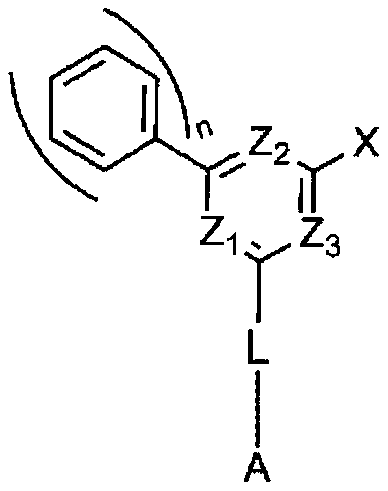
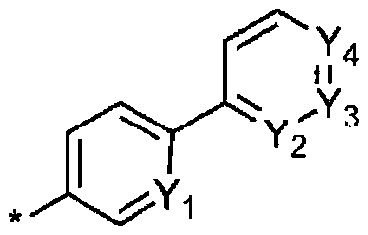
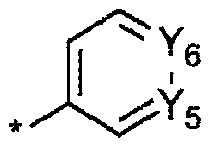
Organic light emitting compound and organic electroluminescent device using same
A compound and chemical formula technology, applied in the field of organic electroluminescent elements, can solve the problems of low glass transition temperature, low triplet energy, poor thermal stability, etc., and achieve the effect of excellent luminescence ability and improved efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Synthetic example 1
[0197] [Synthesis Example 1] Synthesis of Compound 1
[0198]
[0199] Mix PPY-1 3.0g with (9,9-dimethyl-9H-fluoren-2-yl) boronic acid 4.3g and K 2 CO 3 3.3 g was mixed, and after adding 60 ml of toluene, 12 ml of ethanol and 12 ml of water, 500 mg of tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium (0) was added, followed by heating and stirring for 4 hours. After the reaction, the temperature was lowered to normal temperature, and then filtered. Pour the filtrate into water, extract with chloroform, use MgSO 4 The organic layer was dried. After concentration under reduced pressure, column chromatography was performed at MC:Hex=2:1 to obtain 2.8 g of compound 1 as a white solid (55% yield).
[0200] Quality: [(M+H) + ]:502
Synthetic example 2
[0201] [Synthesis Example 2] Synthesis of Compound 2
[0202]
[0203] Mix 3.0g of PPY-1 with 5.1g of 9,9'-spirobis[fluorene]-2-ylboronic acid and K 2 CO 3 3.3 g was mixed, and after adding 60 ml of toluene, 12 ml of ethanol and 12 ml of water, 500 mg of tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium (0) was added, followed by heating and stirring for 4 hours. After the reaction, the temperature was lowered to normal temperature, and then filtered. Pour the filtrate into water, extract with chloroform, use MgSO 4 The organic layer was dried. After concentration under reduced pressure, column chromatography was performed at MC:Hex=2:1 to obtain 3.2 g of compound 2 as a white solid (58% yield).
[0204] Quality: [(M+H) + ]:624
Synthetic example 3
[0205] [Synthesis Example 3] Synthesis of Compound 4
[0206]
[0207] Mix PPY-1 3.1g with (7,7-dimethyl-7H-benzo[c]fluoren-9-yl)boronic acid 4.8g and K 2 CO 3 3.3 g was mixed, and after adding 60 ml of toluene, 12 ml of ethanol and 12 ml of water, 500 mg of tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium (0) was added, followed by heating and stirring for 4 hours. After the reaction, the temperature was lowered to normal temperature, and then filtered. Pour the filtrate into water, extract with chloroform, use MgSO 4 The organic layer was dried. After concentration under reduced pressure, column chromatography was performed at MC:Hex=2:1 to obtain 3.5 g of compound 4 as a white solid (yield 56%).
[0208] Quality: [(M+H) + ]:551
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com