Simulation method for strain regulation and control of selenium disulfide semiconductor device
A technology of selenium disulfide and simulation method, which is applied in the fields of instruments, special data processing applications, electrical digital data processing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
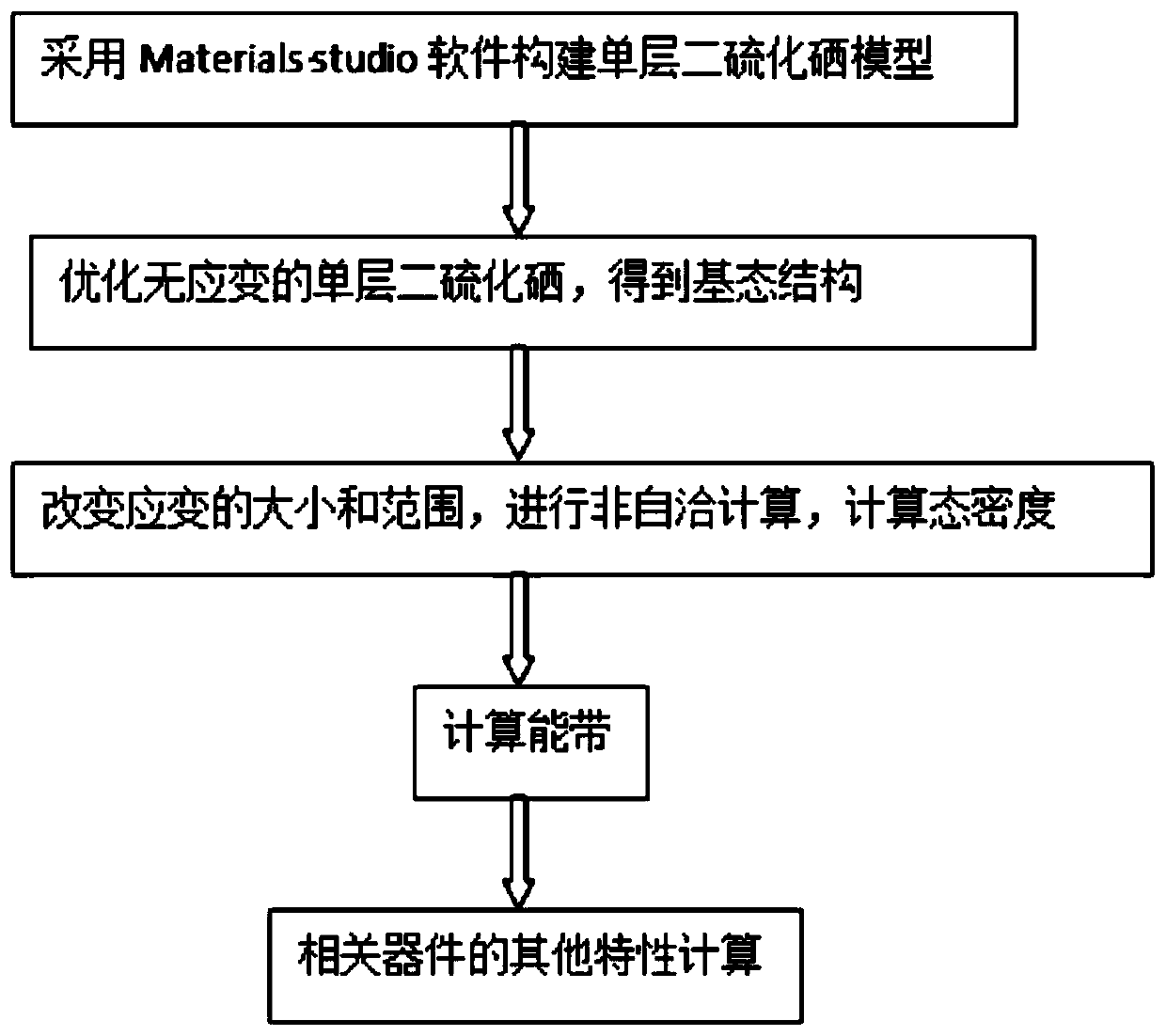
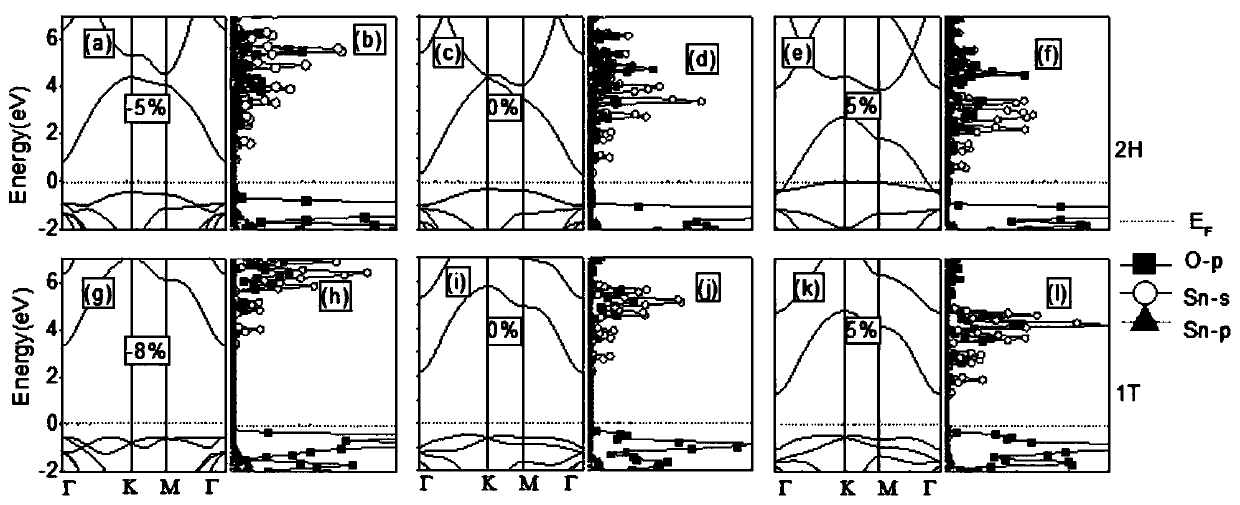
[0019] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic flow chart of the simulation method for strain-regulated selenium disulfide semiconductor devices, including the following steps: use Materials Studio software to construct a single-layer selenium disulfide model → optimize the unstrained single-layer selenium sulfide-free to obtain the ground state structure → change the strained Size and range, perform non-self-consistent calculations → calculate the density of states, calculate energy bands → calculate other characteristics of related devices.
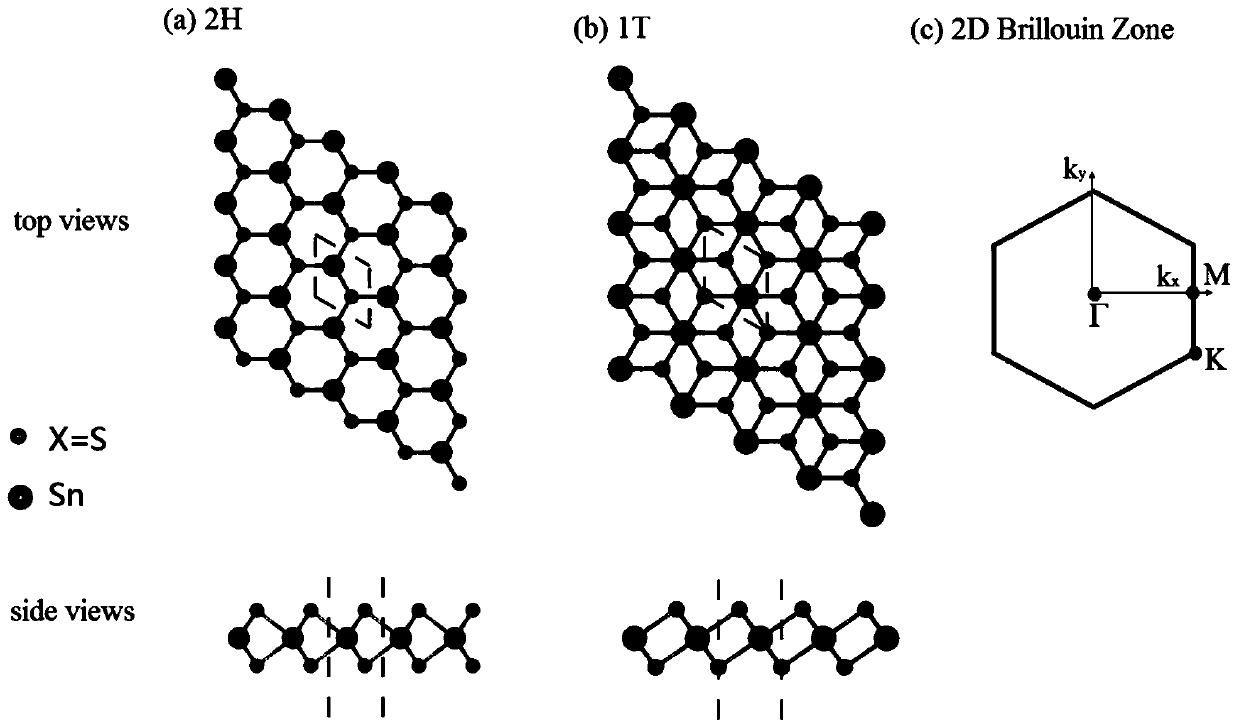
[0020] Using Materials Studio software to build a single-layer selenium disulfide model, including the following steps: selenium disulfide has three atomic planes, the Sn atomic plane in the middle separates the S atoms of the two hexagonal side planes, and the adjacent layers are separated by van der Waals force Combine with lay...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com