Method for adsorbing polystyrene microplastics in water by adopting three-dimensional graphene
A technology of polystyrene and graphene, which is applied in the field of water pollution treatment and can solve problems such as reducing the adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] 1g of graphite powder was added to 23mL of concentrated sulfuric acid (98%), and stirred continuously in an ice-water bath until the two were fully mixed. Under the condition of ice-water bath, slowly add 3g of potassium permanganate (0.3g / min) under the condition of stirring, keep stirring for 30min until completely dissolved, and let it stand for 48h after cooling to room temperature. Subsequently, slowly add 186ml of high-purity water to the above mixture, after stirring evenly, wait for the solution to drop to room temperature, then add 10mL of H 2 o 2 (mass fraction is 30%) and constantly stirs, finally obtains the golden yellow solution, and there are golden flakes in the solution. After the solution is cooled for a period of time, under the condition of 2000r / min, it is centrifuged for 15min each time, the precipitate is retained and washed 3 times with 5% hydrochloric acid, and then washed 6 times with high-purity water until the supernatant is close to neutral...
Embodiment 2
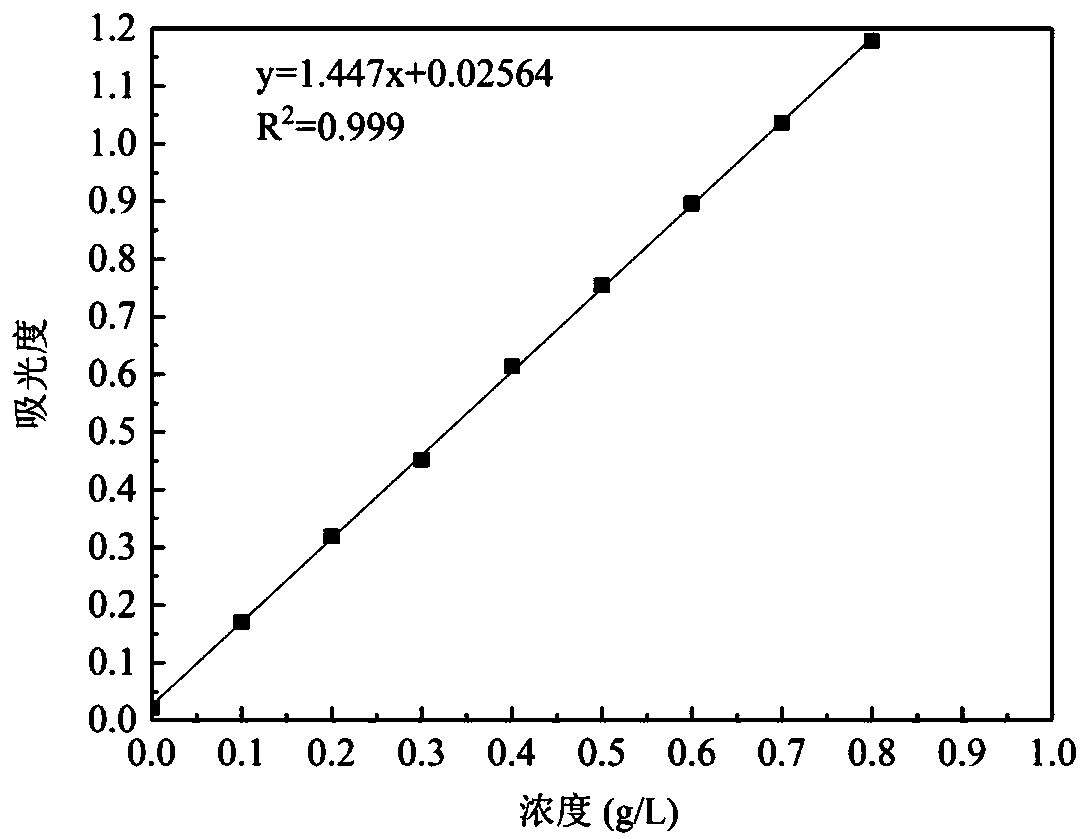
[0034] The original microplastic solution (250mg / ml) was ultrasonically dispersed for 15 minutes to ensure that the microplastics were evenly dispersed in the solution. The microplastic solutions used in this experiment were all diluted from the original solution of microplastics. Take a certain amount of the original solution, add a certain amount of ethanol and distilled water (1:1) to dilute, and prepare a series of microplastic solutions with concentrations of 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, and 0.8 g / L. Ultrasonic disperse the prepared solution for 10 minutes to ensure that the microplastics are evenly dispersed in the solution. The uniformly dispersed microplastic solution was scanned at full wavelength, and the absorption wavelength of the microplastic solution was determined to be 720nm. Test the absorbance of different concentrations of solutions at a wavelength of 720nm and establish a standard curve to obtain the functional relationship between the concentration...
Embodiment 3
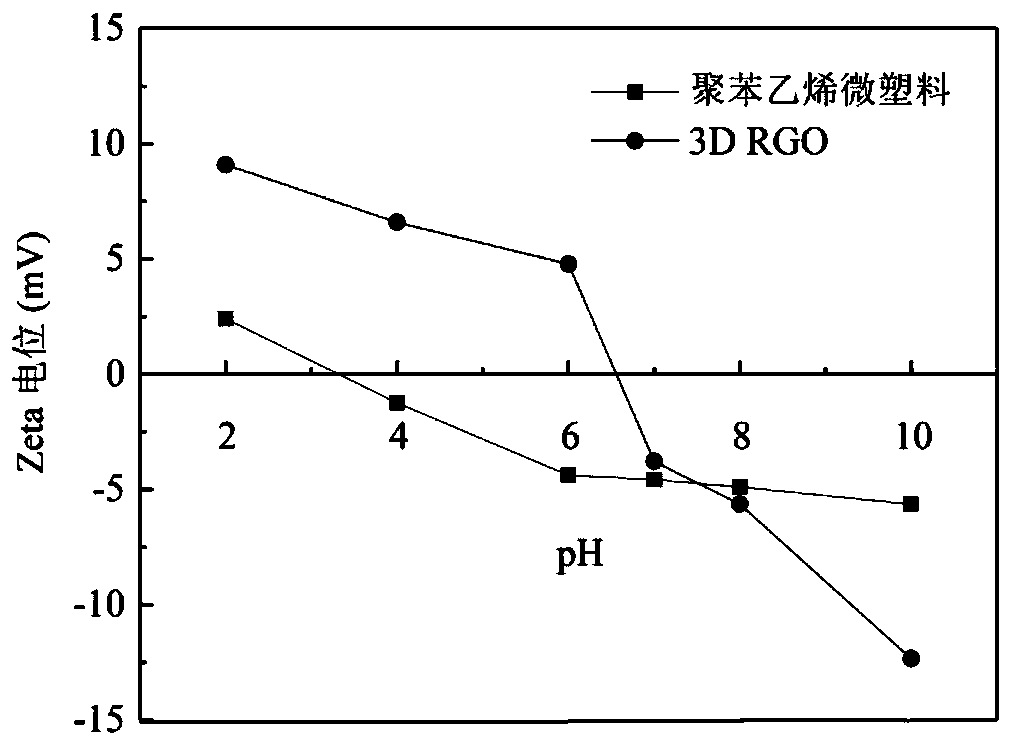
[0039] The pH of the solution was adjusted to pH=2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10 respectively with 1 mol / L HCl or NaOH solution, and a 0.6 g / L microplastic solution was prepared. Then three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide was used for adsorption experiments.
[0040] As the pH value increased, the removal rate of microplastics and the adsorption capacity of RGO both increased first and then decreased. At pH=6, the removal rate of microplastics and the adsorption capacity of RGO reached the highest, which were 66.63% and 522.06 mg / g, respectively. This can be attributed to the difference in electrostatic force between the two at different pHs. Although in an acid-base environment, there is a certain electrostatic repulsion between the two, the removal rate of microplastics is still higher than 55%, the highest adsorption rate The difference with the lowest adsorption rate is also less than 10%, which shows that the removal of polystyrene microplastics with three-dimensional reduced graph...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com