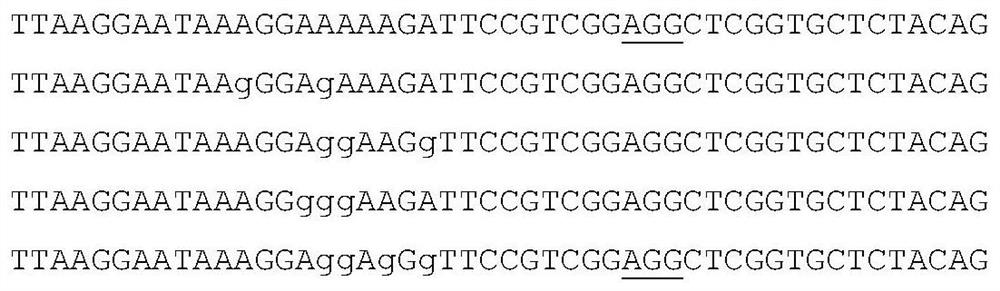A kind of wide window single base editing gene and its application and breeding method
A single-base, editing technology, applied in the fields of biotechnology and plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of rare, low single-base editing efficiency, limited editing window, etc., to achieve excellent genetic resources, significant research significance and The effect of social value and high editing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1——CP1249-OsSpCas9-eABE gene synthesis
[0046] The gene of the present application is named CP1249-OsSpCas9-eABE, and its sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1.
[0047] The gene sequence of CP1249-OsSpCas9-eABE was sent to Suzhou Jinweizhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for synthesis, then PCR amplified and transformed into Escherichia coli XL-blue. It should be noted that the CP1249-OsSpCas9-eABE obtained by the inventors of the present application during the research and development process was obtained through various cross-combination adjustments of gene sequences and fragments. The specific acquisition process is a technical secret and will not be described in detail. Those skilled in the art can also directly synthesize according to the disclosure content of the present invention, which does not affect the realization of the present invention, but the cost will increase.
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2—Construction of plant targeting vector containing CP1249-OsSpCas9-eABE gene
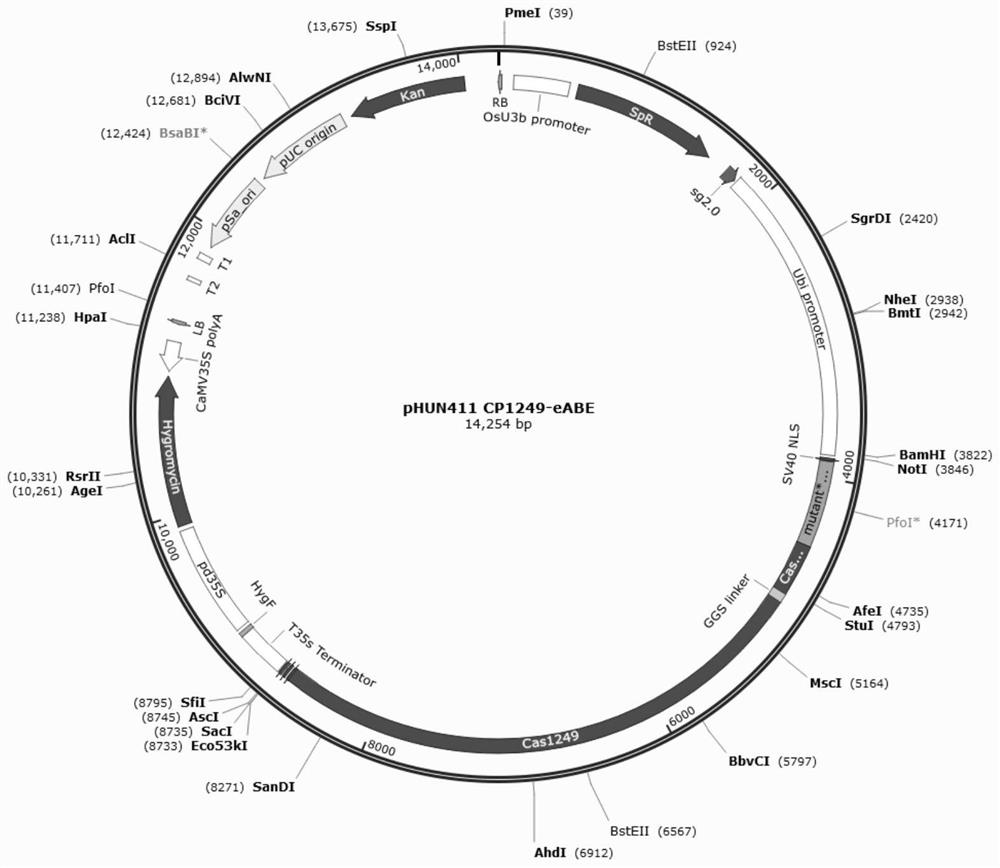
[0050] From the Escherichia coli XL-blue containing the CP1249-OsSpCas9-eABE vector above, use the Axygen plasmid extraction kit to extract the plasmid, digest it with NotI / SacI, and recover the CP1249-OsSpCas9-eABE fragment. At the same time, NotI / SacI enzyme was used to linearize pHUN900, recover pHUN900, and connect the above CP1249-OsSpCas9-eABE fragment and pHUN900 fragment with T4 ligase (purchased from TaKaRa Company) to obtain the plant expression vector pHUN CP1249-OsSpCas9- eABE( figure 1 ), named pHUN411 CP1249-eABE.
[0051] Nucleotide sequence AAGGAAAAAGATTCCGTCGG of exon 1 in selected rice PDS gene (Os03g0184000) AGG , (the underlined part is the PAM sequence of the 5'NGG-3' structure), as the targeting site. The target site sequence was fused to pHUN411 CP1249-eABE to form pHUN41 CP1249-eABE-PDS. The plant expression vector was transformed into Agrobacterium tumef...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3—Genetic transformation of rice using PHUN CP1249-eABE-PDS as a targeting vector and acquisition of mutants.
[0054] 1. Induction and pre-culture of mature embryo callus
[0055] The mature seeds of Nipponbare rice are dehulled, and the seeds with normal appearance and cleanness without mildew are selected, shaken for 90 sec with 70% alcohol, and the alcohol is poured off; Add 1 drop of Tween20) solution to 100 milliliters to wash the seeds, and shake on a shaker for 45 minutes (180 r / min). Pour off the sodium hypochlorite, wash with sterile water 5-10 times until there is no smell of sodium hypochlorite, finally add sterile water, soak overnight at 30°C. Use a scalpel to separate the embryos along the aleurone layer, put the scutellum up on the induction medium (see Table 1 for ingredients), 12 embryos / dish, and culture in the dark at 30°C to induce callus.
[0056] Two weeks later, spherical, rough, light yellow secondary callus appeared, and pre-cultivati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com