Bacillus velezensis for preventing and treating clubroot disease and application of Bacillus velezensis
A technology for bacillus and clubroot, which is applied in the field of agricultural microorganisms and can solve problems such as poor stability, low control effect of clubroot, and easy inactivation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0011] Isolation identification and fermentation culture of embodiment 1 bacterial strain
[0012] 1. Strain screening
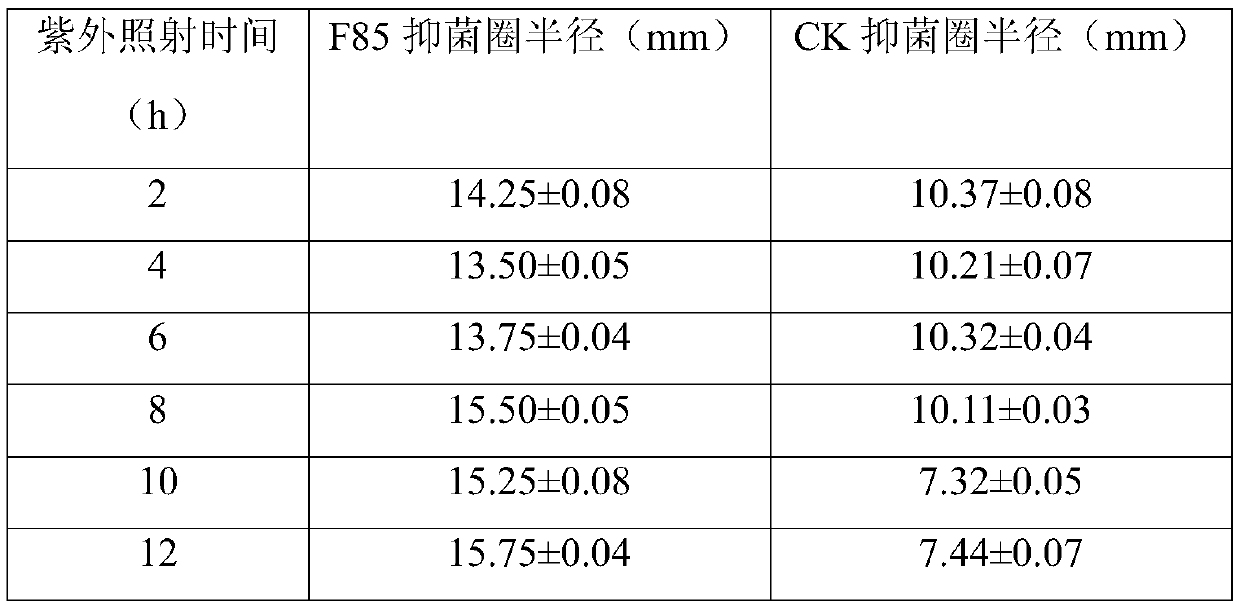
[0013] The microorganism of the present invention is obtained by separating from healthy rapeseed root soil in a field with severe clubroot disease in the Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Crop Disease Detection and Safety Control, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan City, Hubei Province. Take 200 μL soil dilution (10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 and 10 -6 ) was added to the Martin medium plate, and the growth of the colony was observed every day. According to the characteristics of colony color, shape, wet and dry, transparency and edge, a representative single colony was selected for purification and culture, and the obtained pure culture strain was used on the slant of PDA medium Store the tubes at 4°C. Since Plasmodium is an obligate parasite and cannot be cultured artificially, fungi similar to the cell wall components of Plasmodium are used as indicator ...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: Inhibitory effect of Bacillus Velez F85 on vigor and germination of Plasmodium dormant spores
[0023] 1. Inhibitory effect of Bacillus Velez F85 on the activity of dormant spores of Plasmodium
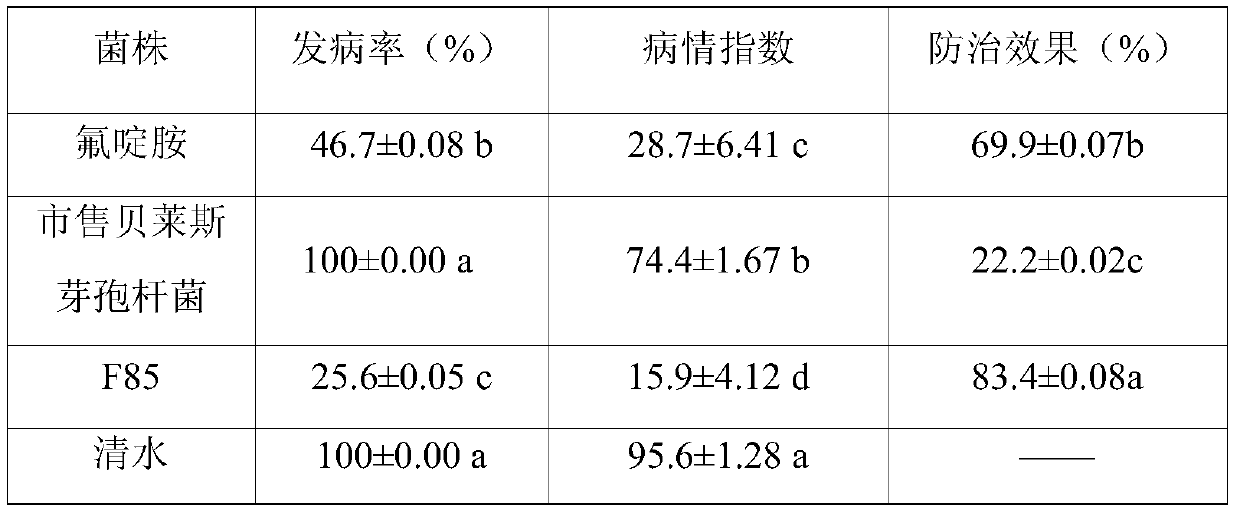
[0024] Dilute the resting spore suspension of Plasmodium to 10 9 Individuals / mL, take an equal volume of dormant spore suspension and Bacillus velesi F85 sterile fermentation broth in a sterile centrifuge tube, and mix evenly; replace Bacillus velesii F85 aseptic fermentation solution was used as a blank control, and fluazinam diluted 1000 times by chemical agents was set as a positive control. Three repetitions were set for each treatment, and all treatments were left standing at room temperature for 2 days. After 2 days, the above-mentioned treatments were uniformly mixed with an equal volume of pH 7.4 phosphate buffer, and 1 / 2 of the total volume of 2% Evans blue solution was added, and after mixing, it was placed at room temperature for 30 minutes. Take a smal...
Embodiment 3
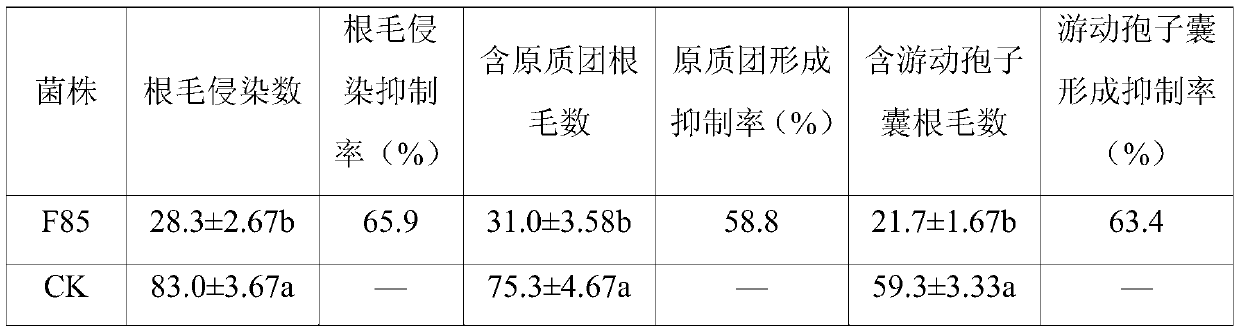
[0033] Example 3: Inhibitory effect of Bacillus velei F85 on root hairs of rapeseed root infection by Plasmodium
[0034] Fill the 50mL beaker with sterilized coarse sand, and wrap it with black paper to form a dark environment to facilitate the germination and infection of dormant spores. The rapeseed seedlings that had germinated for 4 days were moved into beakers (5 plants per beaker). After slowing down the seedlings for 3 days, inoculate 10% Bacillus Velez F85 aseptic fermentation filtrate and Plasmodium dormant spore suspension (final concentration is 10 7 individuals / mL), and inoculated with the same concentration of dormant spore suspension as the control. The plant nutrient solution (pH=6.3) was watered timely, and all treatments were cultured in a plant culture box at 24°C, with a photoperiod of 16 / 8h and a relative humidity of 90%. From the 1st to 15th day after inoculation, samples were taken every day, and the roots were washed and fixed in acetic acid: ethanol ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com