A kind of high-yield bacterial strain of Hubei Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharide and its application
A technology of Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharide and bacteria, which is applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of large influence of climatic conditions, long production cycle of tuberous roots, and high cost of polysaccharide extraction, and achieves the effects of avoiding pollution, avoiding unfavorable factors and having great application value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] The isolation step of the high-yield bacterial strain of the Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharide of embodiment 1
[0049] (1) Sampling: Multiple samples were taken from Hubei Ophiopogon japonicus GAP base, the origin of Hubei Ophiopogon japonicus in Oumiao Town, Xiangyang City, Hubei Province, as plant raw materials for the isolation of high-yielding bacterial strains of Ophiopogon japonicus in Hubei.
[0050] (2) Medium preparation:
[0051] The formula of PDA medium: 200 grams of potatoes, 20 grams of glucose, 15-20 grams of agar, 1000 ml of distilled water
[0052] (3) Isolation of strains: Use a large amount of tap water to fully wash the soil on the surface of fresh Hubei Ophiopogon japonicus plant roots, then put it into a clean beaker, add deionized water, and place it in an ultrasonic cleaner for repeated cleaning until the water after cleaning becomes extremely Clear; use sterile filter paper to dry the moisture on the surface of Ophiopogon japonicus root tube...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The preparation step of embodiment 2 Hubei Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharide
[0054] Take the high-yielding bacterial strain of Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharides obtained in Example 1, under aseptic conditions, pick a small number of colonies with an inoculation needle, insert them into a sterilized PDA medium test tube, and activate and cultivate them at 37°C for 16 hours.
[0055] The activated cultured strains were taken, transferred into sterilized liquid potato seed medium under aseptic conditions, and vibrated at 180 rpm at 37° C. for 16 hours to obtain seeds.
[0056] Put the prepared liquid fermentation medium into 250mL Erlenmeyer flasks, about 100mL per bottle, sterilize and cool for later use; under sterile conditions, insert the seeds according to 10% of the inoculum amount, and shake at 180rpm at 37°C 2 days.
[0057] After the fermentation is completed, the fermented solid-liquid mixture is quickly frozen into a solid state in an ultra-low temperatu...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 Identification of bacterial strains and detection of polysaccharides produced by the bacteria in Ophiopogon japonicus
[0063] (1) Identification of the morphological characteristics of the culture medium
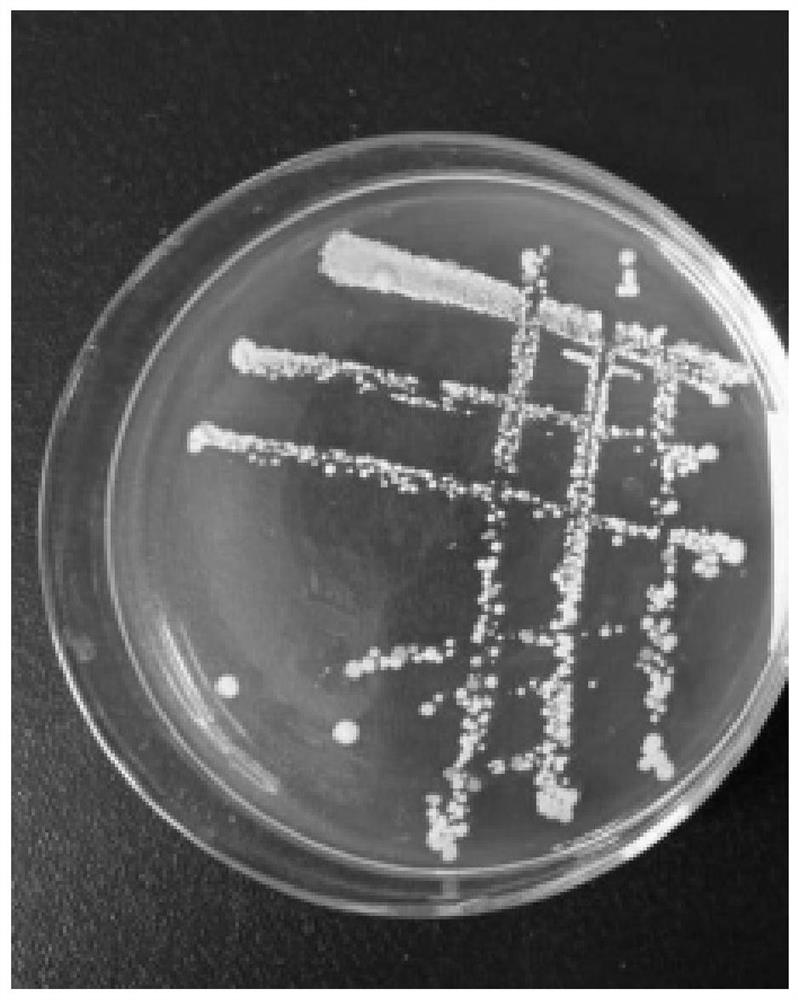
[0064] The high-yielding bacterial strain of Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharides obtained in Example 1 was streaked on a PDA medium plate, cultured at 28° C. for 24 hours, and characteristics such as colony shape, size, and color were observed. Observation results such as figure 1 As shown, the colony of the high-yield bacterial strain of Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharides in Hubei was white, round and smooth.
[0065] (2) 16S rRNA gene sequencing of a high-yielding bacterial strain of Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharides in Hubei
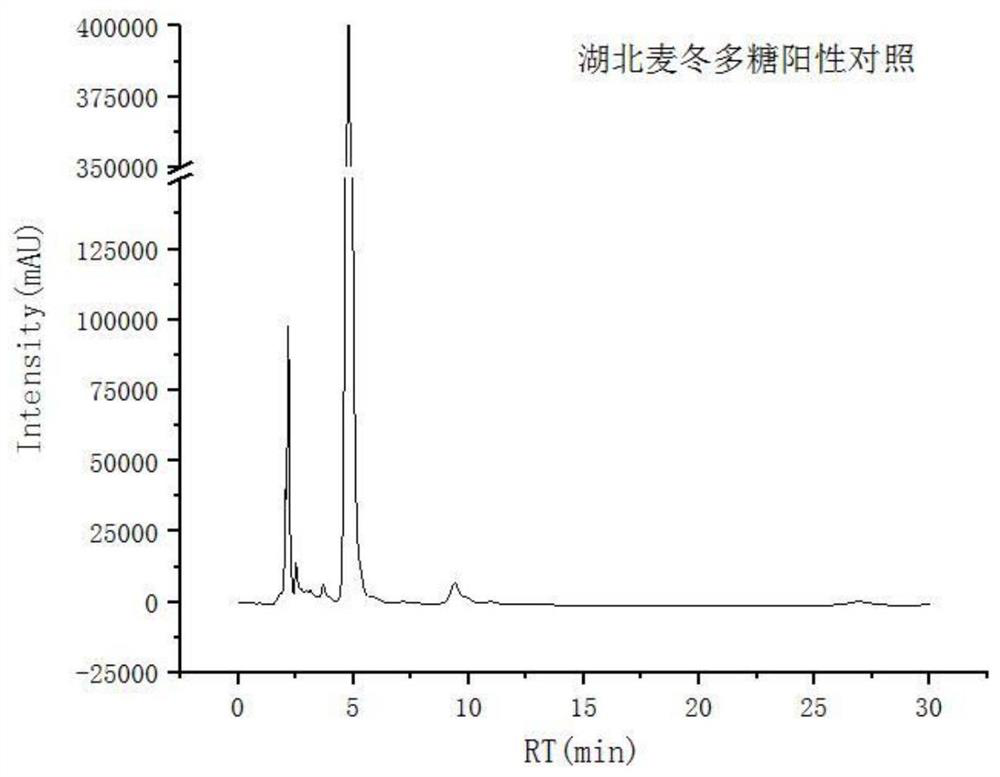
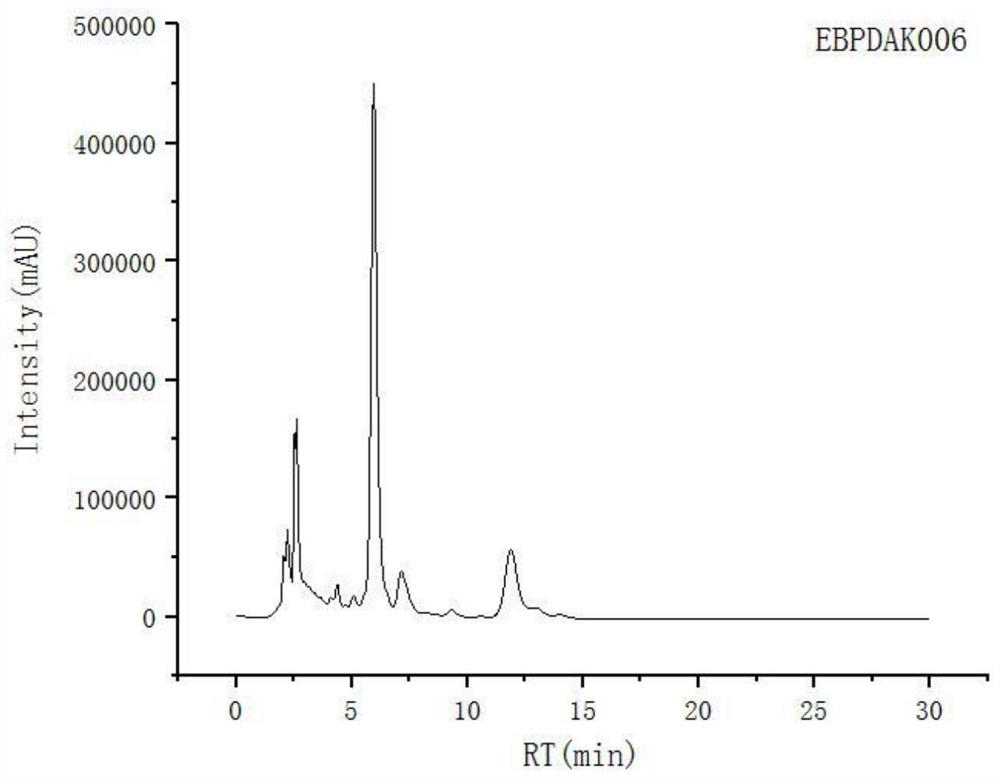
[0066] The 16Sr RNA gene sequence of the high-yielding bacterial strain of Ophiopogon japonicus in Hubei is shown in the attachment, and the sequencing results were compared on the NCBI website (http: / / blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.go...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com