A kind of method for controlling Bemisia tabaci by cooperating with Cordyceps javanica
A technology for the bemiphid wasp and bemisia tabaci, applied in the field of biological control, can solve the problems of Q-type bemisia tabaci hazard aggravation, environmental factors, and unstable control effect, and achieve easy operation and popularization, and improve Efficiency of dispersal, conservation of biodiversity and effects of natural enemy resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
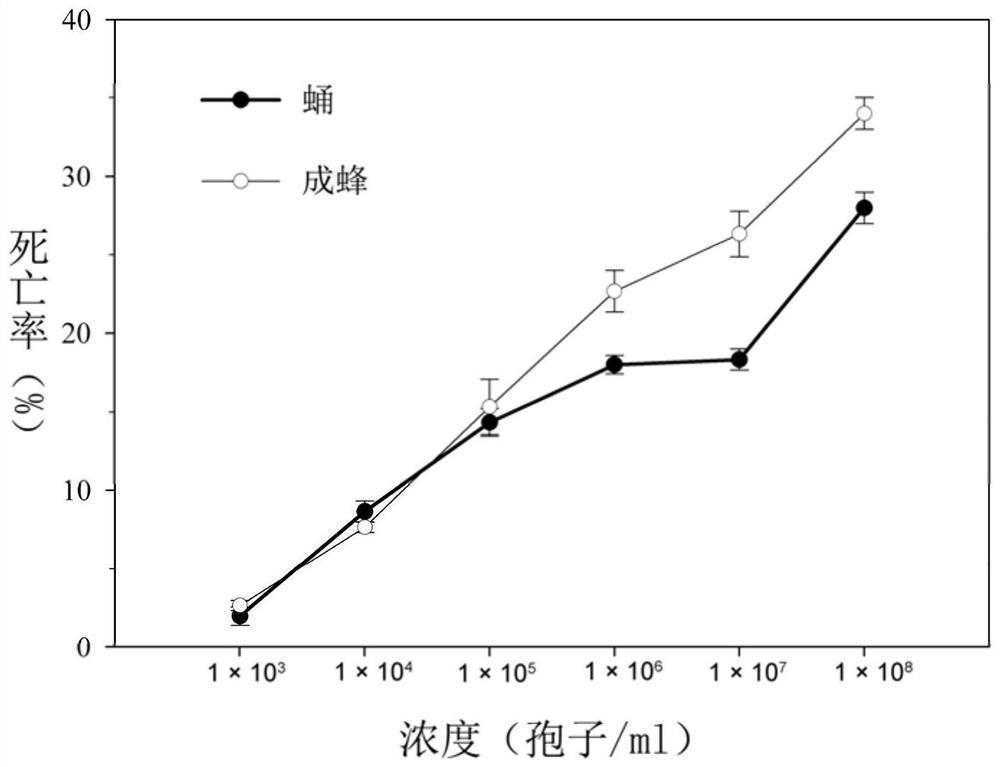
[0048] Example 1 Analysis of the pathogenicity of the Cordyceps javanica GZQ-1 strain to the wasp
[0049] 1. The pathogenicity experiment of Cordyceps japonica on the pupae of Aphid spp.
[0050] (1) Experimental method
[0051] Cotton seedlings with the same growth status were selected, and 60 pairs of adult whitefly were inserted into each box by using the inoculation box, and the adult whitefly were removed after 24 hours. When Bemisia tabaci developed to the second instar, it was inserted into the wasp of Aphididae, and it was used in the experiment when the wasp developed to the pupal stage.
[0052] Using the soaking method, the cotton leaves with the pupae of Aphid spp. were immersed in the spore suspension of Cordyceps javanica for 15s (1×10 3 Spores / mL, 1×10 4 Spores / mL, 1×10 5 Spores / mL, 1×10 6 Spores / mL, 1×10 7 Spores / mL, 1×10 8 spores / mL), and 1% Tween-80 was used as a control. Put the cotton leaves in agar (10g.L -1 ) in a petri dish, sealed with perfora...
Embodiment 2
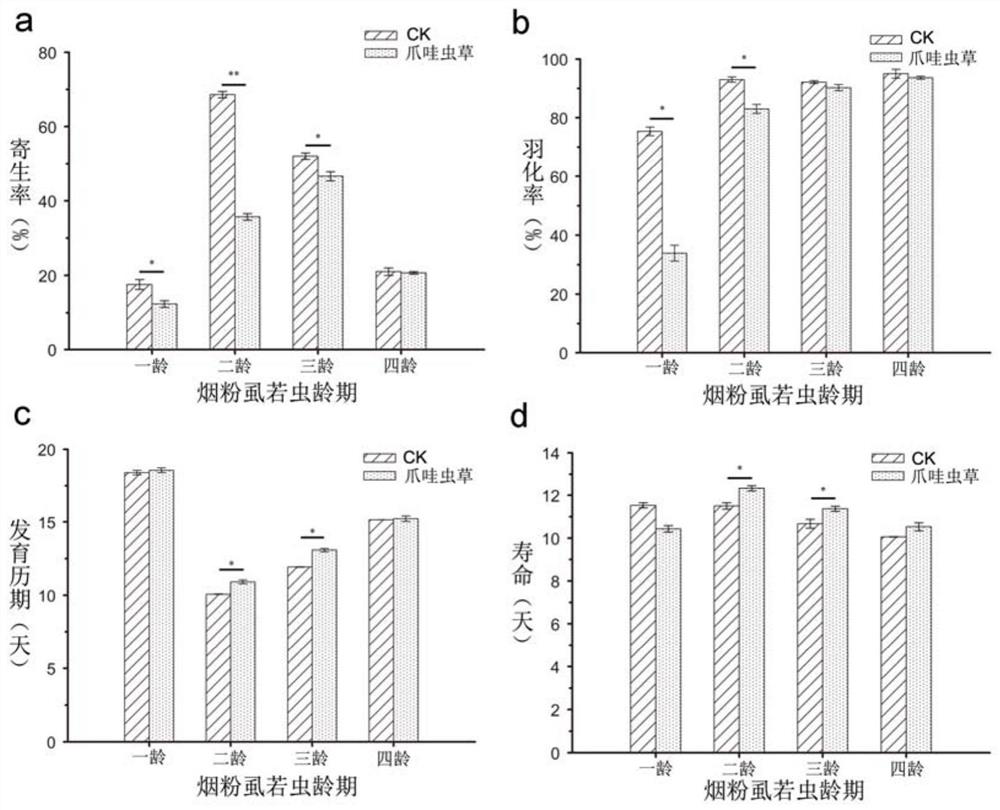
[0064] Example 2 Effects of Cordyceps Javanese GZQ-1 Strain on the Parasitic Potential of the Aphid spp.
[0065] 1. Non-selective experiment (single age)
[0066] (1) Experimental method
[0067] Cotton seedlings with the same growth conditions were selected, put on the inoculation boxes, and 40 pairs of adult whitefly were inserted into each box, and the adults of whitefly were removed after 24 hours of oviposition. Each treated Bemisia tabaci was used in the experiment when it developed to the corresponding age (1-4). Java Cordyceps spore suspension (1 × 10 8 spores / mL) were evenly sprayed onto the leaves with nymphs of various ages until there were droplets dripping down, and after drying naturally, a box with a larger diameter was selected to clamp the whitefly nymphs and connected to the paddles that had just emerged. Horned aphid wasps, remove the parasitic wasps after 24 hours. Tween-80 was used as a control experiment, and each treatment was repeated 5 times. Obs...
Embodiment 3
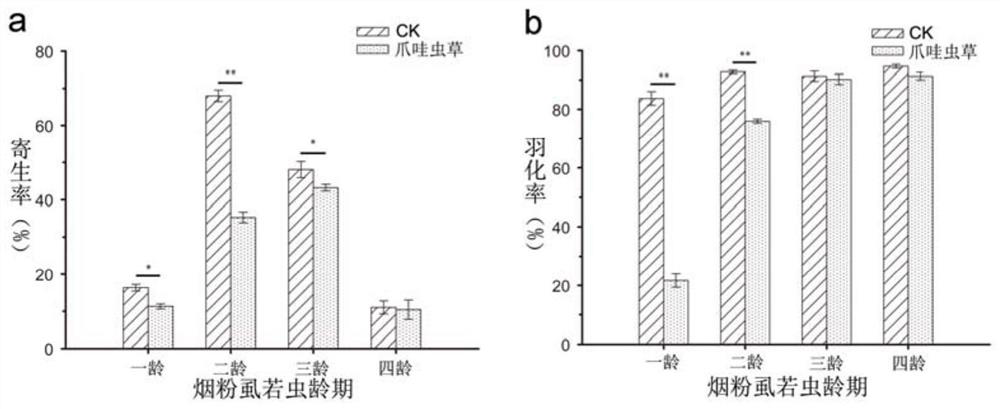
[0079] Example 3 Cordyceps javanica GZQ-1 strain combined with Aphidia spp. to control Bemisia tabaci
[0080] 1. Experimental method
[0081] (1) Breeding of the tested population of whitefly: select healthy cotton seedlings with the same growth, insert the adults of whitefly by using the miniature insect box, after 24 hours of laying eggs, remove the adults of whitefly, and put the cotton seedlings connected with tobacco powder The cotton seedlings of the lice are put into insect cages, raised at a temperature of 26±1° C. and a humidity of 60 to 80%, and regularly fertilized and watered;
[0082] (2) Breeding of the tested population of Aphididae wasps: select cotton seedling plants with 2nd to 3rd instar nymphs of Bemisia tabaci, use a small finger-shaped tube to absorb Aphididae wasps, and inoculate them for 24 hours through a miniature inoculation box. Afterwards, it was removed and used for experiments after 3 to 5 generations of breeding;
[0083] (3) Cultivation of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com