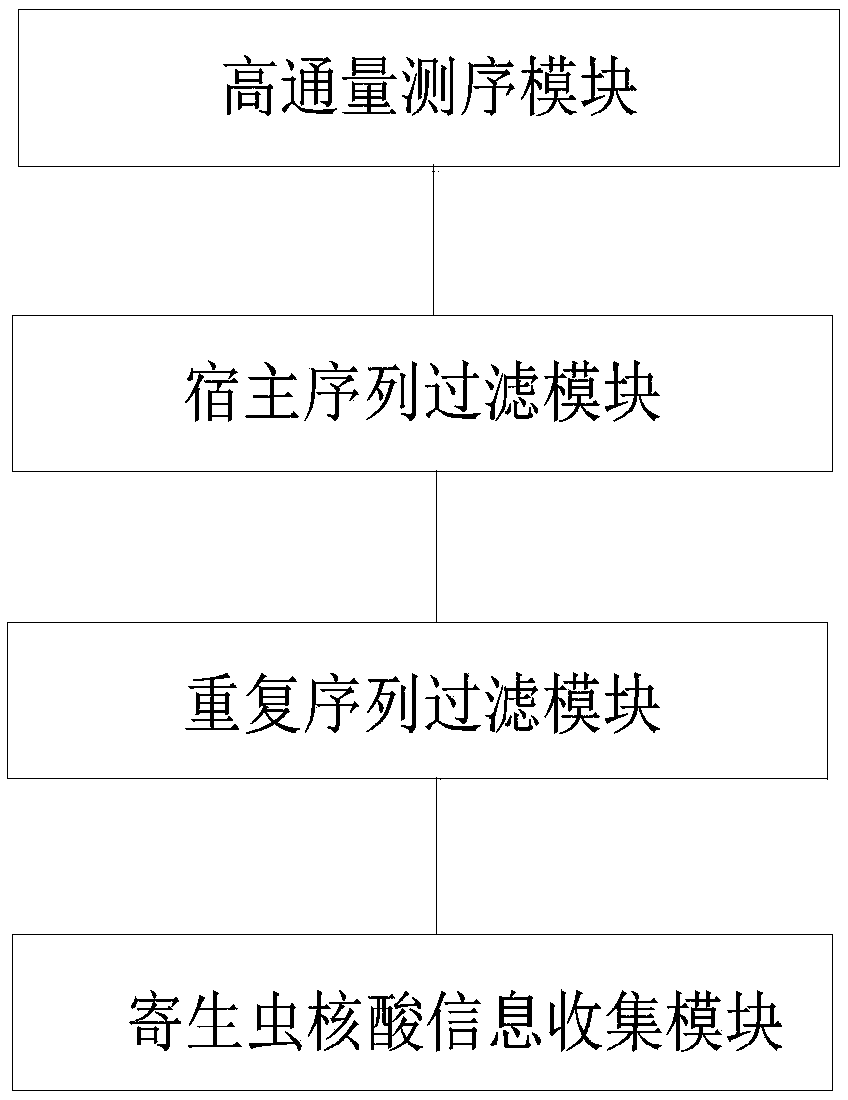
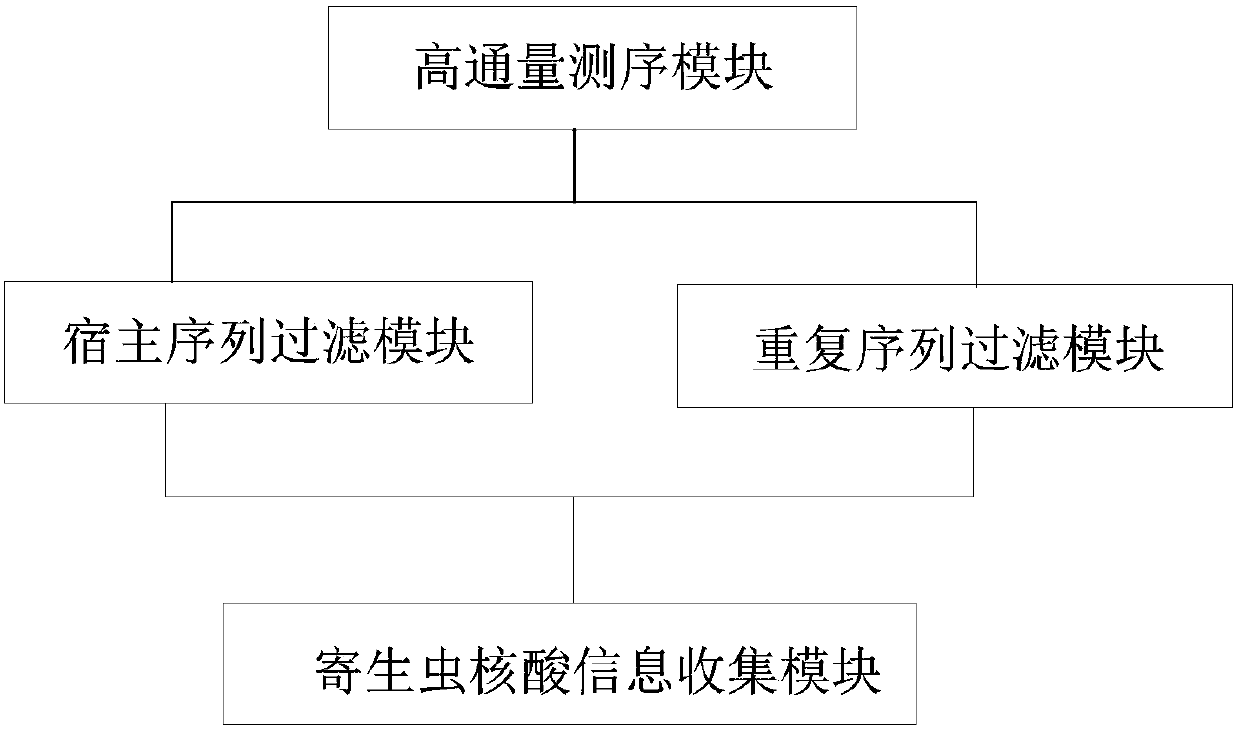
Methods and systems for acquiring nucleic acid information of parasites and classifying parasites by sequencing
A parasite and sequencing technology, applied in the field of high-throughput sequencing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] Cell-free DNA was isolated from human peripheral blood and subjected to high-throughput sequencing as follows.
[0102] 1. Select experimental samples, which come from peripheral blood samples collected by cooperative hospitals.
[0103] Including 25 samples clinically identified as echinococcosis infection and 12 negative control samples. The negative control sample is a sample not infected by echinococcosis. Among them, echinococcosis is a chronic parasitic disease caused by human infection with the larvae (echinococcus) of Echinococcus.
[0104] 2. Extraction of free DNA (cfDNA) from peripheral blood plasma.
[0105] 3. Use Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent) to detect the concentration and quality of the extracted DNA.
[0106] 4. Fragment 2 μg of DNA with Covaris E210 (Covaris):
[0107] Fragmentation processing uses Covaris E210 interrupter, the target length is 150bp-200bp, and the relevant parameters are as follows: Duty / cycle: 20, Intensity: 5, Cycle / burst: 20...
Embodiment 2
[0111] In this embodiment, biological analysis is performed on the sequencing data obtained by sequencing according to the following method, so as to determine the type of parasite.
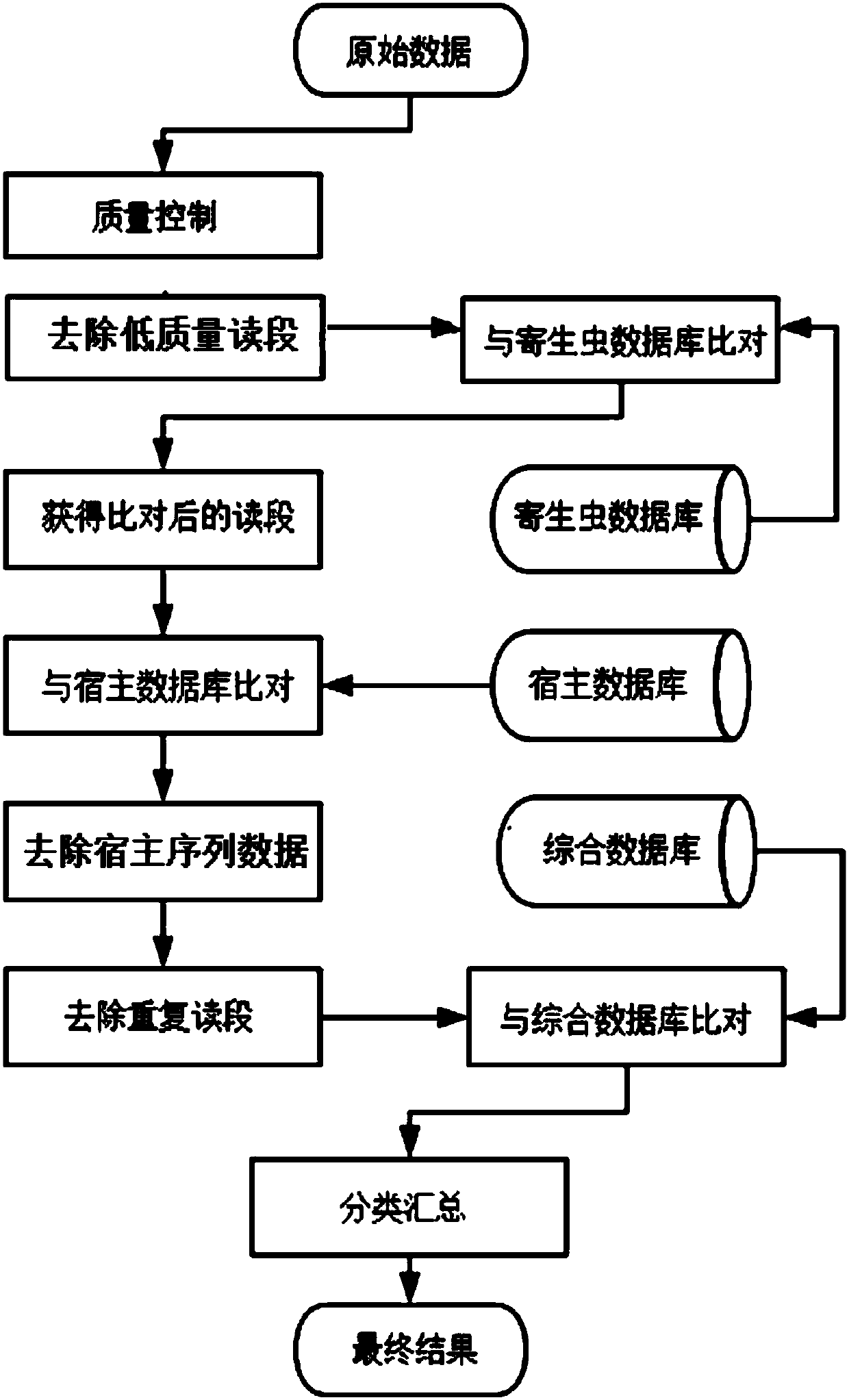
[0112] 1. Construction of parasite reference database. At present, the known parasites that infect humans mainly include protozoa (Protozoa) and worm (Helminths), so the database is constructed based on these two categories. The protozoa reference sequences are from the protozoa database in NCBI refseq, and the worms are from the WormBase ParaSite database. The reference sequences of the two types of data were then pooled together to construct a parasite reference sequence database.
[0113] 2. Use SOAPnuke (-l 15-q 0.2-n 0.05) to perform quality control on the data obtained by high-throughput sequencing in Example 1, and remove the sequencing reads with low quality values and those containing more N.
[0114] Among them, the parameters shown in the brackets of SOAPnuke are the various parame...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com