GNSS-R shore-based platform sea surface oil spill area detection method
A technology of sea surface oil spill and detection method, applied in the field of sea surface oil spill area detection of GNSS-R shore-based platform, can solve the problems of poor mobility, only monitoring specific sea areas, and limited application popularization, and achieves flexible simulation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] like Figure 1 to Figure 5 As shown, a GNSS-R shore-based platform sea surface oil spill area detection method includes the following steps:
[0028] (1) Through the detection equipment, calculate the area of the effective coverage area, and obtain the platform position and the assumed height data of the antenna, and calculate the coverage area of the transmitted signal received by the antenna at different times, as the flashing area;
[0029] (2) According to the blazed area calculated in step (1), the dielectric constant is inverted for the emission signal in the blazed area;
[0030] Calculation of signal reflectivity polarization ratio: for received direct and reflected signals, use the calculation method of signal correlation value and reflectivity, the relationship between reflectivity and related power is as follows, where Γ represents reflectivity, Indicates the relative power:
[0031]
[0032] According to the above formula, the left-handed reflectiv...
Embodiment 2
[0040] A GNSS-R shore-based platform sea surface oil spill area detection method, comprising the following steps:
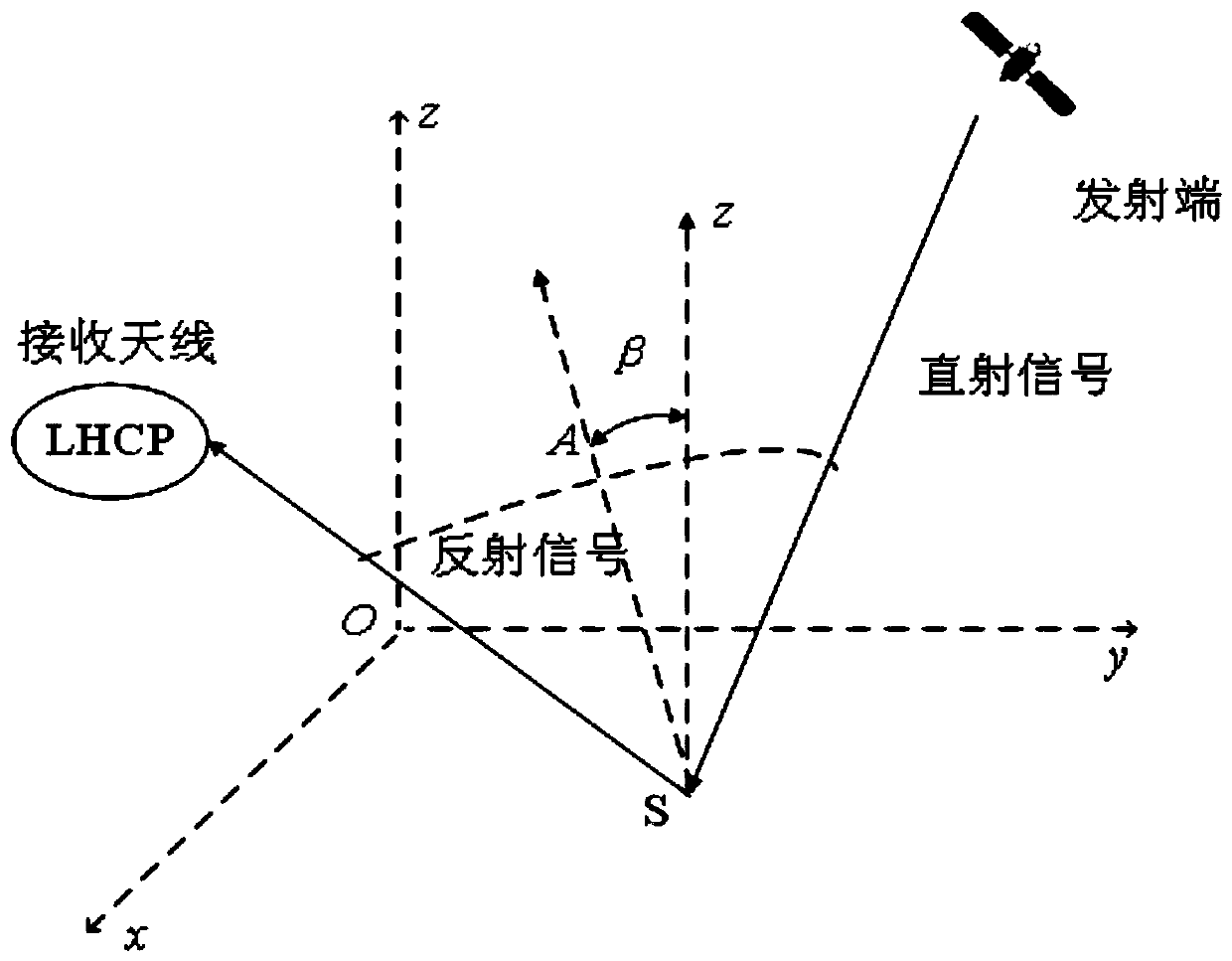
[0041] (1) Through the detection equipment, calculate the area of the effective coverage area, and obtain the platform position and the hypothetical height data of the antenna, calculate the coverage area of the transmitted signal received by the antenna at different times, and use it as the flashing area; image 3 and Figure 4 As shown, point O is the origin of the coordinates, indicating the projection point of the receiving antenna on the sea surface, the X-axis points to the south, the Y-axis points to the east, the Z-axis passes through point O and is perpendicular to the XOY plane; SP is the mirror reflection point; θ is the satellite altitude angle; is the azimuth angle of the satellite, and the RHCP antenna is a right-handed circularly polarized antenna for receiving satellite direct signals; the LHCP antenna is a left-handed circularly polarized a...
Embodiment 3
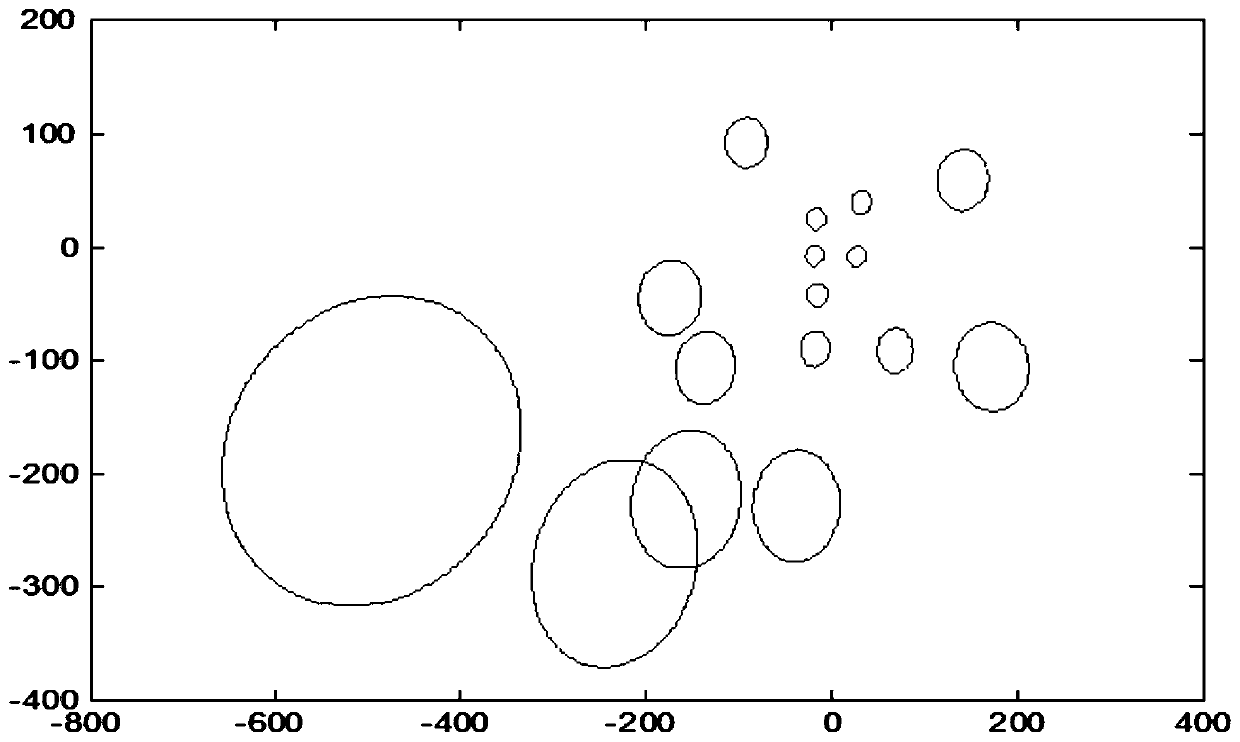
[0054] The applicable scattering model of GNSS-R used in this embodiment is based on the geometrical optics model of Kirchhoff approximation. Under ideal conditions, when the reflective surface is smooth, the specular reflection strictly satisfies the law of Fresnel reflection, so only when the reflection vector direction to receive the signal. Under the actual sea surface conditions, considering the influence of roughness, the direction of some small facets on the reflective surface changes, so that the mirror reflection direction of the facet changes accordingly. , can also receive specular reflection signals, the greater the roughness of the reflecting surface, the greater the number of specular reflection signals acceptable to the receiving antenna, and the larger the range of bin distribution. This area with obvious microwave reflection is called the blaze area, such as Figure 5 Shown:
[0055] Point O in the figure represents the specular reflection point, point S rep...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com