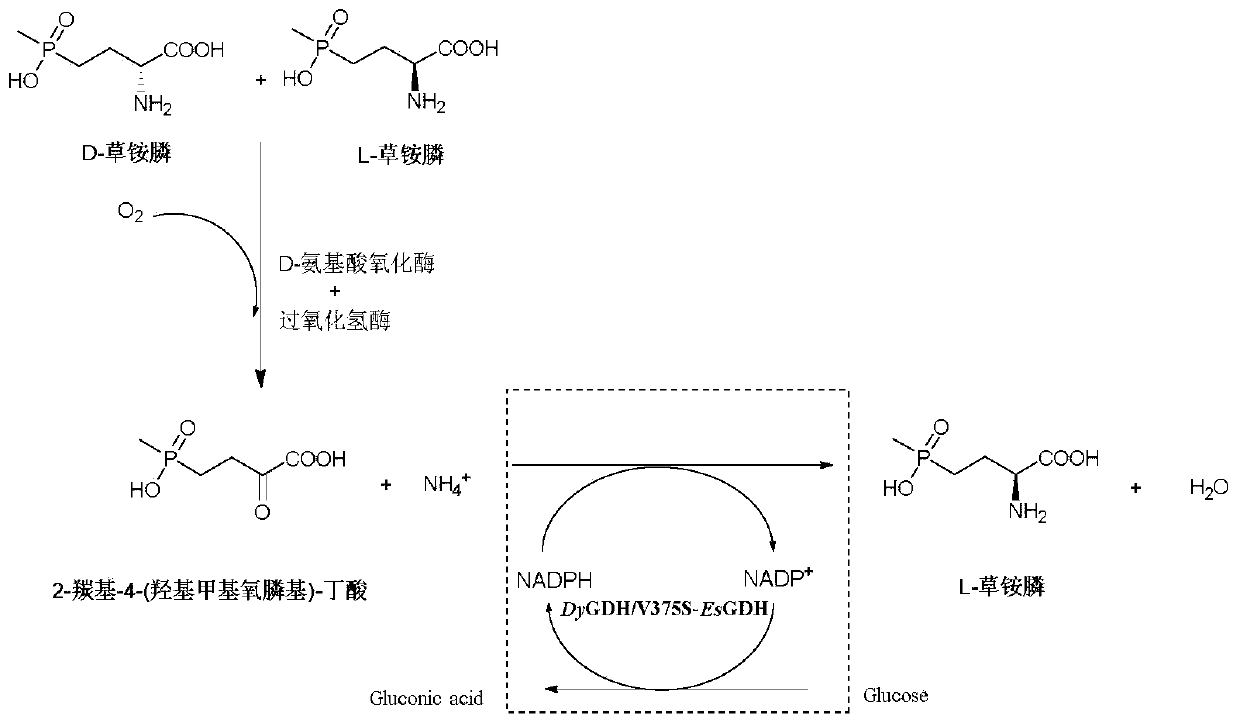
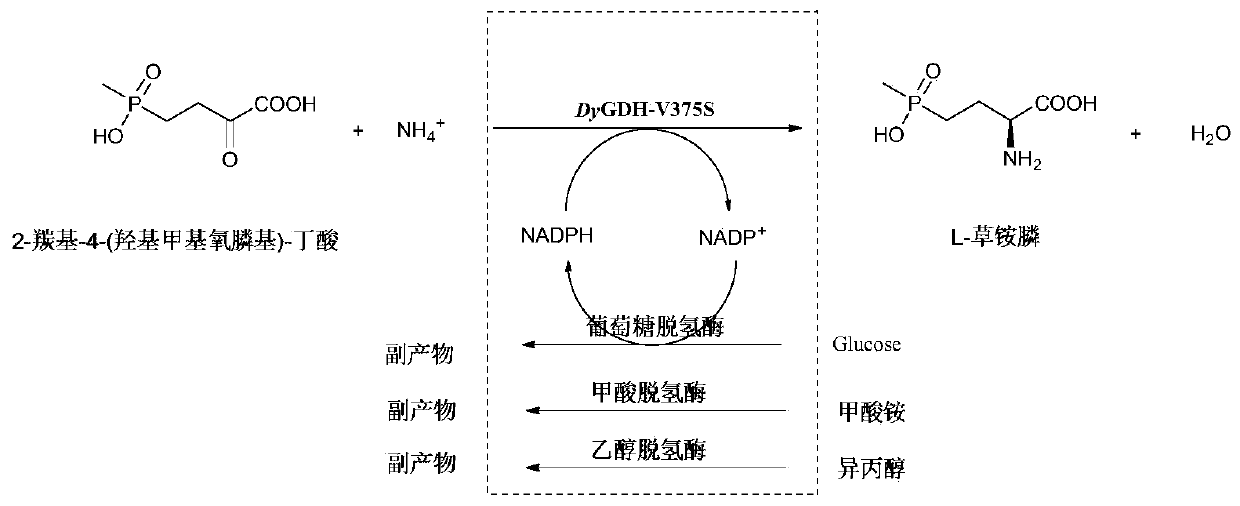
Glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant, and application thereof in producing L-glufosinate-ammonium
A glufosinate-ammonium and dehydrogenase technology, applied to the glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and its application in the production of L-glufosinate-ammonium, can solve the problem of low activity of asymmetric amination reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Construction and screening of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant library
[0039] The glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase gene dygdh cloned from Pseudomonas monteilii (Pseudomonas monteilii) WP_060477601.1 1 (The nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.2), the glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase gene dygdh obtained from Pseudomonas japonicaWP_042124798.1 clone 2 (The nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.3, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.4), the glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase gene dygdh obtained from Thiopseudomonas denitrificansWP_101496154 clone 3 (The nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.5, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.6), and the expression vector pETDuet-dygdh was constructed respectively 1 , pETDuet-dygdh 2 , pETDuet-dygdh 3 , keep the His-Tag gene of the vector itself, transform it into Escherichia coli E.coli BL21(DE3), and obtain the pa...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2: Induced expression of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase parent engineering bacteria, glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant engineering bacteria, formate dehydrogenase engineering bacteria, D-amino acid oxidase engineering bacteria, alcohol dehydrogenase engineering bacteria
[0056] 1. Construction of engineering bacteria
[0057] Construction of D-amino acid oxidase engineering bacteria E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET24b-daao:
[0058] The D-amino acid oxidase gene sequence (GenBank: NO.XM_016418953.1, nucleotide sequence: SEQ ID No.9) derived from yeast Rhodotorula gracilis was introduced into the vector pET-24b(+) to construct the recombinant The expression vector pET-24b-daao uses E.coli BL21(DE3) as the host bacterium to construct the engineering bacterium E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET24b-daao.
[0059] Formate dehydrogenase engineering bacteria construction:
[0060] The formate dehydrogenase gene sequence (GenBank: No.WP_013726924.1, nucleotide sequence: SEQ ID No....
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3: Mutant library screening
[0069] The glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase parent and glucose dehydrogenase prepared by the method in Example 2 co-express wet thallus or glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutants and glucose dehydrogenase co-expression wet thallus as a catalyst, with intermediate The product 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-butyric acid is used as the substrate, glucose is used as the coenzyme regeneration substrate, ammonium sulfate is added, no exogenous NADPH or NADP+ is added, and the endogenous NADPH of the bacteria is used. Use pH 7.4, 100mM phosphate buffer as the reaction medium to form a 10mL reaction system, the amount of catalyst is 25g / L based on the final concentration of wet bacteria, the final concentration of substrate is 300mM, the final concentration of glucose is 450mM, and the final concentration of ammonium sulfate is 750mM. React at 600 rpm for 5 minutes, take 100 μL of the reaction solution, add 5 μL of hydrochloric...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com