Method for producing a semiconductor or conductir material, and use thereof
A conductor material, semiconductor technology, applied in nano-carbon, graphene, electrolytic components and other directions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
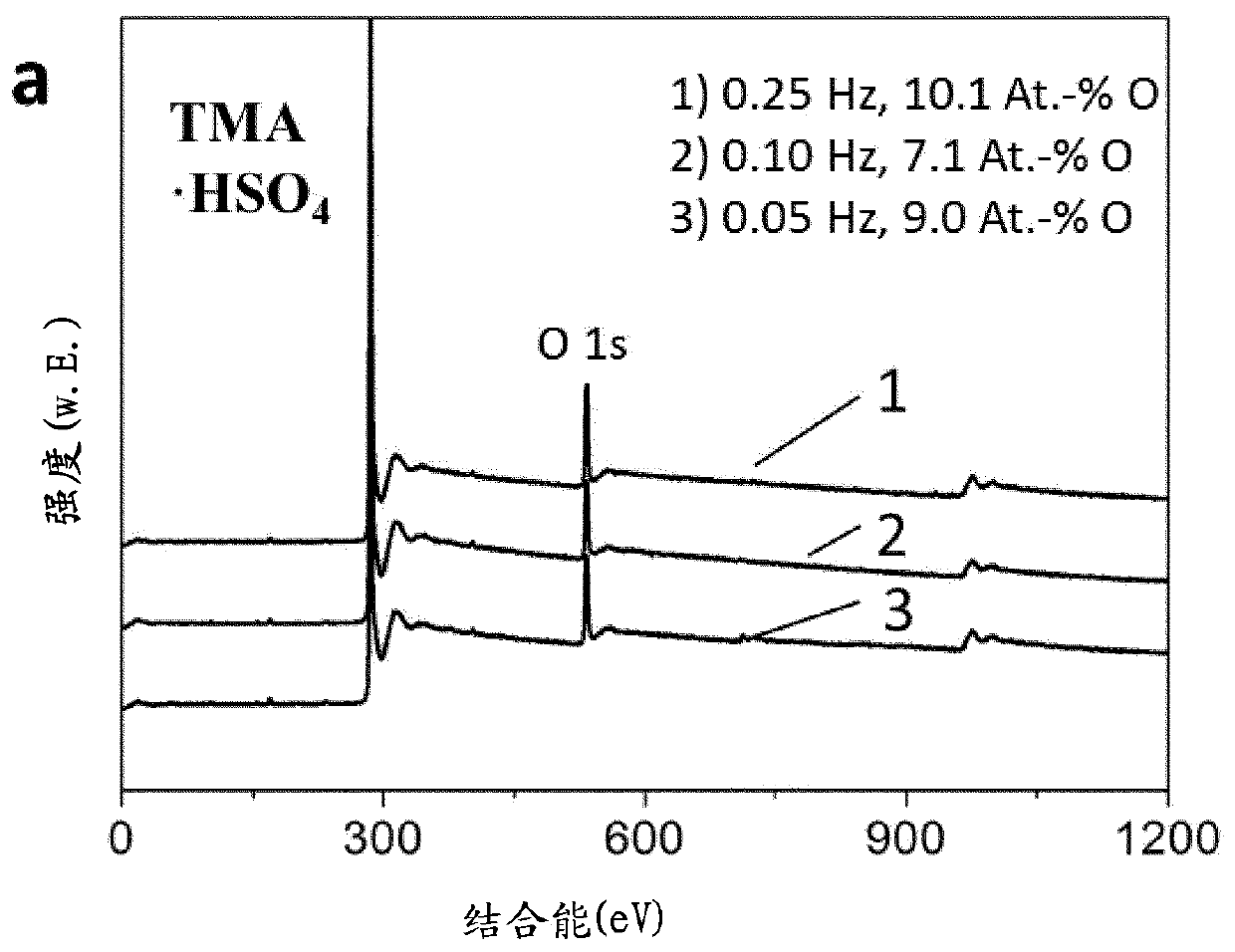
[0100] Graphene exfoliation was performed with an electrode pair consisting of two graphite foils (1.5*5 cm, 100 mg each foil) (Alfa Aesar).
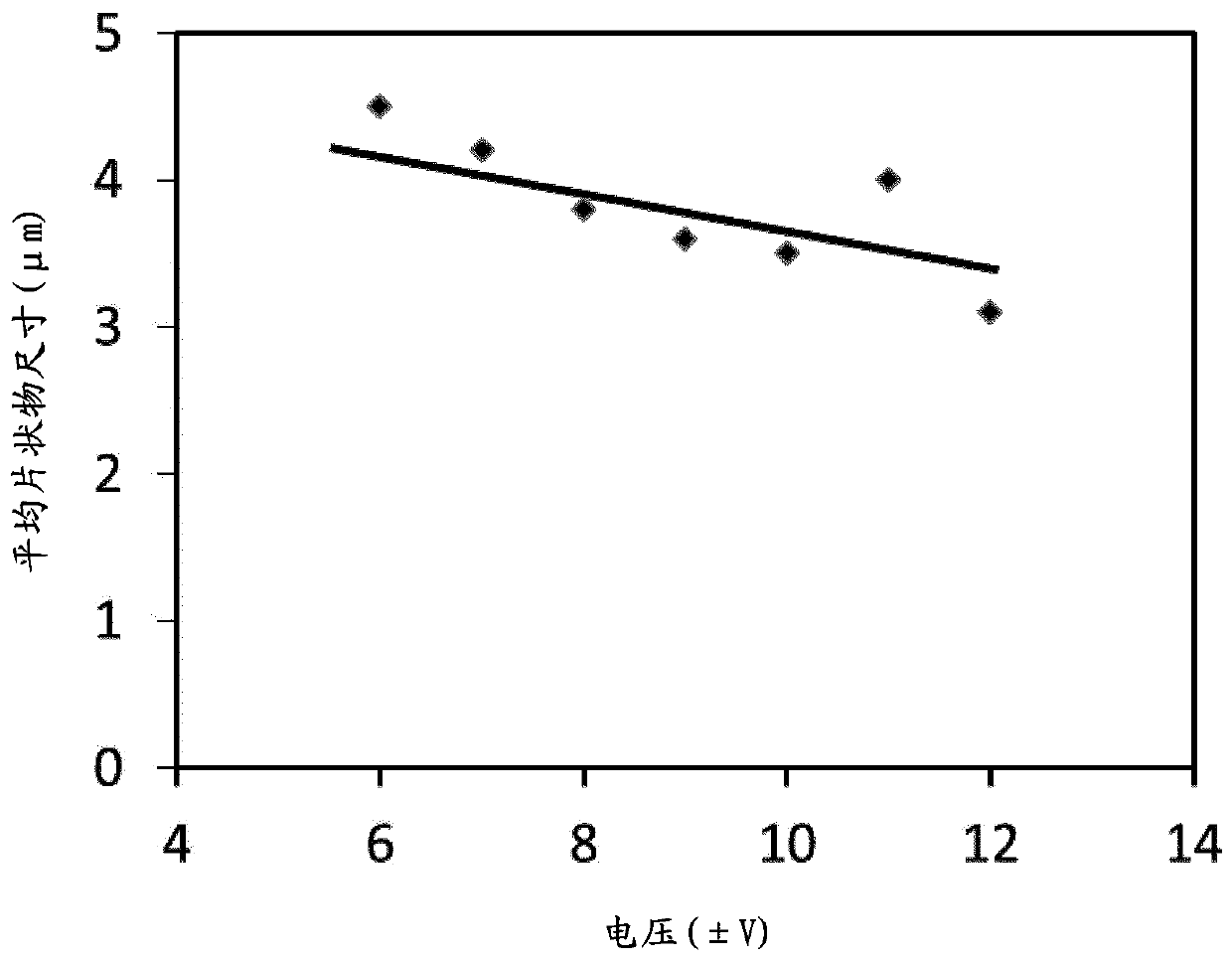
[0101] The electrodes of the electrode pair were arranged in parallel at a fixed distance of 1.5 cm. An electrolyte solution was prepared by dissolving tetrabutylammonium bisulfate powder in deionized water (0.1 M, 1.7 g of salt in 50 ml of water). The pH of the electrolyte solution was adjusted to 7 with NaOH. An alternating current with an operating voltage of + / −10 V and a frequency of 0.1 Hz was applied in order to dissociate the graphene layer. The orientation of the anode operating voltage was changed every 5 s from positive to negative and vice versa. To prevent overheating of the electrolytic cell, it was cooled in an ice bath throughout the exfoliation process.
[0102]The graphene suspended in the electrolyte solution was separated off by means of a 0.2 μm PTFE membrane filter and washed three times with water and three tim...
Embodiment 2
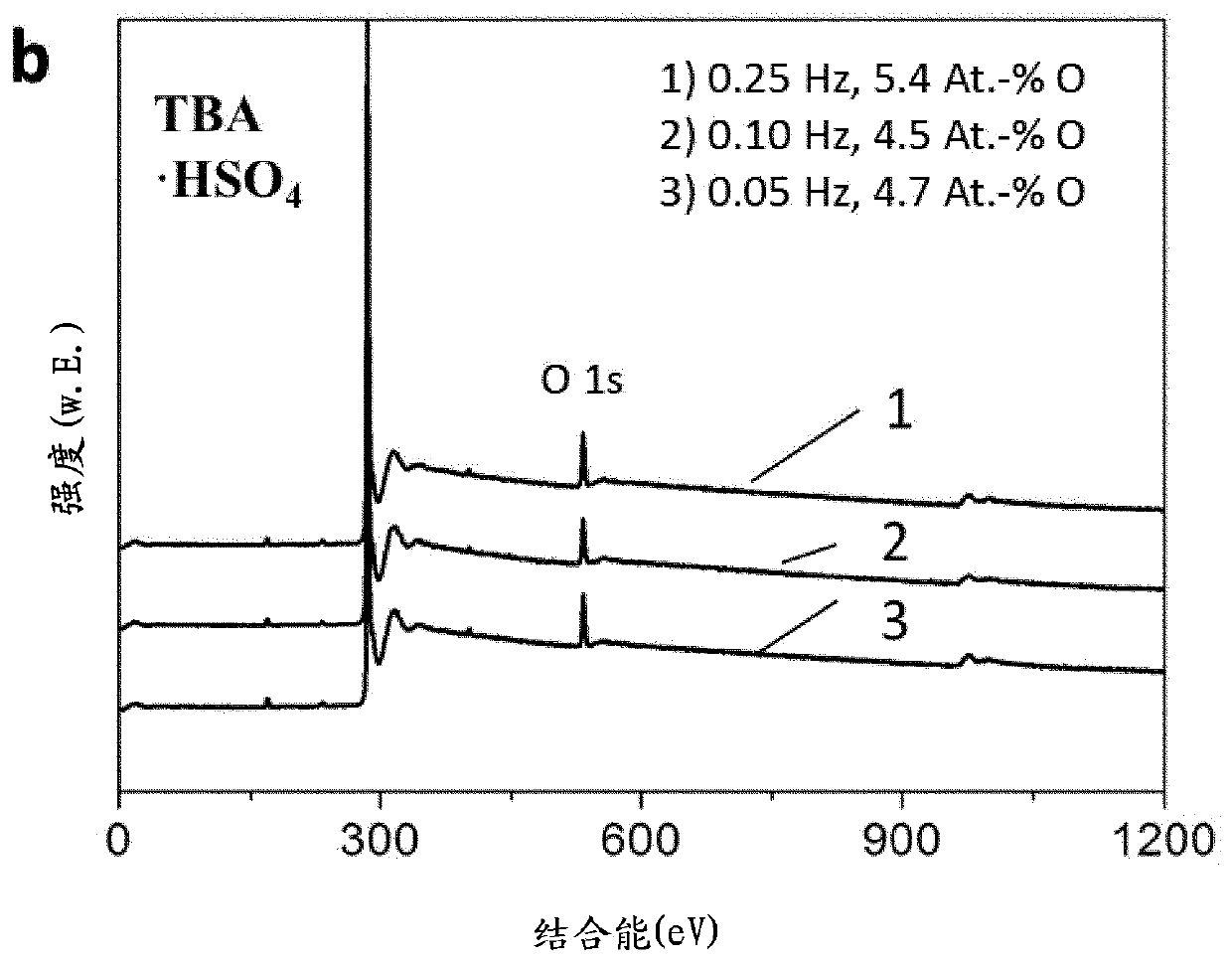
[0105] In order to prepare graphene on a larger scale, five electrode pairs formed of graphite foils (6*12 cm, 1.02 g each foil) were connected in series with a distance of 2 cm between each electrode pair.
[0106] Electrolysis was performed under the same conditions as detailed in Example 1. However, 1000 ml of electrolyte solution (34 g tetrabutylammonium bisulfate in 1000 ml deionized water) with a concentration of 0.1 M was used. The stripping ends automatically when the graphite material has been consumed.
[0107] The graphene suspended in the electrolyte solution was separated off by means of a 0.2 μm PTFE membrane filter and washed three times with water and three times with ethanol in order to remove electrolyte residues. 5.5 g of graphene was produced in 15 min.
[0108] The graphene powder is subsequently dispersed in N,N-dimethylformamide in an ultrasonic bath and can be stored or further used as such. To this end, 120 mg of graphene were dispersed in 1 L of DM...
Embodiment 3
[0130] To illustrate the potential of graphene prepared according to the present invention for use in battery applications, a commercially available cathode material (LiFePO4 powder, 20 mg, particle size 4 The (EG-LFP) particles were filtered off and dried in an oven at 100°C overnight.
[0131] The EG-LFP working electrode was prepared by mixing EG-LFP, activated carbon (super-P), and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) at a mass ratio of 80:10:10. The mixture was applied to aluminum foil, dried and punched out into circular cells (Zellen) with a diameter of 10 mm. It was dried under vacuum at 80° C. for 12 hours.
[0132] A coin cell of type CR 2032 was assembled under an inert atmosphere with lithium foil (Sigma Aldrich) as the counter electrode and polypropylene as the separator. The electrolyte was prepared from 1 M LiPF6 in ethylene carbonate / diethyl carbonate (3:7 v / v with 2m% ethylene carbonate) and used to fill the battery. Load the EG-LFP working electrode.
[0133] Al...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com