Nanocellulose electrothermal film and preparation method thereof
A technology of nanocellulose and electric heating film, which is applied to electric heating devices, ohmic resistance heating, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of changing the intrinsic properties of carbon nanotubes, unfavorable dispersion of carbon nanotubes, and increasing the cost of carbon nanotubes. The effect of protecting and enhancing the electrothermal film structure, good environmental compatibility, and improving the bonding performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
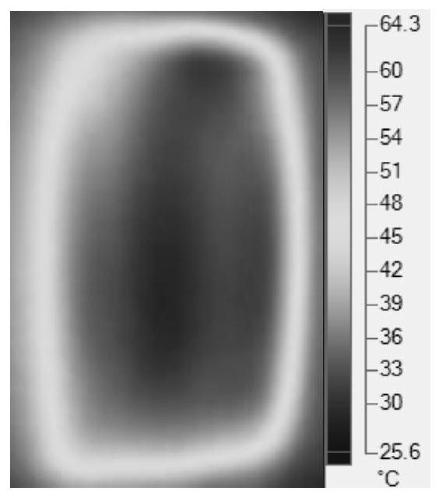
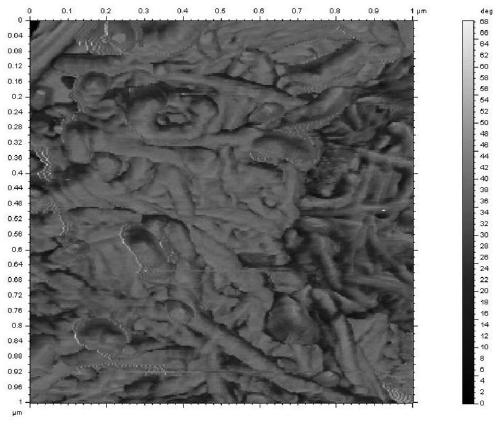
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] A preparation method of nanocellulose electrothermal film, which specifically includes:
[0061] Step 1. Prepare a nanocellulose dispersion with a dispersion concentration of 2 mg / ml, disperse the nanocellulose dispersion at high speed for 5 minutes, and then ultrasonically disperse with 600W power for 25 minutes;
[0062] Prepare a carbon nanotube dispersion with a dispersion system of 2mg / ml, disperse the carbon nanotube dispersion at high speed for 20 minutes, and then disperse it ultrasonically for 20 minutes with a power of 600W;
[0063] Prepare a graphene dispersion with a dispersion system of 1 mg / ml, disperse the graphene dispersion at high speed for 5 minutes, and then disperse it with 600W ultrasonic for 5 minutes;
[0064] Step 2: Mix the nanocellulose dispersion, carbon nanotube dispersion and graphene dispersion according to the ratio, then add a certain proportion of high molecular conductive polymer, after high-speed dispersion for 10 minutes, use 1000W ...
Embodiment 2
[0073] The difference with Example 1 is: the proportion of nanocellulose dry weight in step 2: 50%, the proportion of carbon nanotubes, graphene and high molecular conductive polymer total dry weight: 50%; graphene dry weight accounts for 3% of the total dry weight of carbon nanotubes, graphene, and high-molecular conductive polymers; the dry weight of high-molecular conductive polymers accounts for 2% of the total dry weight of carbon nanotubes, graphene, and high-molecular conductive polymers. The high molecular conductive polymer is polyaniline.
Embodiment 3
[0075] The difference with Example 1 is: the proportion of nanocellulose dry weight: 70%, the proportion of carbon nanotubes, graphene and high molecular conductive polymer: 30%; the dry weight of graphene accounts for carbon nanotubes, graphene and 4% of the total dry weight of the conductive polymer; the dry weight of the conductive polymer accounts for 3% of the total dry weight of the carbon nanotubes, graphene and the conductive polymer. The high molecular conductive polymer is polypyrrole.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Square resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Insulation resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com