Method for purification of albumin
A technology for albumin and total protein, applied in the field of purifying albumin, which can solve the problems of aggregate pollution and protein yield reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0108] Material
[0109] Starting solution: plasma, partially fractionated plasma (eg plasma depleted of IgG using Cohnfractionation or expanded bed adsorption chromatography).
[0110] NaCP: sodium octanoate, 0.6M stock solution, pH 7.5; Acid: 0.5M-1M stock solution; P300: P300 filter aid; P1000: P1000 filter aid; NaOH: 1M stock solution; Water: WFI; pH meter: Mettler Toledo; Depth filter: Pall K700 depth filter; and fiberglass filter: Pall (10 μm).
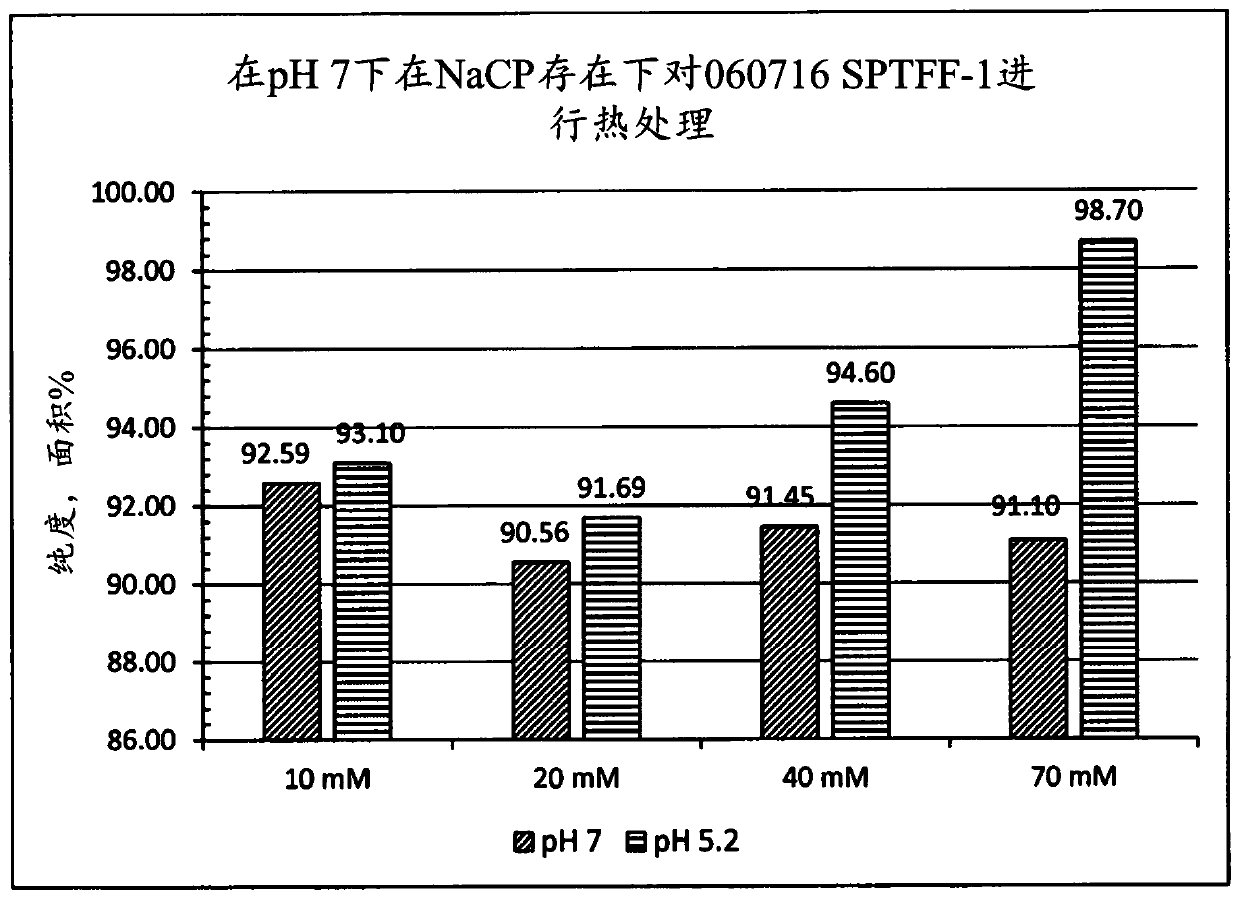
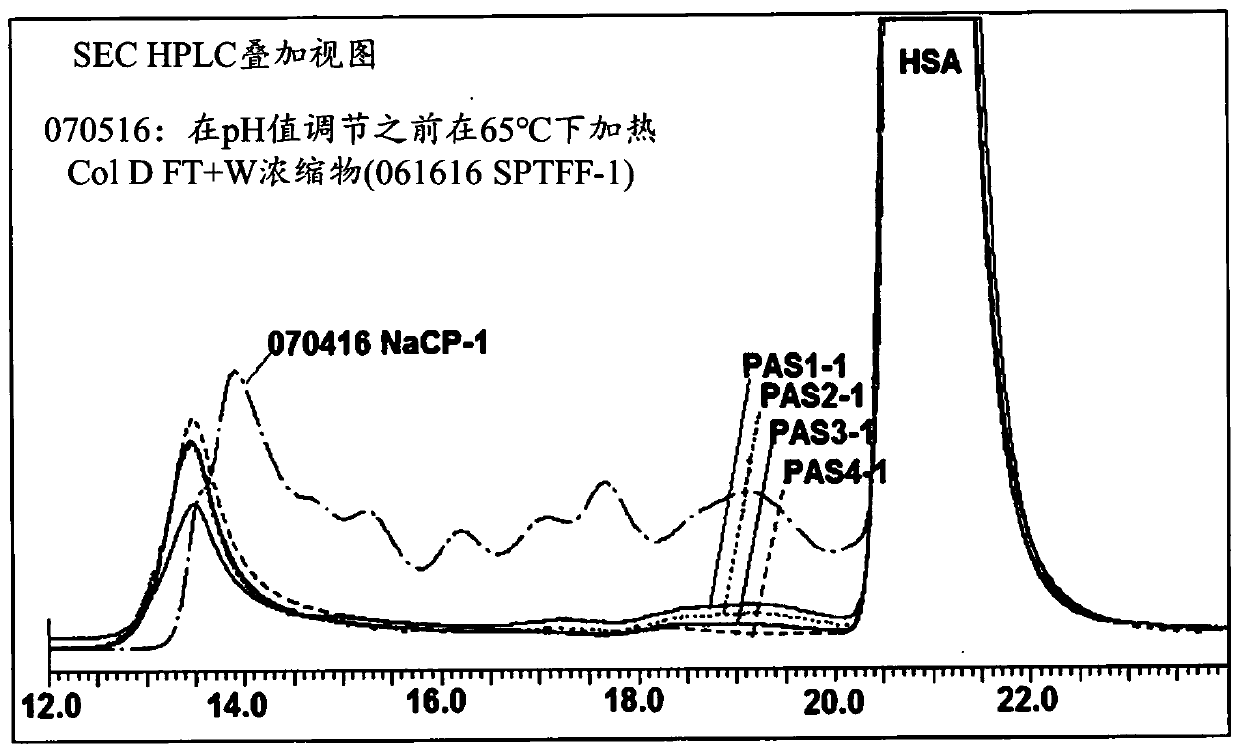
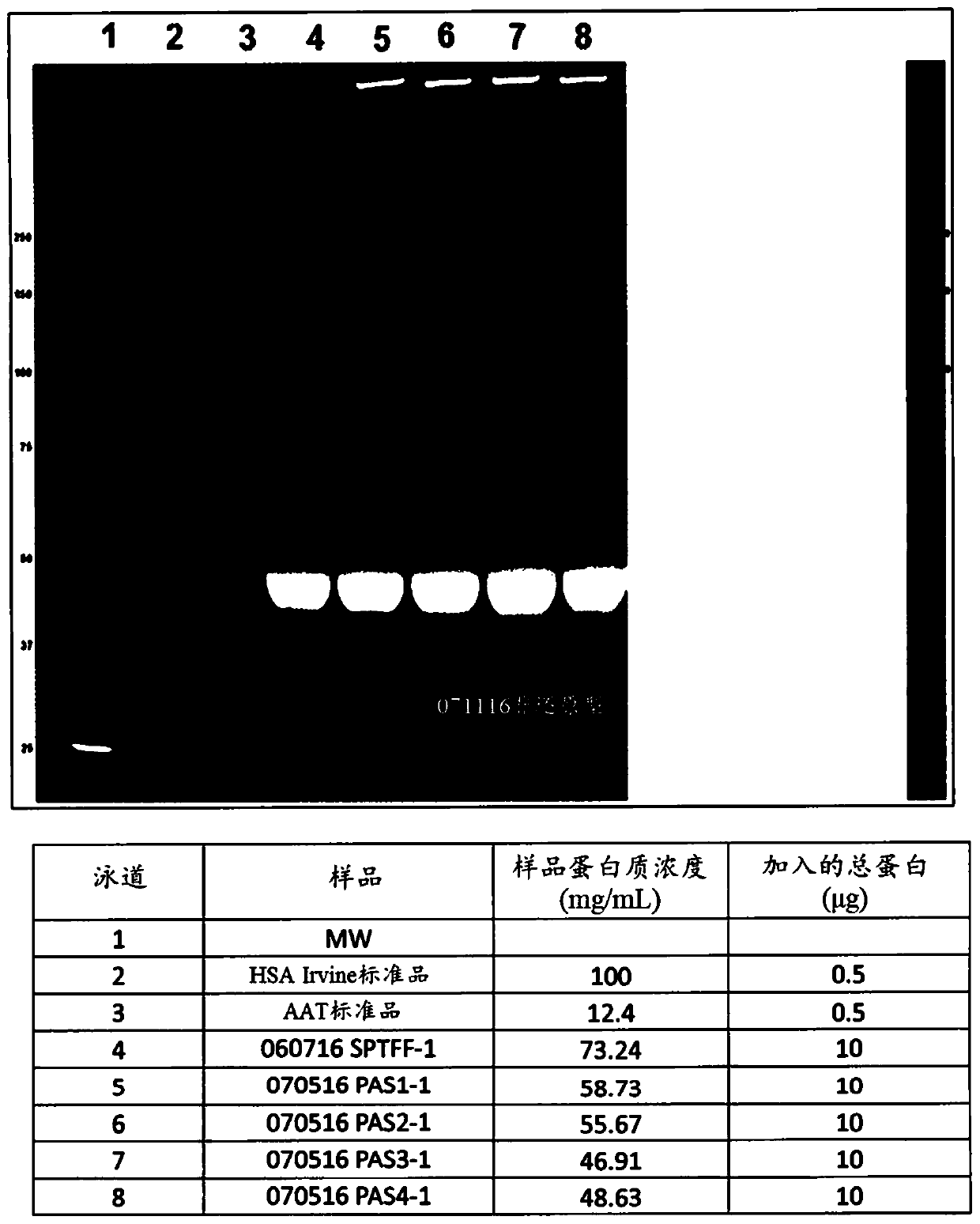
[0111] Pasteurization of column D FT+W concentrate in the presence of NaCP
[0112] The column D FT+W concentrated solution was mixed with NaCP, adjusted to pH 7, and then heated at 60°C. The heated solution was cooled to room temperature and then adjusted to pH 5.2 using citric acid.
[0113] The total protein concentration (060716 SPTFF-2) was assumed to be about 1.1 mM. The total protein concentration was estimated by using the molecular weight of albumin (66,500 Da), because by SEC HPLC, the proportion of album...
Embodiment 2
[0127] Pasteurization of column D FT+W concentrate in the presence of NaCP - increasing NaCP concentration and variable bar Sterilization time
[0128] Three different concentrations of NaCP were used such that the final concentration of NaCP in the solution before pH adjustment was 50 mM, 70 mM and 90 mM. The solution was then adjusted to pH 7, followed by pasteurization at 60°C-65°C. Pasteurization at 50 mM and 90 mM NaCP was continued for 4 hours, followed by pH adjustment using citric acid. The 70 mM NaCP condition was aliquoted at 0.5, 1, 2 and 4 hours prior to pH adjustment.
[0129] The total protein concentration (060716SPTFF-2) was assumed to be about 1.1 mM. The NaCP / total protein ratios were 45.5, 63.6 and 81.8 for 50 mM, 70 mM and 90 mM NaCP, respectively. Sample preparation is summarized in Tables 5 and 6. The results of the experiments are expressed as HSA purity based on SEC HPLC analysis (Table 7 and Figure 4 and Figure 5 ). Table 7 shows that inco...
Embodiment 3
[0139] Ratio of NaCP to total protein – three NaCP concentrations to a fixed total protein concentration
[0140] Three different concentrations of NaCP were used such that the final concentration of NaCP in the solution before pH adjustment was 70 mM, 90 mM and 110 mM. The solution was then adjusted to pH 7, followed by pasteurization at 60°C-65°C. Aliquots were taken at 3 hours and 6 hours and the pH was adjusted to 5.2 using citric acid. Prior to centrifugation, the pH adjusted samples were mixed with P-1000 filter aid (0.7% final concentration).
[0141] The total protein concentration (071316SPTFF-2) was assumed to be about 1.8 mM. The NaCP / total protein ratios were 39, 50 and 61 for 70 mM, 90 mM and 110 mM NaCP, respectively. Sample preparation is summarized in Table 8 and Table 9. The results of the experiments are expressed as HSA purity based on SEC HPLC analysis (Table 10 and Figure 7 and Figure 8 ). As shown in Table 9 (see also Figure 7 Results in ), P...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com