Methods for growing light emitting devices under ultra-violet illumination
A technology of epitaxial growth and light irradiation, which is used in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., and can solve problems such as reducing device efficiency, reducing p-type material concentration, and deactivating p-type features.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] It should be understood that the figures and descriptions of the methods for growing light emitting devices under ultraviolet irradiation have been simplified to illustrate elements relevant to a clear understanding, while many other elements found in typical device processes have been removed for the sake of clarity . Those of ordinary skill in the art can recognize that other elements and / or steps are desirable and / or required in implementing the present invention. However, because such elements and steps are well known in the art, and because they would not facilitate a better understanding of the present invention, discussion of such elements and steps is not provided herein.
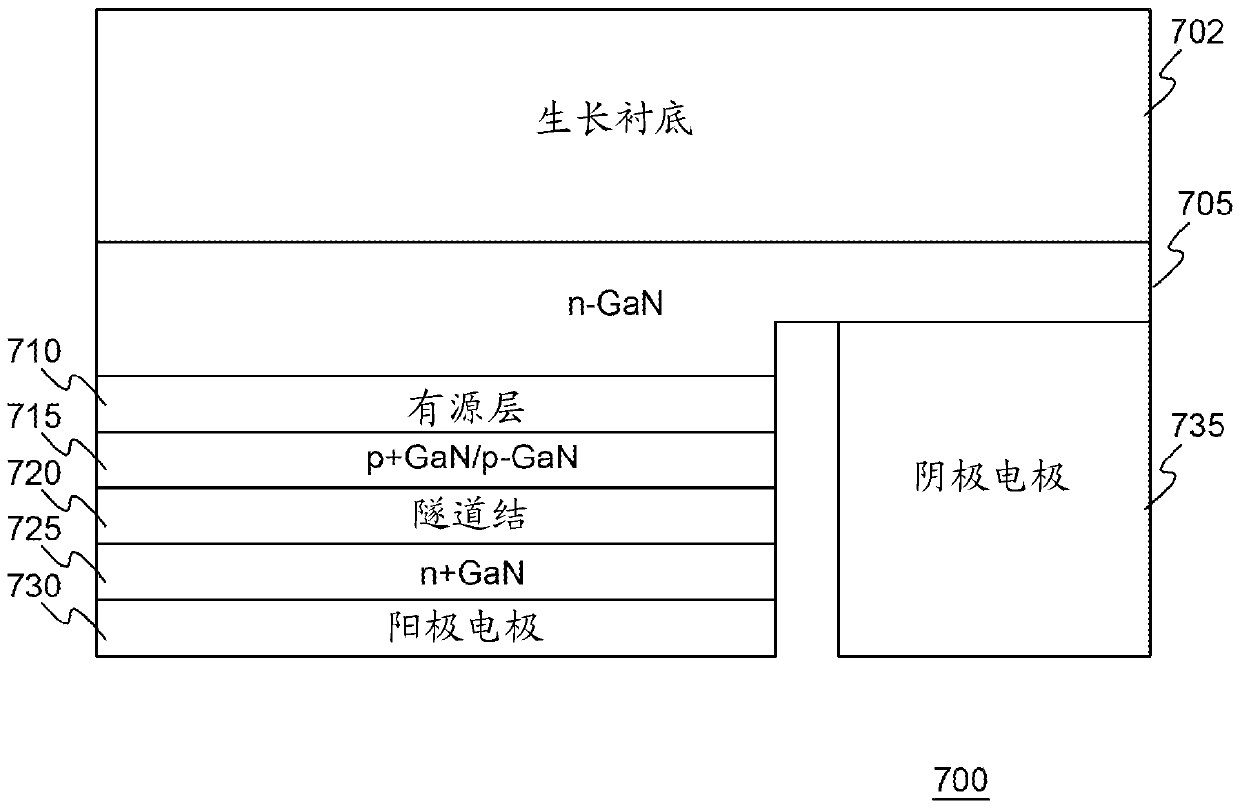
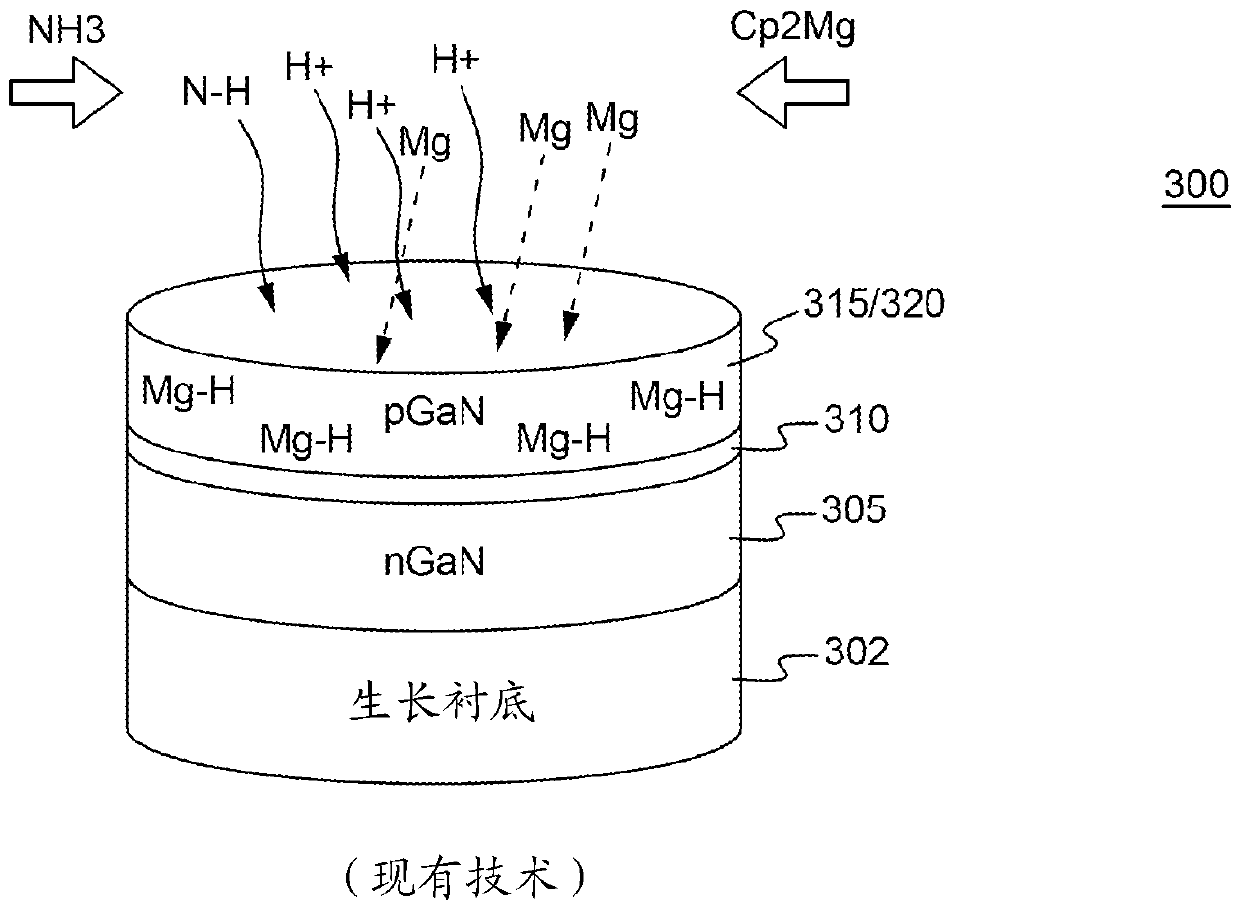
[0024] In a conventional III-nitride light-emitting diode (LED), the n-type layer is first grown on the substrate, followed by the active layer (or light-emitting layer) and the p-type layer. As used herein, the term layer refers to at least one of the identified layers, for example, a p-typ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com