Method for removing insoluble quinoline particles on surfaces of carbon microspheres
A carbon microsphere and quinoline technology, applied in the field of coking, can solve the problem of insoluble particles of quinoline being unable to be removed, and achieve the effects of improving the first charge and discharge efficiency, being beneficial to engineering promotion, and improving the specific capacitance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] After classification, the carbon microspheres with an average particle size of 12 μm are retained, and 1 kg is put into the muffle furnace. After nitrogen replacement, the temperature was increased to 180°C at a temperature increase rate of 15°C / min. Switch the air source into the muffle furnace, the heating rate is 8°C / min, the temperature is raised to 380°C, and the temperature is maintained for 3h. Then cool to room temperature at a rate of 20°C / min. The carbon microsphere product with an average particle diameter of 12 μm was recovered by a classifier, the yield was 97.4%, the specific capacitance was 324 mAh / g, and the first charge-discharge efficiency was 93.6%.
Embodiment 2
[0024] After classification, the carbon microspheres with an average particle size of 23μm are retained, and 5kg is taken into the muffle furnace. After nitrogen replacement, the temperature is increased to 150°C at a temperature increase rate of 10°C / min. Switch the air source into the muffle furnace, the heating rate is 5℃ / min, the temperature is raised to 350℃, and it is kept for 2h. Then cool to room temperature at a rate of 15°C / min. The carbon microsphere product with an average particle diameter of 23μm was recovered by the classifier, the yield was 98.6%, the specific capacitance was 334mAh / g, and the first charge-discharge efficiency was 94.3%.
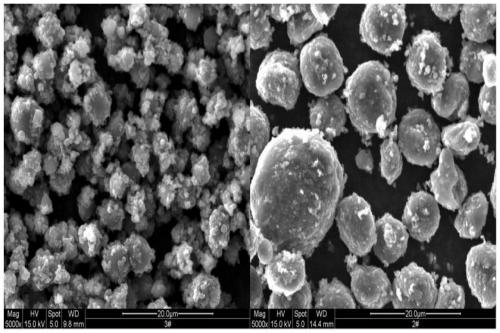
[0025] figure 1 with figure 2 The scanning electron micrographs of the carbon microspheres before and after treatment respectively show the reduction of quinoline insoluble particles on the surface. After the electrochemical test, the specific capacitance increased from 285mAh / g to more than 310mAh / g, and the first charge-di...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com