Method for gradient recovering of copper, cobalt and zinc from sulfur concentrate through low-temperature roasting
A low-temperature roasting, sulfur concentrate technology, applied in rotary drum furnaces, crucible furnaces, furnaces, etc., can solve the problems of waste of resources, poor leaching performance, inability to recover efficiently and economically, and achieve high maturity, easy leaching, comprehensive The effect of high recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
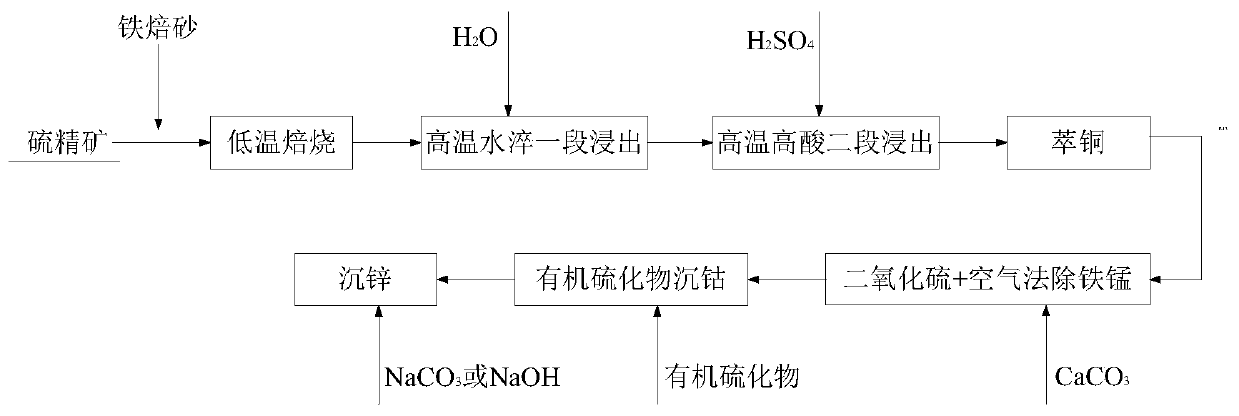
[0027] A method for recovering copper-cobalt-zinc from sulfur concentrate by low-temperature roasting gradient, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0028] S1. Roasting at low temperature: 150 g of sulfur concentrate and 17 g of iron calcined sand were oxidized and roasted at 450° C. for 1 hour; the number of particles with a particle size of -200 mesh in the sulfur concentrate accounted for 65%.
[0029] S2. High-temperature water quenching and one-stage leaching: After low-temperature roasting is completed, take out all the calcined sand obtained by roasting and directly add 334g of water for water quenching; the ore slurry obtained after water quenching is transferred to a stirring tank for one-stage leaching at a stirring rate of 300rpm for 1 hour , the leaching temperature is 80°C.
[0030] S3. High-temperature and high-acid secondary leaching: heat and control the temperature of the pulp after the first stage of leaching to 80°C, add concentrated sul...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A method for reclaiming copper-cobalt-zinc by gradient roasting of sulfur concentrate at low temperature, comprising the steps of:
[0037] S1. Roasting at low temperature: take 150g of sulfur concentrate and 64g of iron calcined sand and oxidize and roast at 700°C for 2 hours. The number of particles with a particle size of -200 mesh in the sulfur concentrate accounts for 65%.
[0038] S2. High-temperature water quenching one-stage leaching: after the low-temperature roasting is completed, take out all the calcined sand obtained by roasting and directly add 428g water for water quenching; the ore slurry obtained after water quenching is transferred to a stirring tank for one-stage leaching, the stirring rate is 500rpm, and the leaching rate is 0.5 h, the leaching temperature is 100°C.
[0039] S3. High-temperature and high-acid secondary leaching: heat and control the temperature of the pulp after the first stage of leaching to 100°C, add concentrated sulfuric acid to...
Embodiment 3
[0045] A method for reclaiming copper-cobalt-zinc by gradient roasting of sulfur concentrate at low temperature, comprising the steps of:
[0046] S1. Roasting at low temperature: take 150g of sulfur concentrate and 50g of iron calcined sand and oxidize and roast at 500°C for 3h. The number of particles with a particle size of -200 mesh in the sulfur concentrate accounts for 65%.
[0047] S2. High-temperature water quenching and one-stage leaching: after the low-temperature roasting is completed, take out all the calcined sand obtained by roasting and directly add 400g of water for water quenching; the ore pulp obtained after water quenching is transferred to a stirring tank for one-stage leaching at a stirring rate of 400rpm for 1h , the leaching temperature is 90°C.
[0048]S3. High-temperature and high-acid secondary leaching: heat and control the temperature of the pulp after the first stage of leaching to 85°C, add concentrated sulfuric acid to the pulp at a rate of 50 g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com