Preparation method of artificial graphite film and graphite film material
A technology of artificial graphite and graphite film, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, non-metallic elements, etc., can solve the problems of no obvious improvement in thermal conductivity of graphite film, poor thermal conductivity of graphite film, and unsatisfactory thermal conductivity. , to achieve the effect of high crystallinity, high conductivity and high thermal conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
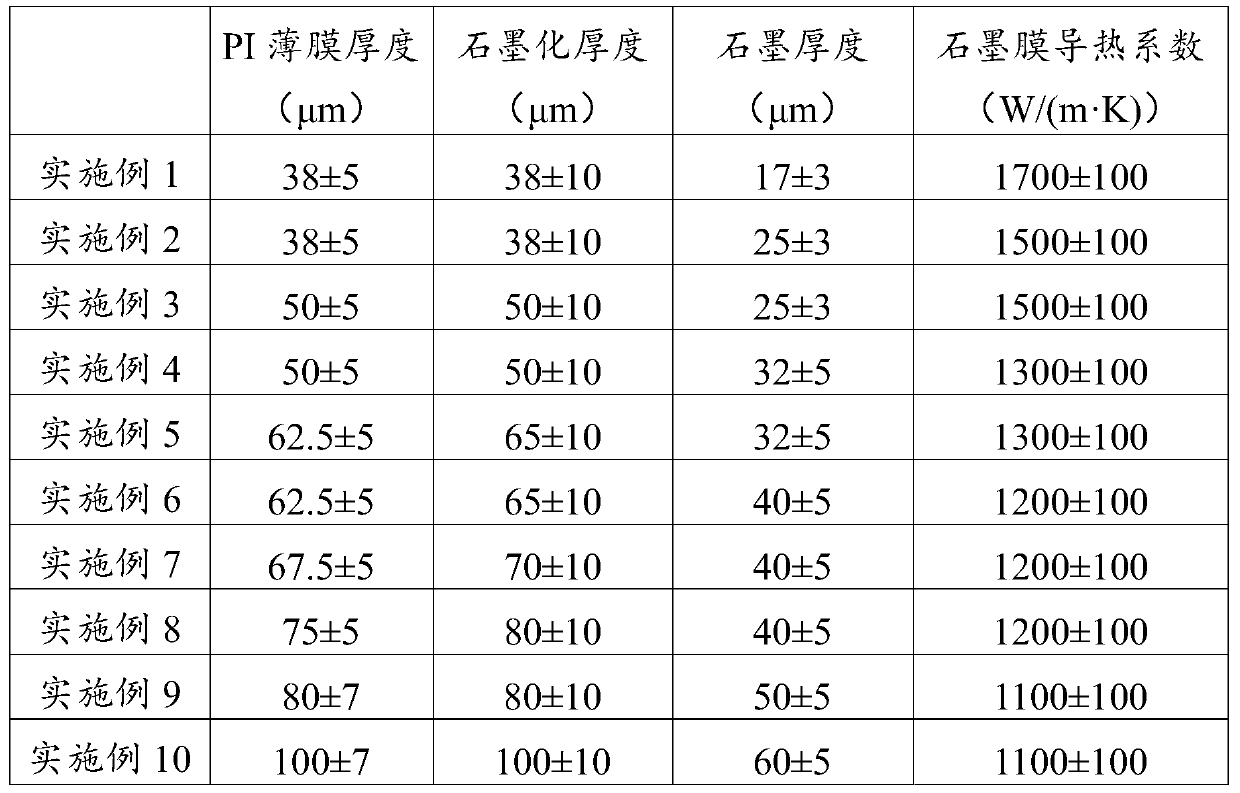
[0069] (1) The first staged temperature rise: use the PI film with a thickness of 38±5μm as the raw material, place it in a carbonization furnace with an internal pressure of -0.08MPa, and use the following staged temperature rise program to carry out the first staged temperature rise: The heating rate is 8°C / min from room temperature to 440°C, then the temperature is raised to 480°C at the rate of 0.5°C / min, and then the temperature is raised to 620°C at the rate of 0.5°C / min, and then the temperature is increased to 1.5°C / min Continue to raise the temperature to 690°C at a heating rate of 3°C / min, then continue to raise the temperature to 890°C at a heating rate of 3°C / min, and finally continue to raise the temperature to 1300°C at a heating rate of 3°C / min, keep the temperature for 60 minutes and then cool to obtain a carbonized film;
[0070] (2) The second staged temperature rise: place the carbonized film obtained in step (1) in a graphitization furnace filled with argon,...
Embodiment 2
[0072] (1) The first staged temperature rise: the PI film with a thickness of 38±5μm is used as a raw material, placed in a carbonization furnace with an internal pressure of -0.09MPa, and the first staged temperature rise is carried out using the following staged temperature rise program: The heating rate is 10°C / min from room temperature to 450°C, and then the heating rate is 1.5°C / min to 470°C, and the heating rate is 1°C / min to 610°C, and then the heating rate is 2°C / min. Continue to raise the temperature to 680°C at a heating rate of 3.5°C / min, then continue to raise the temperature to 900°C at a heating rate of 3.5°C / min, and finally continue to raise the temperature to 1100°C at a heating rate of 4°C / min, and cool down at a constant temperature for 80 minutes to obtain a carbonized film;
[0073] (2) The second staged temperature rise: place the carbonized film obtained in step (1) in a graphitization furnace filled with argon, and use the following staged temperature ri...
Embodiment 3
[0075] The steps are the same as in Example 2, except that the thickness of the PI film used in step (1) is 50±5 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com