A strain of Escherichia coli engineering bacteria and its whole cell catalytic production method of steviol
A technology that catalyzes stevioside with Escherichia coli, which is applied in the field of bioengineering technology and the biosynthesis of natural compounds to achieve high conversion efficiency, save cumbersome steps, and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
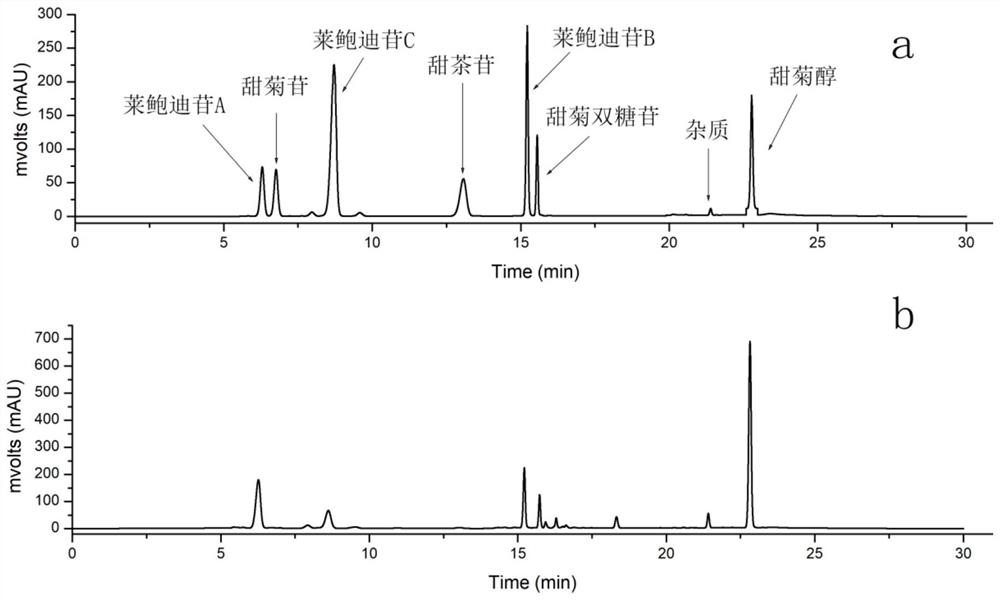
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The β-glucosidase SPBGL1 (accession number WP_029622673.1) with stevioside hydrolysis activity was cloned from Sphingomonas elodea ATCC 3146. According to the report of patent ZL201210387271.8, the target gene sbgl (accession number KC986399) was cloned.
[0033] A strain of Escherichia coli engineering bacteria, its construction method operation steps are as follows:
[0034] (a) Clone the target gene sbgl, design the upstream primer sbgl-F (including NcoI restriction site) and the downstream primer sbgl-R (including EcoRI), and use pUC19-Ebgl1 as a template to amplify the target gene sbgl by PCR. After endonuclease NcoI and EcoRI target gene sbgl, it was ligated with the expression vector pSE380 that had also been digested by NcoI and EcoRI to obtain recombinant plasmid pSE-sbgl, which was transformed into Escherichia coli JM109;
[0035] sbgl-F: 5′-AACA CCATGG ATATGCAGGAAGCCGGTGCCCCGC-3′
[0036] sbgl-R:5′-ATT GAATTC TCAATCCTTCCAGCTACGCGCCGG-3′
[0037] (b) Clo...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Utilize embodiment 1 to construct the method for the co-expressed Escherichia coli engineering bacteria pSE-sbgl-spbgl1 catalyzed stevioside to produce steviol, the operation steps are as follows:
[0042] (1) 20°C, 0.5mM IPTG induced culture for 22 hours obtained in Example 1 co-expressed Escherichia coli engineered bacteria pSE-sbgl-spbgl1, after the fermentation was completed, the bacteria were collected and the wet weight of the bacteria was weighed;
[0043] (2) Wash the 0.1g wet weight thalli 3 times with 0.9% NaCl solution, 2 HPO 4 -resuspended bacteria in citric acid buffer to obtain 0.02g / ml co-expressed Escherichia coli engineering bacteria pSE-sbgl-spbgl1 whole cell catalytic solution; Na 2 HPO 4 - 0.2M Na in citrate buffer 2HPO 4 and 0.1M citric acid, pH 6.0;
[0044] (3) Adding stevioside at a concentration of 50 g / L to the whole-cell catalytic solution of the co-expressed Escherichia coli engineering bacteria pSE-sbgl-spbgl1 obtained in step (2), and ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Utilize embodiment 1 to construct the method for the co-expressed Escherichia coli engineering bacteria pSE-sbgl-spbgl1 catalyzed stevioside to produce steviol, the operation steps are as follows:
[0048] (1) 20°C, 0.5mM IPTG induced culture for 22 hours obtained in Example 1 co-expressed Escherichia coli engineered bacteria pSE-sbgl-spbgl1, after the fermentation was completed, the bacteria were collected and the wet weight of the bacteria was weighed;
[0049] (2) Wash the 0.1g wet weight thalli 3 times with 0.9% NaCl solution, 2 HPO 4 -resuspended bacteria in citric acid buffer to obtain 0.02g / mL co-expressed Escherichia coli engineering bacteria pSE-sbgl-spbgl1 whole cell catalytic solution; Na 2 HPO 4 - 0.2M Na in citrate buffer 2 HPO 4 and 0.1M citric acid, pH 5.5;
[0050] (3) Adding stevioside at a concentration of 100 g / L to the whole-cell catalytic solution of the co-expressed Escherichia coli engineering bacteria pSE-sbgl-spbgl1 obtained in step (2), an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com