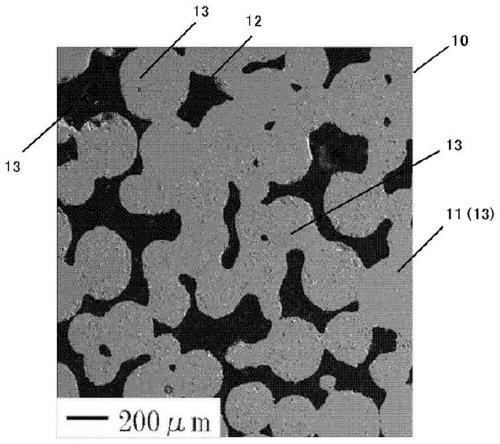
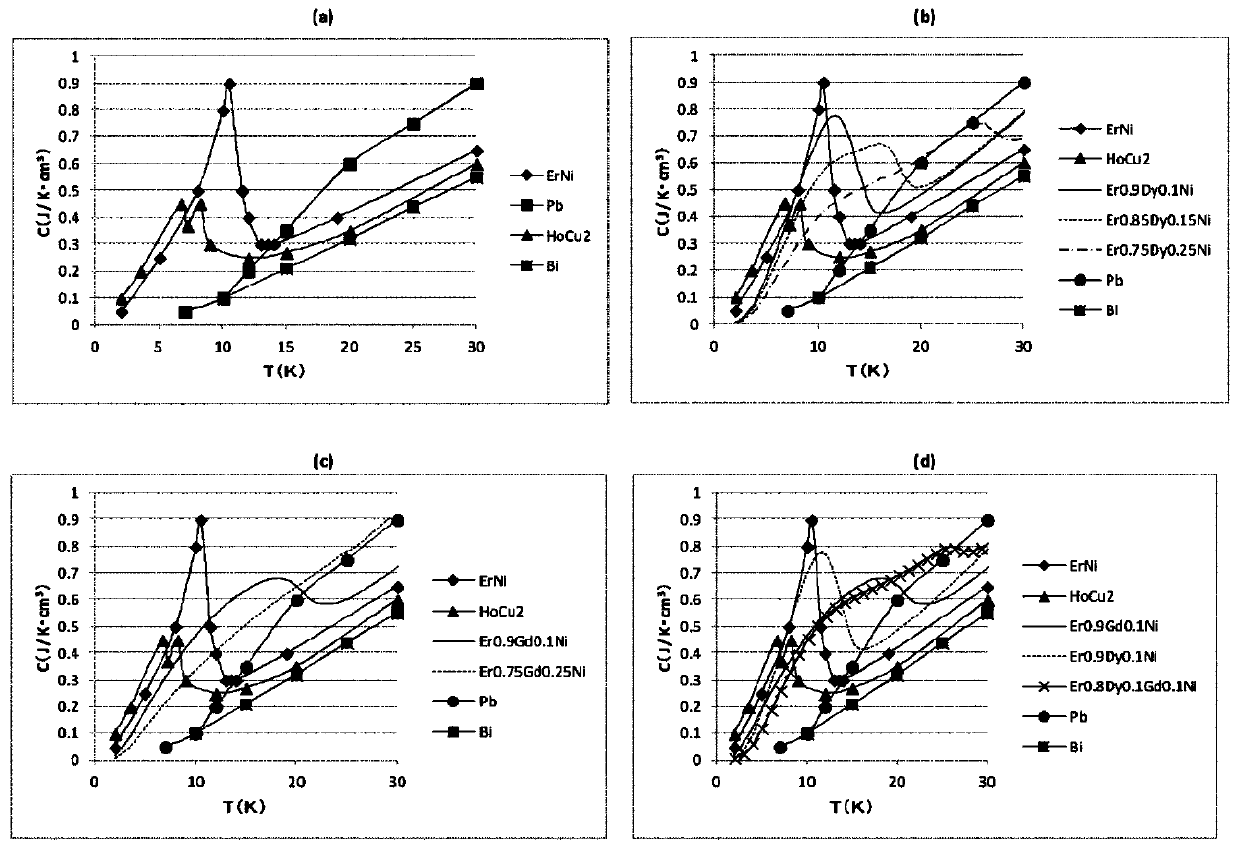
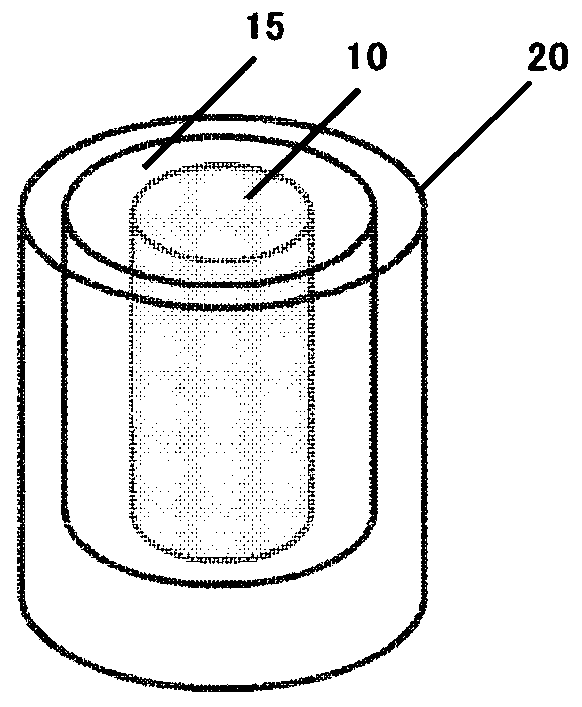
Cooling storage material and method for producing same, cooling storage device, and refrigerating machine
A technology for cold storage materials and manufacturing methods, applied in refrigerators, gas cycle refrigerators, refrigeration and liquefaction, etc., can solve the problems of refrigerant gas pressure loss, heat exchange efficiency decline, etc., and achieve high filling rate and high refrigeration capacity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~8、 comparative example 1~3
[0131] Manufacture of HoCu using known atomization method 2 Particles, for the obtained HoCu 2 The particles passed through sieves of 100 μm and 300 μm (Examples 1 to 5, Comparative Examples 1 and 3) or sieves of 200 μm and 400 μm (Examples 6 to 8, Comparative Example 2) to remove fine particles and coarse particles. Thus, raw material particles having particle sizes and particle size distributions shown in Table 1 below were obtained. Perform DTA (differential thermal analysis) of the obtained raw material particles to determine HoCu 2 The melting point of the particles.
[0132] Next, a quartz tube with an inner diameter of 29.8 mm was used as a mold for forming a sintered body, and 200 g of raw material particles were filled therein, charged in a heat treatment furnace, and then sintered in an argon atmosphere. Thus a sintered body was obtained. The sintering temperature and sintering time are shown in Table 1. The sintering temperature is set so as to be 99% or less o...
reference example 1
[0148] Manufacture HoCu with the same method as embodiment 1 2 Particles were obtained to obtain raw material particles having particle diameters and particle size distributions shown in Table 1 below. The resulting raw material particles are filled to the inner diameter without sintering In the tube 31 made of plastic. In this filling, use felt with high fluidity (i.e., low pressure loss) as a filter, and a metal mesh as a support to insert the pipe 31 together, then throw 200 g of the above-mentioned raw material particles into the top to fill, and then fill the filled raw material particles Insert the same felt and metal mesh as above, and keep a pair of felts sandwiching the raw material particles. The above-mentioned pressure loss was measured with the raw material particles filled in this way. In addition, the porosity in this case was calculated by obtaining the apparent volume of the filling part of the raw material particles from the distance between the felts and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| voidage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com