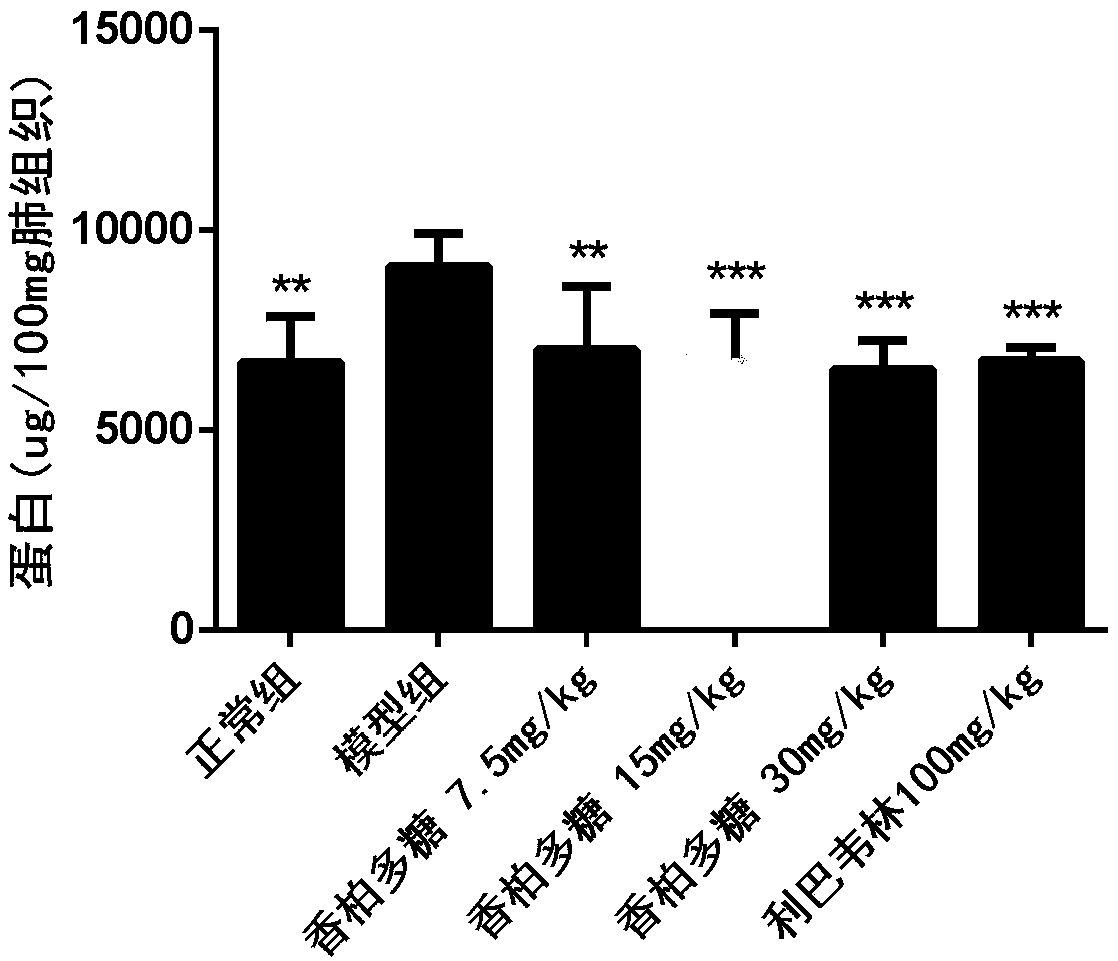
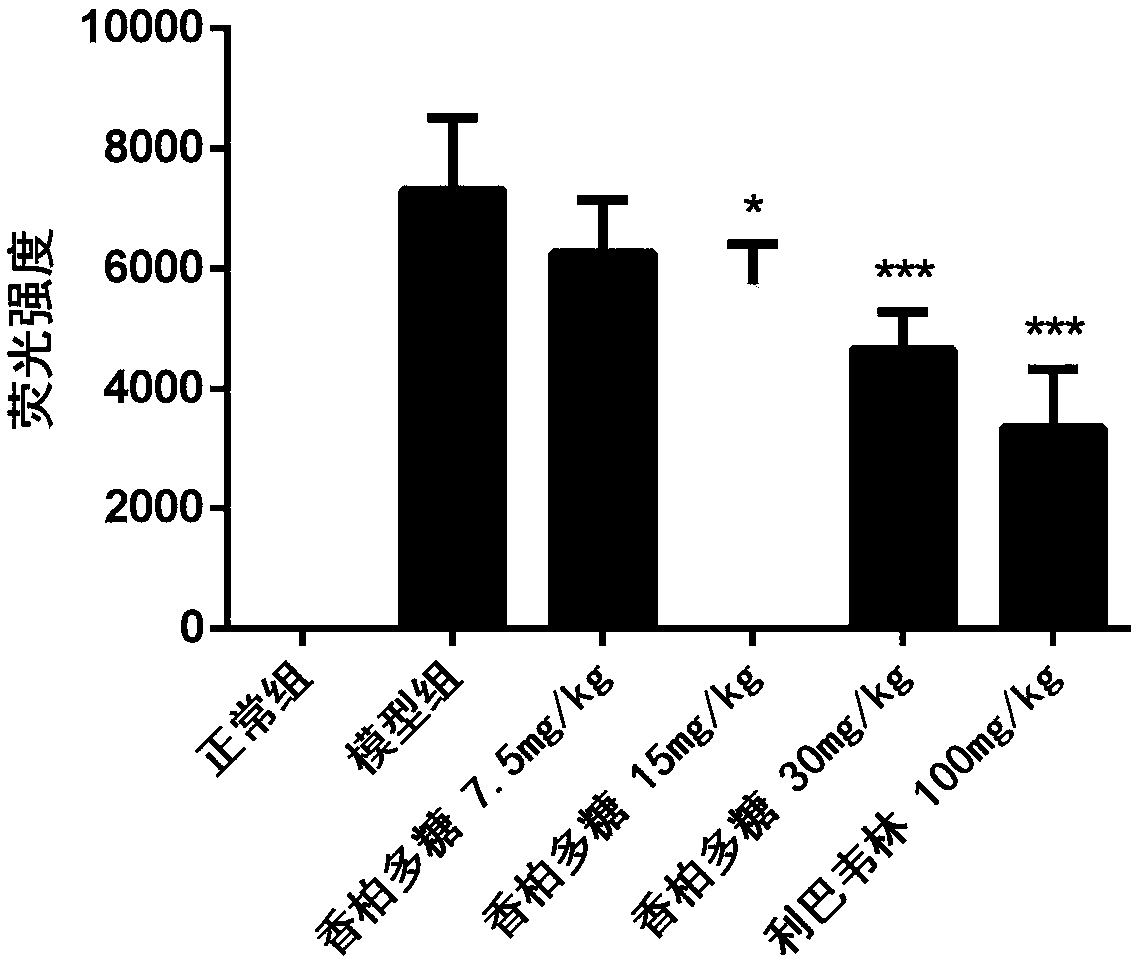
[0039] 36 BALB / C mice (14-16g) were randomly divided into 6 groups (N, M, A, B, C, P) according to body weight: group N was the normal group, group M was the H1N1 virus model group, and group A was the Cedar polysaccharide 7.5mg / kg, group B was cedar polysaccharide 15mg / kg, group C was cedar polysaccharide 30mg / kg, group P was positive drug ribavirin 100mg / kg, 6 animals in each group, all animals were treated with C. Poofol was anesthetized by tail vein injection, and 30 μL of 1640 culture solution was instilled in the nose in the N group as a control; the other groups were infected with 5LD via nasal infusion 50 30 μL of H1N1 virus solution was administered by intragastric administration two hours after H1N1 infection. Group N and group M were intragastrically administered with 0.5% CMC, as normal and virus controls, administered once a day for four consecutive days, H1N1 virus challenged for 96 hours After that, the body weight was weighed, the eyeball was taken out for bloo...
Embodiment 3
[0046] 60 BALB / C mice (14-16g) were randomly divided into 6 groups (N, M, A, B, C, P) according to body weight: N group was normal control group, M group was H1N1 virus model group, A group Cedar polysaccharide group 7.5mg / kg, B group cedar polysaccharide group 15mg / kg, C group cedar polysaccharide group 30mg / kg, P group ribavirin 100mg / kg, 10 in each group; all groups Animals were anesthetized with propofol, and 30 μL of 1640 culture medium in group N was used as control; 50 30 μL of H1N1 virus was administered by intragastric administration 2 hours after H1N1 infection in groups A and P, while groups N and M were intragastrically administered with 0.5% CMC, as normal and virus controls, administered once a day for seven consecutive days and then stopped. The drug was observed for 14 days, and the number of animals that survived and died was recorded every day, and the life protection rate of the drug on mice with severe influenza infection and pneumonia was calculated;
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com