A nanocomposite material based on CE-based amorphous alloy, its preparation method and its application in the treatment of dye wastewater
A technology of nanocomposite materials and amorphous alloys, applied in nanocomposite materials based on Ce-based amorphous alloys and its preparation, and in the application field of dye wastewater treatment, which can solve the problems of unclear reaction mechanism and low TOC removal rate, etc. Achieve the effect of good dispersion, simple reaction method and high decolorization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
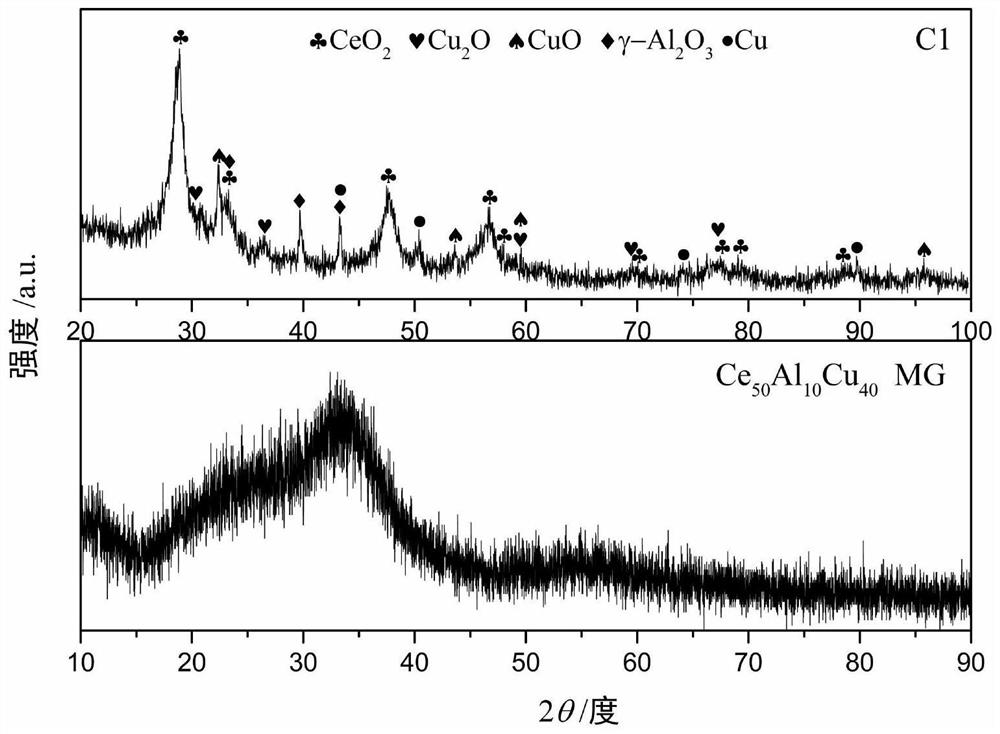
[0032] Embodiment 1, based on Ce 50 Al 10 Cu 40 Nanocomposites of Amorphous Alloys
[0033]In this example, Ce 50 Al 10 Cu 40 Amorphous alloy strips are used as raw materials to prepare nanocomposites. The specific steps are as follows:
[0034] (1) At room temperature, weigh about 0.4g of Ce 50 Al 10 Cu 40 Place the amorphous alloy strip in a container, then add 20mL of dilute HCl (1M), and react until no bubbles emerge (black CuO is generated in this step);
[0035] (2) Under the condition of magnetic stirring at 200rpm, add 1.5M NaOH solution dropwise to the container until the pH is 8.5 to form a suspension;
[0036] (3) Transfer the suspension into a 50mL reaction kettle lined with polytetrafluoroethylene, and keep it warm at 100°C for 12 hours; after the reaction is completed, cool it down to room temperature naturally, centrifuge the product at 15,000 rpm for 5 minutes, and wash the precipitate with water and alcohol respectively. 4 times each, and dried at 60...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2, the contrast of nanocomposite material obtained by different sedimentation pH
[0047] The present embodiment presses the same method of embodiment 1, with Ce 50 Al 10 Cu 40 Amorphous alloy strips are used as raw materials to prepare nanocomposites, the only difference being that in step (2), the pH adjusted by adding NaOH solution is different.
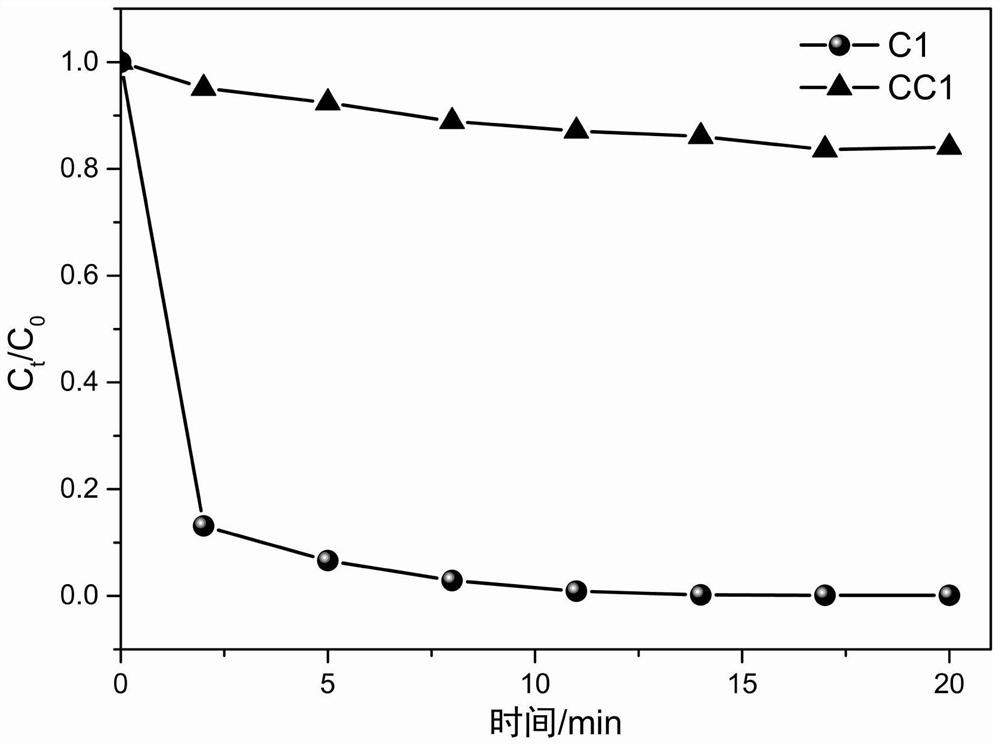
[0048] The nanocomposites obtained under different sedimentation pH conditions were used to degrade Orange II in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0049] Figure 5 It is the curve graph of the nanocomposite degradation orange II obtained under different sedimentation pH conditions, Image 6 The fitted reaction kinetic curve (ln(C 0 / C t )=kt) graph. from Figure 5 with Image 6 Visible, decolorization rate and reaction kinetics constant k change less obviously in the scope of pH8.0-10.5 (the decolorization rate after 2 minutes has good linear relationship with reaction kinetics k, therefore, the present...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3, the contrast of nanocomposite material obtained by different amorphous alloy raw materials
[0051] In this embodiment, the nanocomposite material is prepared according to the same method as in Example 1, the only difference is that the raw materials used are respectively changed to Ce 60 Al 10 Cu 30 、Ce 70 Al 10 Cu 20 、Ce 70 Cu 30 The amorphous alloy strips and the corresponding obtained nanocomposites are marked as C2, C3, and C4, respectively.
[0052] By the same method as in Example 1, each sample was used to degrade Orange II. Figure 7 It is the graph of the degradation of Orange II for each sample (including C1). It can be seen from the figure that compared with C1, C2 and C3, the decolorization speeds of the three materials are not much different, but by the treatment of Ce 70 Cu 30 The decolorization speed of the product C4 obtained by MG to Orange II is obviously not as good as that of the first three, and the decolorization rate in t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| decolorization rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| decolorization rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com