A kind of rheological preparation method of aluminum-zinc alloy melt
A melt rheology and alloy technology, applied in the field of metal melt processing, can solve the problems of limited application scope, easy occurrence of hot cracking, poor casting performance, etc., and achieves high preparation efficiency, improved casting performance, and good fluidity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
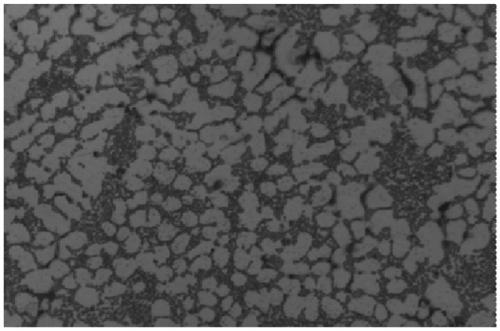
[0039] Such as figure 1As shown, a rheological preparation method of an aluminum-zinc alloy melt is suitable for binary or multi-element Al-Zn alloys with a Zn content of 1-30wt%, in this embodiment it is an Al-2Si-1Zn (mass fraction) alloy , which includes the smelting process of the previous process and the rheological melt processing process of the post-process. The smelting process melts and uniformly stirs each alloy masterbatch to obtain an alloy melt, and then the alloy melt undergoes a rheological melt processing process. The dendrites are broken into a near-spherical microstructure and a melt slurry with a certain solid phase ratio is prepared. The primary phase of the melt slurry is round and uniform, which can maximize the advantages of semi-solid processing technology and improve the casting performance and mechanical properties of aluminum-zinc alloys. It can be directly used for casting molding of subsequent castings, and can also be used for thixotropy Shaped a...
Embodiment 2
[0046] A rheological preparation method of an aluminum-zinc alloy melt, which is different from Embodiment 1 in that the time factor of the smelting process is changed, and the preferred temperature and mechanical stirring conditions of the rheological melt processing process are different.
[0047] In the smelting process, firstly, each alloy masterbatch is preheated in the temperature range of 100-200°C, and the preheating time is more than two hours, and then each alloy masterbatch is melted in a crucible resistance furnace or other industrial electric furnace, and waited for each After the alloy masterbatch is melted, stir evenly at 680°C and let it stand for 20 minutes, then add refining agent to the alloy melt, and refine at 660°C for 15 minutes, and finally clean up the waste slag in the alloy melt ( That is, slag removal) and stand still for 20 minutes, so as to complete the pre-process operation in the rheological preparation process of aluminum-zinc alloy melt. In th...
Embodiment 3
[0050] A rheological preparation method of an aluminum-zinc alloy melt, the difference from Embodiment 1 lies in: the time change of the smelting process, the preferred temperature and the mechanical stirring conditions of the rheological melt processing process.
[0051] In the smelting process, firstly, each alloy masterbatch is preheated in the temperature range of 100-200°C, and the preheating time is more than two hours, and then each alloy masterbatch is melted in a crucible resistance furnace or other industrial electric furnace, and waited for each After the alloy masterbatch is melted, stir evenly at 680°C and let it stand for 10 minutes, then add refining agent to the alloy melt, and refine at 660°C for 20 minutes, and finally clean and remove the waste slag in the alloy melt (that is, slag removal) and stand still for 20 minutes, so as to complete the pre-process process in the rheological preparation process of aluminum-zinc alloy melt. In the rheological melt proc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com