Preparation method of thin film on substrate
A technology of substrate and thin film, which is applied in the field of thin film preparation on substrate, can solve problems such as difficult to achieve high-quality single crystal thin film preparation, fragmentation, wafer debonding, etc., to improve film quality and yield, reduce dosage, The effect of reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
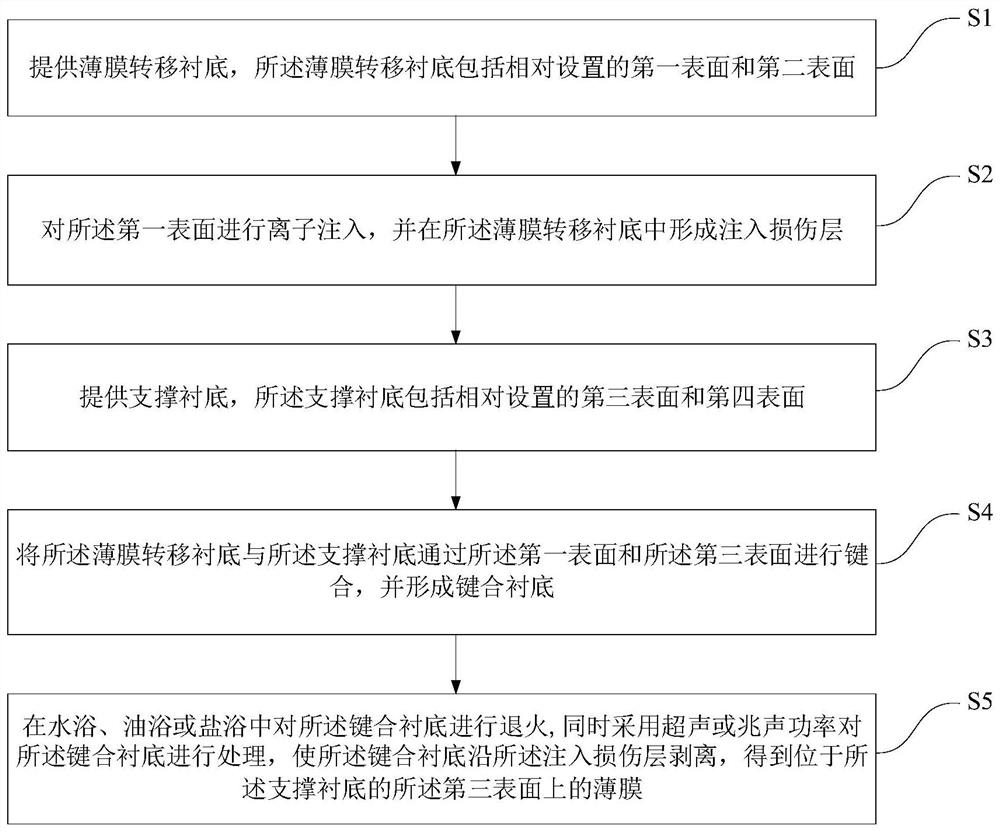
[0054] see Figure 1 to Figure 9 , the present embodiment provides a method for preparing a thin film on a substrate, comprising the following steps:
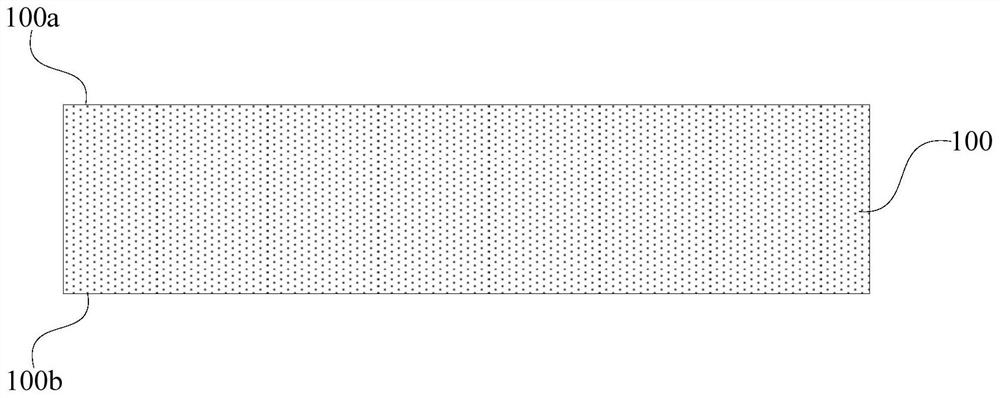
[0055] 1) providing a thin film transfer substrate, the thin film transfer substrate includes a first surface and a second surface oppositely arranged;
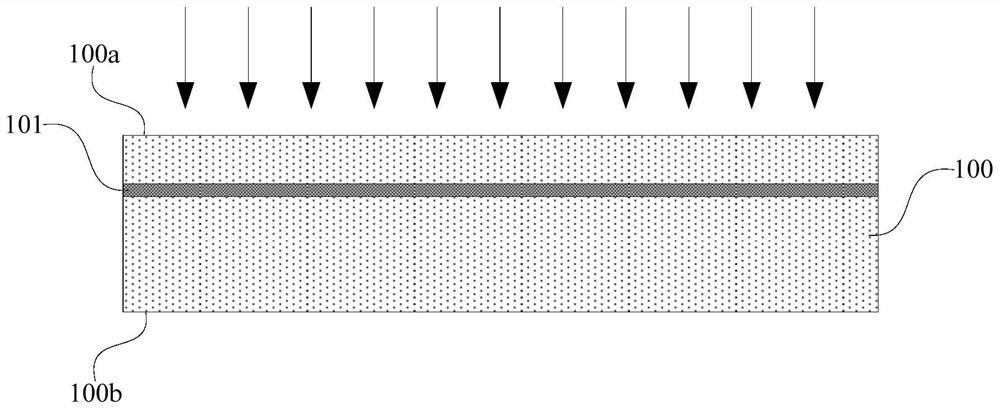
[0056] 2) performing ion implantation on the first surface, and forming an implantation damage layer in the thin film transfer substrate;
[0057] 3) providing a supporting substrate, the supporting substrate includes a third surface and a fourth surface oppositely arranged;
[0058] 4) bonding the film transfer substrate and the support substrate via the first surface and the third surface to form a bonded substrate;
[0059] 5) annealing the bonded substrates in a water bath, an oil bath or a salt bath, and simultaneously using ultrasonic or megasonic power to treat the bonded substrates so that the bonded substrates are damaged along the implanted The layers are peeled o...
Embodiment 2
[0078] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a thin film on a substrate. Compared with Embodiment 1, the difference of this embodiment is that the process of annealing the bonded substrate in the annealing medium includes oil The bonded substrates were annealed in a bath.
[0079] As an example, when the bonded substrates are annealed in an oil bath, the annealing medium includes at least one of high-temperature silicone oil, a mixture of glycerin and dibutyl phthalate, or polyethylene glycol, so The heating rate of the annealing is between 0.5° C. / min and 10° C. / min. Compared with Example 1, this example adopts a water-bath annealing process in which high-temperature silicone oil, a mixture of glycerin and dibutyl phthalate, or polyethylene glycol and other oil bath media are used instead of deionized water. Both the oil bath and the water bath are liquid annealing media, and the annealing media can be selected according to the annealing temperature or the material...
Embodiment 3
[0082] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a thin film on a substrate. Compared with Embodiment 1, the difference of this embodiment is that the process of annealing the bonded substrate in the annealing medium includes salt The bonded substrates were annealed in a bath.
[0083] As an example, when the bonded substrate is annealed in a salt bath, the annealing medium includes sodium chloride, potassium chloride, barium chloride, sodium cyanide, potassium cyanide, sodium nitrate or potassium nitrate At least one, the heating rate of the annealing is between 0.5°C / min and 10°C / min. Compared with the water bath or oil bath provided in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2, a salt bath is used as an annealing medium in this embodiment, which provides a more comprehensive solution for the annealing temperature used in the present invention or the material composition of the bonded substrate. Wide range of options. According to the selection of different salt bath media, the h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com