Process of crudely extracting SBTI proteins by taking soybean whey as raw material based on soybean deep processing waste liquid
A technology of clear water and protein, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of resource waste, environmental pollution, failure to achieve resource reuse and environmental protection purposes, and achieve the effect of reducing microbial load, reducing relative proportion, and increasing protein concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
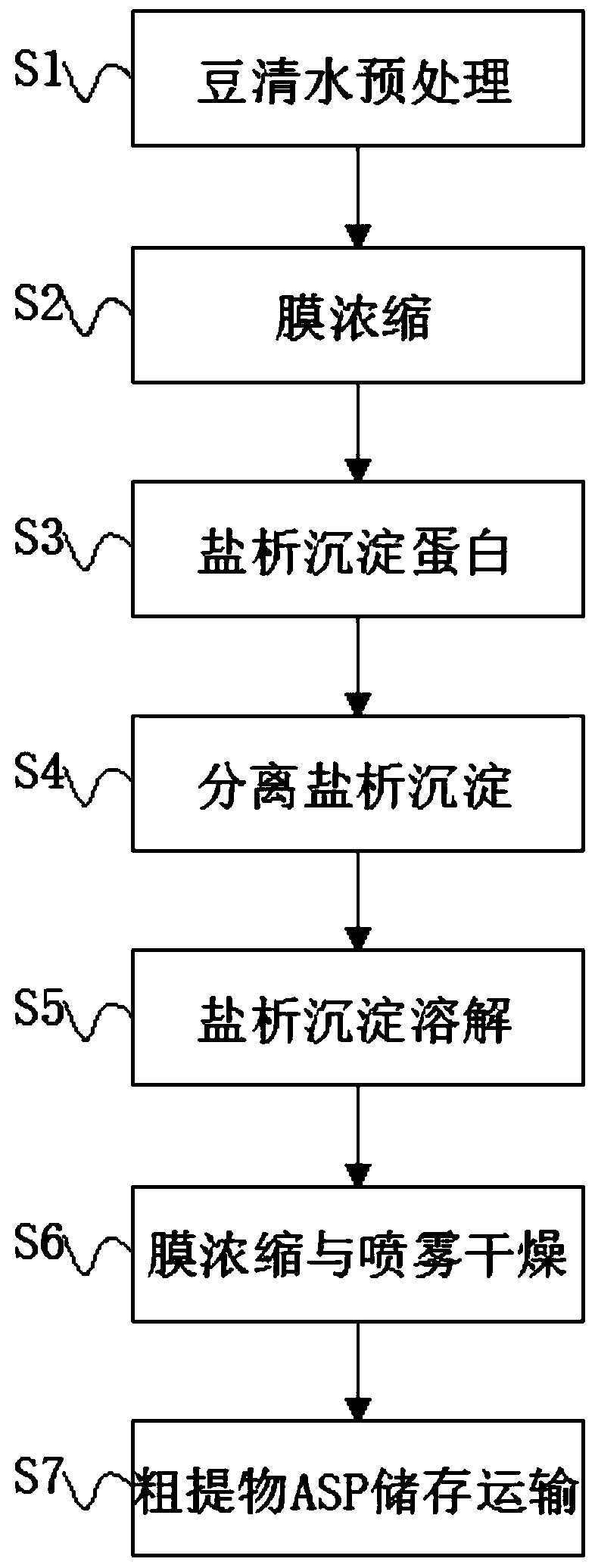
[0027] S1. Soy water pretreatment: Fresh bean water is rich in sources, with a pH of about 4.5 and a temperature of about 40°C. Because it contains a large number of microorganisms, and contains sugars, proteins, and inorganic salts, if it is not treated in time, it will soon become rancid . Therefore, after the soy clear water is received, it must be pretreated immediately. First, the residual insoluble matter in the soy clear water is removed by physical means to obtain clear pretreated soy clear water. The microbial load has been significantly reduced; for the smooth operation of the subsequent process, it is very necessary to ensure the quality of the crude extract. The physical means to remove insolubles in soy water are disc centrifuge clarification, 1 micron filter bag filtration clarification and 250kDa hollow fiber membrane method Combined process method of filtration and clarification;
[0028] S2. Membrane concentration: use ultrafiltration membrane to concentrate,...
Embodiment 2
[0035] S1. Soy water pretreatment: Fresh bean water is rich in sources, with a pH of about 4.5 and a temperature of about 40°C. Because it contains a large number of microorganisms, and contains sugars, proteins, and inorganic salts, if it is not treated in time, it will soon become rancid . Therefore, after the soy clear water is received, it must be pretreated immediately. First, the residual insoluble matter in the soy clear water is removed by physical means to obtain clear pretreated soy clear water. The microbial load is significantly reduced; for the smooth operation of the subsequent process, it is very necessary to ensure the quality of the crude extract, and the physical means to remove the insoluble matter in the soy water is the clarification process of the disc centrifuge;
[0036] S2. Membrane concentration: use ultrafiltration membrane to concentrate, moderately increase protein concentration, reduce the relative proportion of oligosaccharides, and the molecular...
Embodiment 3
[0043] S1. Soy water pretreatment: Fresh bean water is rich in sources, with a pH of about 4.5 and a temperature of about 40°C. Because it contains a large number of microorganisms, and contains sugars, proteins, and inorganic salts, if it is not treated in time, it will soon become rancid . Therefore, after the soy clear water is received, it must be pretreated immediately. First, the residual insoluble matter in the soy clear water is removed by physical means to obtain clear pretreated soy clear water. The microbial load is significantly reduced; for the smooth operation of the subsequent process, it is very necessary to ensure the quality of the crude extract. The physical means to remove insoluble matter in soybean water is the 1 micron filter bag filtration clarification process;
[0044] S2. Membrane concentration: use ultrafiltration membrane to concentrate, moderately increase protein concentration, reduce the relative proportion of oligosaccharides, and the molecular...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com