A method of improving strength and windability of zirconia continuous fibers
A technology of continuous fiber and zirconia, which is applied in the field of inorganic non-metallic oxide fiber materials, can solve the problems of insufficient windability and poor winding performance of continuous fiber of zirconia, which is beneficial to classification, improved mechanical properties, The effect of improving mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0055] (1) Preparation of zirconium polyacetylacetonate precursor
[0056] ① Weigh 100g zirconium oxychloride ZrOCl 2 ·8H 2 O, dissolve in absolute ethanol according to the ratio of zirconium oxychloride: absolute ethanol = 100g: 640g, measure acetyl Acetone 31.1g and triethylamine 60.9g, first acetylacetone is slowly added in the ethanolic solution of zirconium oxychloride, fully stirs to form mixed solution; Then the mixed solution of triethylamine and ethanol (mixing ratio is 60.9g three Ethylamine: 160g ethanol) was slowly added to the above mixed solution, fully reacted and stirred for 2 hours to obtain a golden yellow reaction solution, that is, a solution containing zirconium polyacetylacetonate.
[0057] ②Concentrate under reduced pressure to remove the solvent ethanol and water at a temperature of 40-45°C and a vacuum of 0.09MPa until a light yellow powder is obtained. Add acetone according to the ratio of zirconium oxychloride: acetone = 100g: 300ml to dissolve the...
Embodiment 1
[0067] A method for improving the strength and windability of continuous zirconia fibers, comprising the following steps:
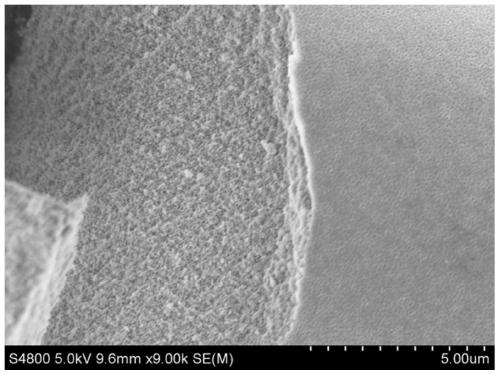
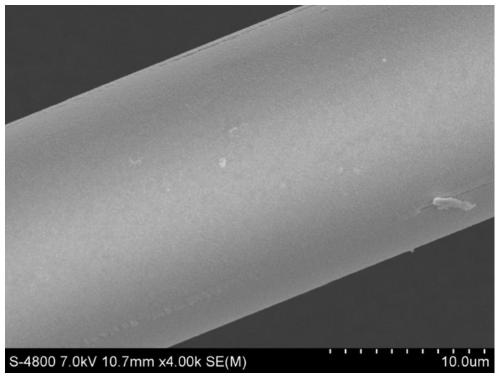
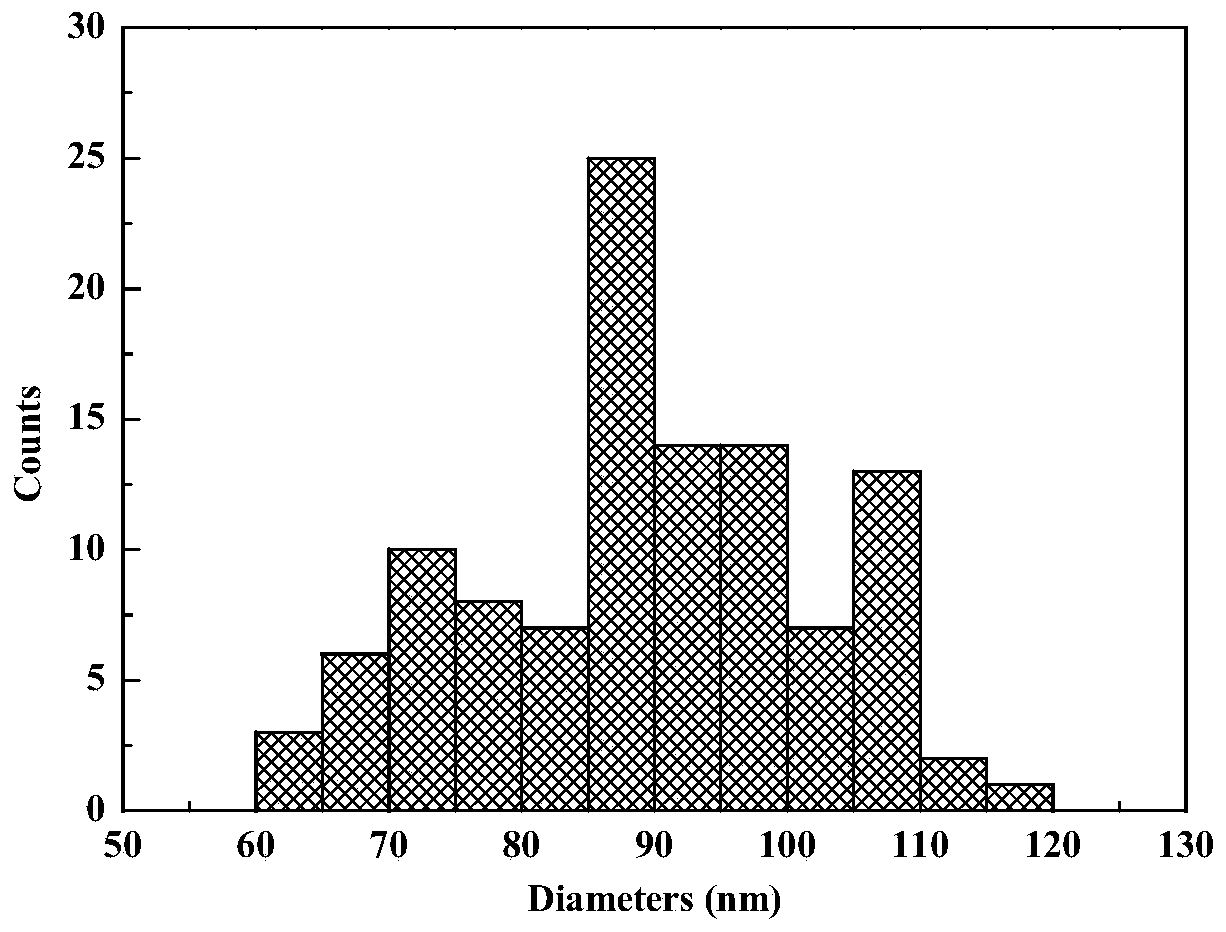
[0068] The zirconia continuous fiber was quickly entered into the high temperature zone of 1300°C, the residence time in the high temperature zone was 2s, and the tension was 50cN, and then the fiber was directly placed at room temperature to cool. The measured tensile strength of monofilament fiber is about 1.5GPa. SEM photos as figure 2 As shown, the grain distribution diagram is shown in image 3 shown. Depend on figure 2 , 3 It can be seen that after the treatment of this embodiment, the fibers are dense and uniform, and the fiber grain size is small, mainly distributed in the range of 80-100 nm.
[0069] The zirconia continuous fibers cooled to room temperature are wound in an orderly manner, the winding line speed is controlled to be 1000mm / min, the tension is 150cN, and the fiber rolls are orderly and have a certain degree of bulkiness.
Embodiment 2
[0071] As described in Example 1, the difference is that the continuous zirconia fiber enters the high temperature zone at 1400°C quickly, the residence time in the high temperature zone is 10s, the tension is 100cN, and then the fiber is directly placed at room temperature to cool. The measured tensile strength of the monofilament fiber is about 2.0GPa, up to 3.0GPa.
[0072] The zirconia continuous fibers cooled to room temperature are wound in an orderly manner, the winding line speed is controlled to 2000mm / min, the tension is 250cN, and the fiber rolls are orderly and tightly arranged.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com