Whole-cell vaccine for inhibiting or preventing melanoma, and preparation method for whole-cell vaccine
A melanoma cell, whole cell vaccine technology, applied in the direction of tumor/cancer cells, genetically modified cells, biochemical equipment and methods, etc. The effect of improving the level and improving the immune killing ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
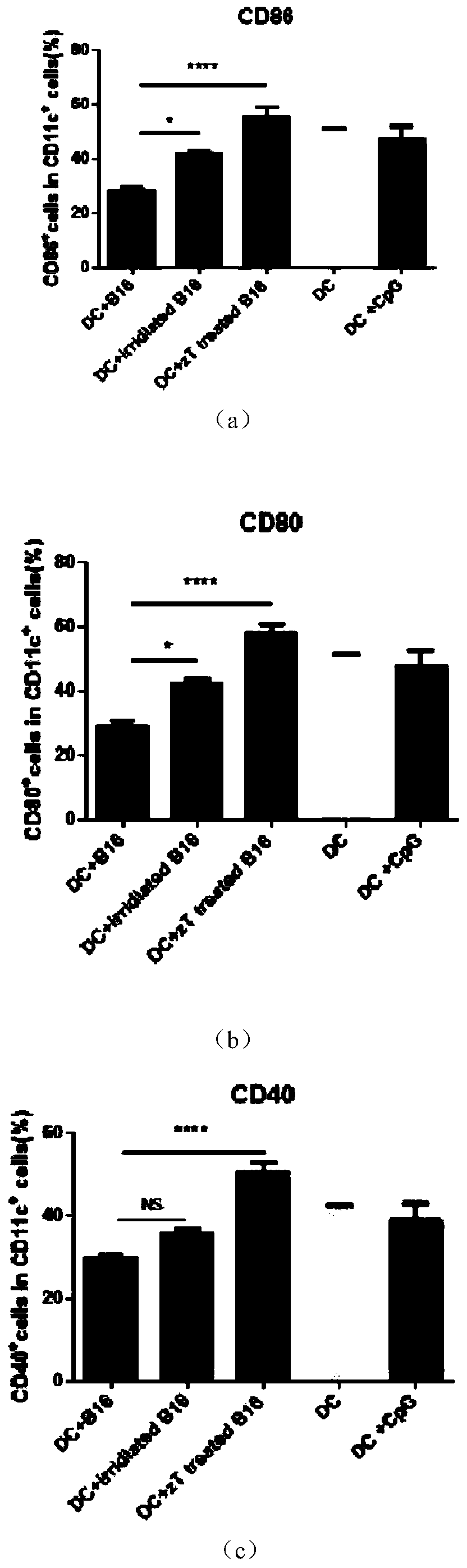
[0024] Embodiment one: see figure 1 , Take the bone marrow cells of C57 / B6J mice and add GM-CSF (10ng / ml) and IL4 (10ng / ml) in vitro, and culture until the 7th day; the tumor cells are first treated with zVAD (20uM) for 2 hours and then treated with TNF-a (100ng / ml) treatment for 24 hours, heated in a 65-degree water bath for 5 minutes; co-cultured 1.25 million DCs with 0.25 million B16 in a 24-well plate, and detected the activated markers CD86, CD80, and CD40 on the surface of DC cells after 24 hours. The control group was DC without co-culture treatment after induction of maturation; DC treated with CPG after 7 days of maturation; DC co-cultured with 50gy irradiated tumor cells; DC, compare the statistical graphs obtained; this graph proves that zVAD and TNF-A treatment of necroptotic tumor cells and co-culture of DCs can significantly improve the activity of DCs presenting tumor antigens.
[0025] Treat B16 cells with zVAD and TNF-A to cause necroptosis; when the necropto...
Embodiment 2
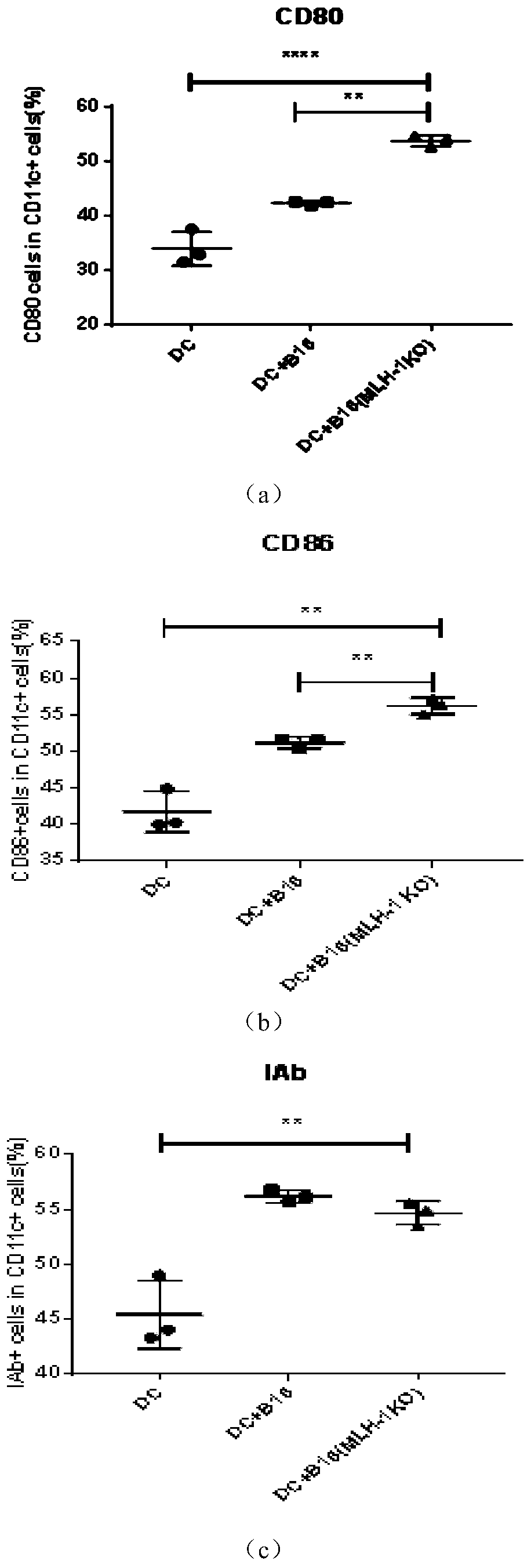
[0026] Embodiment two: see figure 2, using the same method as in Example 1 to treat tumor cells to cause necroptosis, compare normal melanocytes and knock out the MLH-1 gene on the melanoma cells to inactivate DNA damage repair enzymes, and produce a large number of neoantigens Tumor cells were co-cultured with DCs. Before co-culture with DC cells, the treated tumor cells were heated in a 65°C water bath for 5 minutes to determine the complete inactivation of tumor cells. Then culture 1 million DC cells and 0.25 million treated neoantigen tumor cells in a 24-well plate, and detect the expression of markers on the surface of DC cells after 24 hours; the diagram shows that the MLH-1 gene on tumor cells is knocked out, after Attached figure 1 Co-cultivation with DC cells after treatment by the method can significantly improve the activation degree of DC. Moreover, tumor cells expressing knockout MLH-1 but expressing neoantigens have a better ability to increase the degree of ...
Embodiment 3
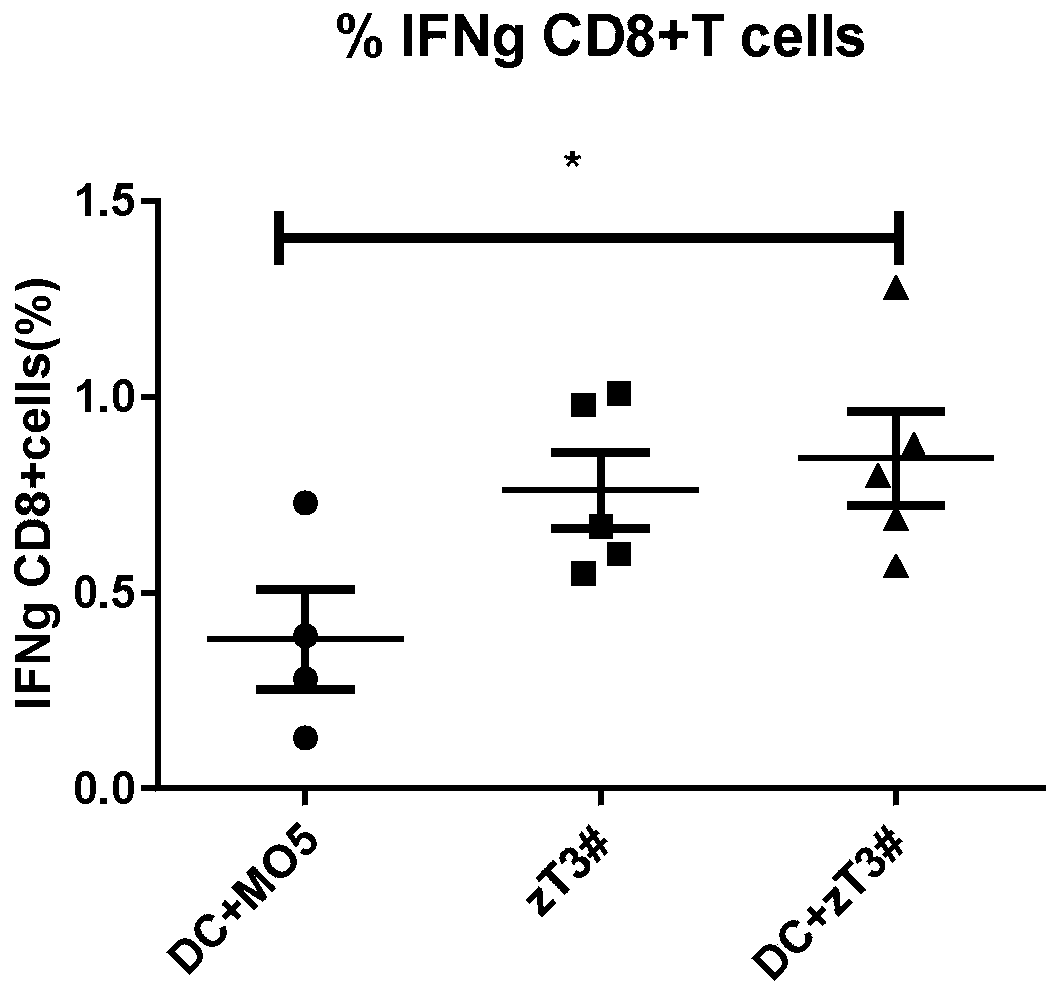
[0027] Embodiment three: see image 3 , the vaccine obtained by co-culturing common tumor cells and DCs described in Example 2 and the vaccine obtained by co-culturing neoantigen cells and DCs were resuspended to 200ul in PBS and injected into mice. One week later, the mouse spleen cells were taken, and the spleen cells were stimulated with the tumor cell lysates of the corresponding components of the two vaccines, and 6 million spleen cells were stimulated with 1 million tumor lysates in a 24-well plate, and cultured in an incubator with 1640 as the medium for 4 Hours later, the ratio of intracellular secreted IFN-g of CD8+T cells was detected. The obtained value is the proportion of specific CD8+ T cells, and the figure shows that the vaccine obtained by co-cultivating neoantigen cells treated with necroptosis and DC is better than the vaccine obtained by co-culturing DC and ordinary tumor cells.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com