Method for promoting decomposition of straws returned to fields by using urea-alkali composite agent
A compound agent and straw technology, applied in the field of straw biomass resource utilization, can solve the problem of slow decomposition of straw returning to the field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
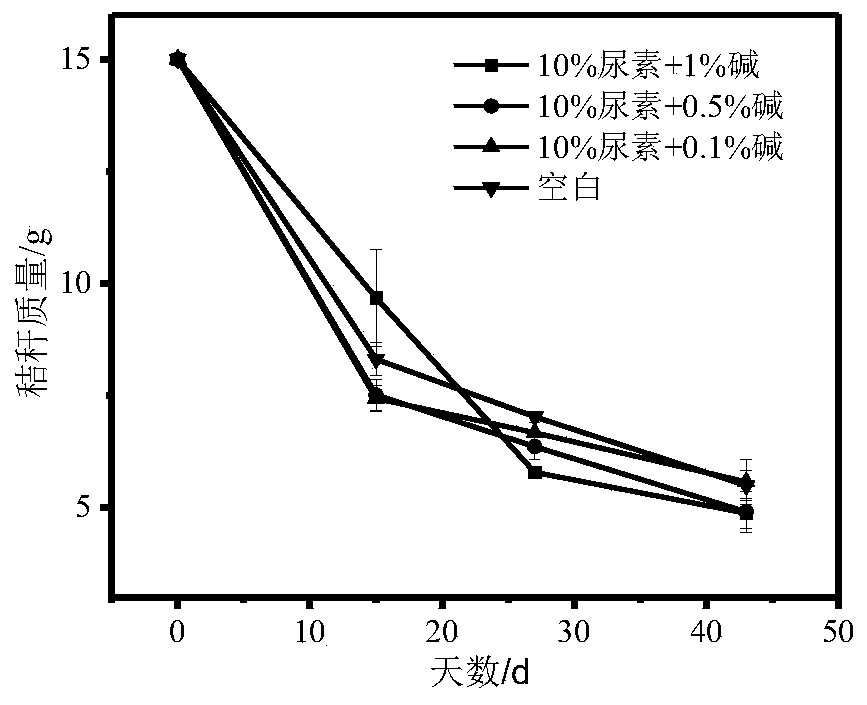
[0018] The promoting effect of embodiment 1 composite agent on the decomposition of stalks
[0019] By configuring different proportions of urea-alkali compound agent solutions, spray them evenly on the surface of straw, put them into nylon mesh belts, pack 15 or 20g of straw in each bag, bury the bags in the farmland soil with a depth of 10-20cm, and manage the rest in the field. Proceed normally; take out the nylon bags according to the set date, take at least 5 bags each time, carefully wash with clean water to remove the soil adhered to the surface of the straw, dry at 60°, seal and store, and measure the quality of the straw. The test results at 43 days showed that different proportions of urea-alkaline compound agents had different degrees of promotion on the decomposition of straw ( figure 1 ). 15 days before the cultivation, the two compound agents of 10% urea + 0.5% alkali and 10% urea + 0.1% alkali (the proportion of straw dosage) had a significant effect on promoti...
Embodiment 2
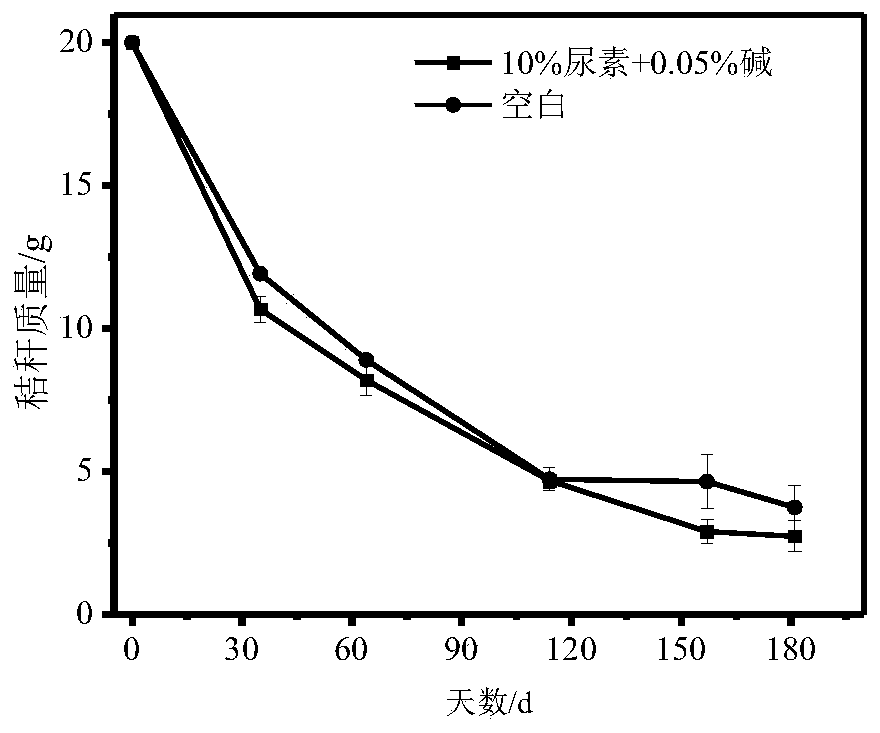
[0020] The impact of embodiment 2 compound medicament on soil pH
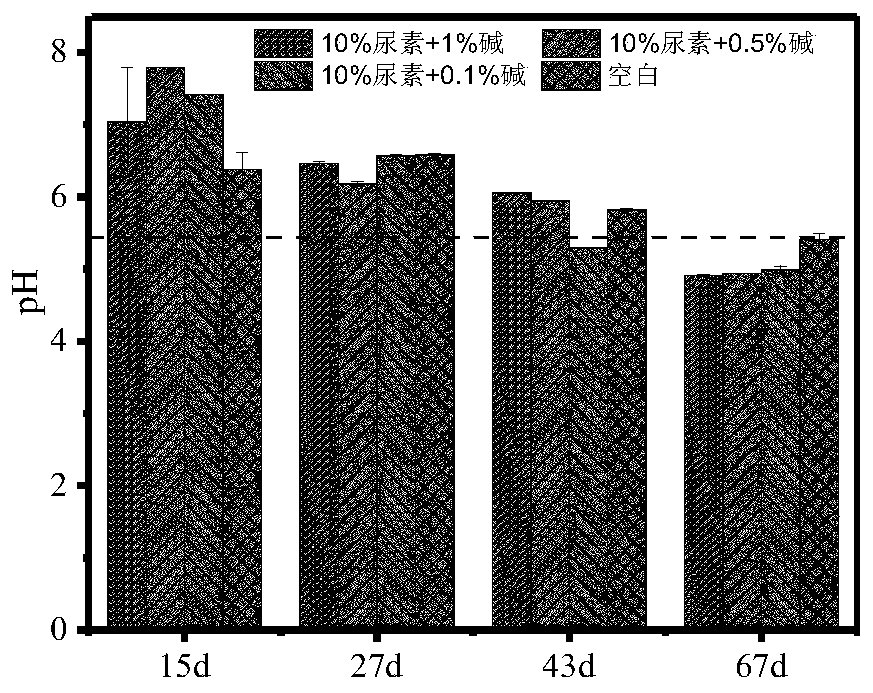
[0021] The straw nylon bag retrieved in Example 1 was vibrated and tapped to obtain the soil around the returned straw, and the pH of the fresh soil was tested to investigate the effect of the pesticide application on the soil pH. The soil pH was tested with a water-to-soil ratio of 2.5:1. image 3 The results showed that, compared with the blank control, the pH of the soil increased by 10.26-22.10% when the compound agent was applied for 15 days, but they were all below 7.79, and there was no partial alkalinity; The ratios were all decreased accordingly, and there was no significant difference in pH between the chemical treatment group and the control group, which indicated that the application of the compound chemical agent would not change the pH of the common straw returning soil. The 181d field test results showed that there was no significant difference between the compound agent 10% urea+0.05% alkali tre...
Embodiment 3
[0022] The impact of embodiment 3 composite medicament on soil dehydrogenase
[0023] The straw nylon bag retrieved in Example 1 was vibrated and tapped to obtain the soil around the returned straw, and the activity of dehydrogenase in the fresh soil was tested to investigate the effect of the agent application on the activity of soil dehydrogenase. Triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) reduction method was used to measure soil dehydrogenase activity. Take 5.0g of fresh soil and react with 5mL of 0.5% TTC-Tris-HCl solution at 37°C for 20h in the dark. After the cultivation, add 5mL Formaldehyde terminates the reaction, shake at 25°C and 200r / min for 1h, filter into a 50mL colorimetric tube, dilute with methanol appropriately according to the color depth, and measure the dehydrogenase activity at 485nm with a UV-Vis spectrophotometer. Dehydrogenase activity (mgTPF / g dry soil / h)=(c*V) / (dry soil quality*20), c is the measured triphenylformazan TPF concentration, V is the filtrate v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com