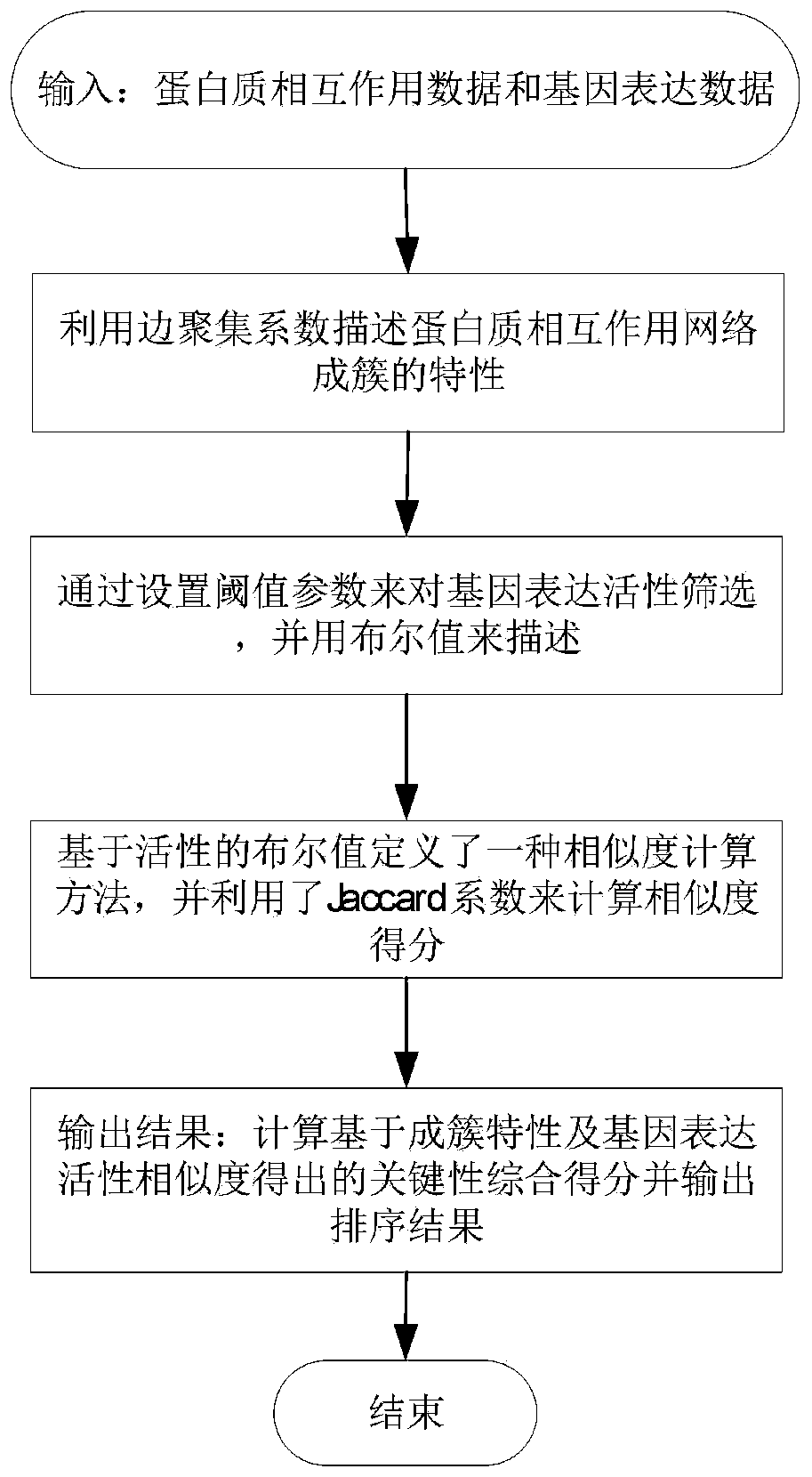
Key protein identification method based on protein clustering characteristics and activity co-expression
A recognition method and protein technology, which is applied in the field of key protein recognition based on protein clustering characteristics and active co-expression, can solve the problems of affecting accuracy, deviation of prediction results, ignoring influence, etc., and achieve accuracy improvement, high accuracy, Effect of Noise Cancellation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] 1. Selection of protein interaction network (PPI) data and gene expression data.
[0046] Since the yeast data is relatively complete among all species and is widely used in various key protein prediction methods, the present invention uses the data of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Bakers Yeast) for testing. The genome-wide protein interaction data of yeast was downloaded from DIP, and the repeated interaction data and self-interaction data were discarded. The resulting yeast PPI network had 5093 proteins and 24743 edges. The key proteins are integrated with four databases of MIPS, SGD, DEG and SGDP, among which there are 1285 key proteins of yeast (1167 key proteins appear in yeast PPI). Gene expression data reflect the dynamic properties of genes in the metabolic cycle. The gene expression data of yeast was downloaded from the NCBI GeneExpression Omnibus website. After preprocessing, 6777 gene products and 36 samples were obtained, of which 4858 genes participated in the...
Embodiment 2
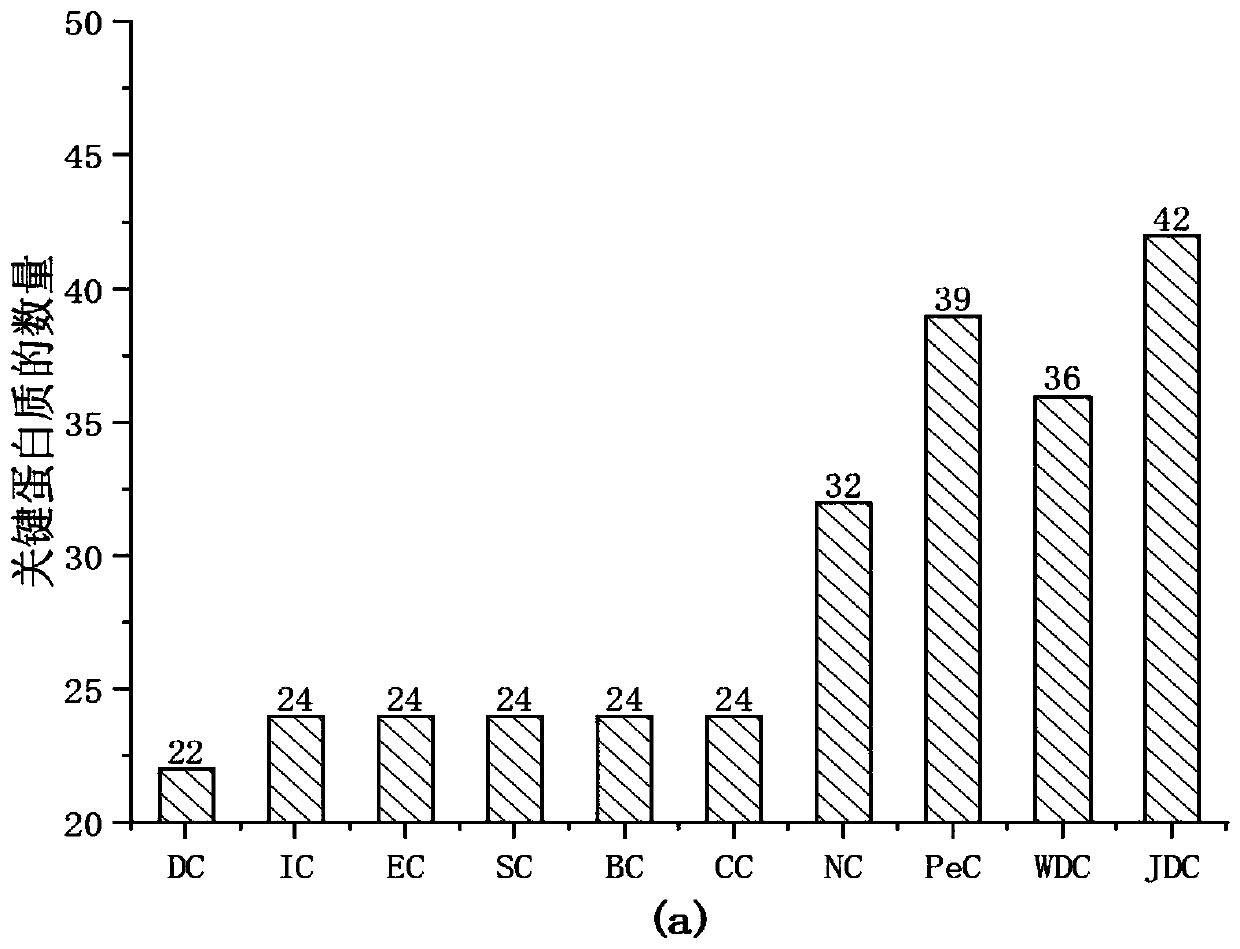
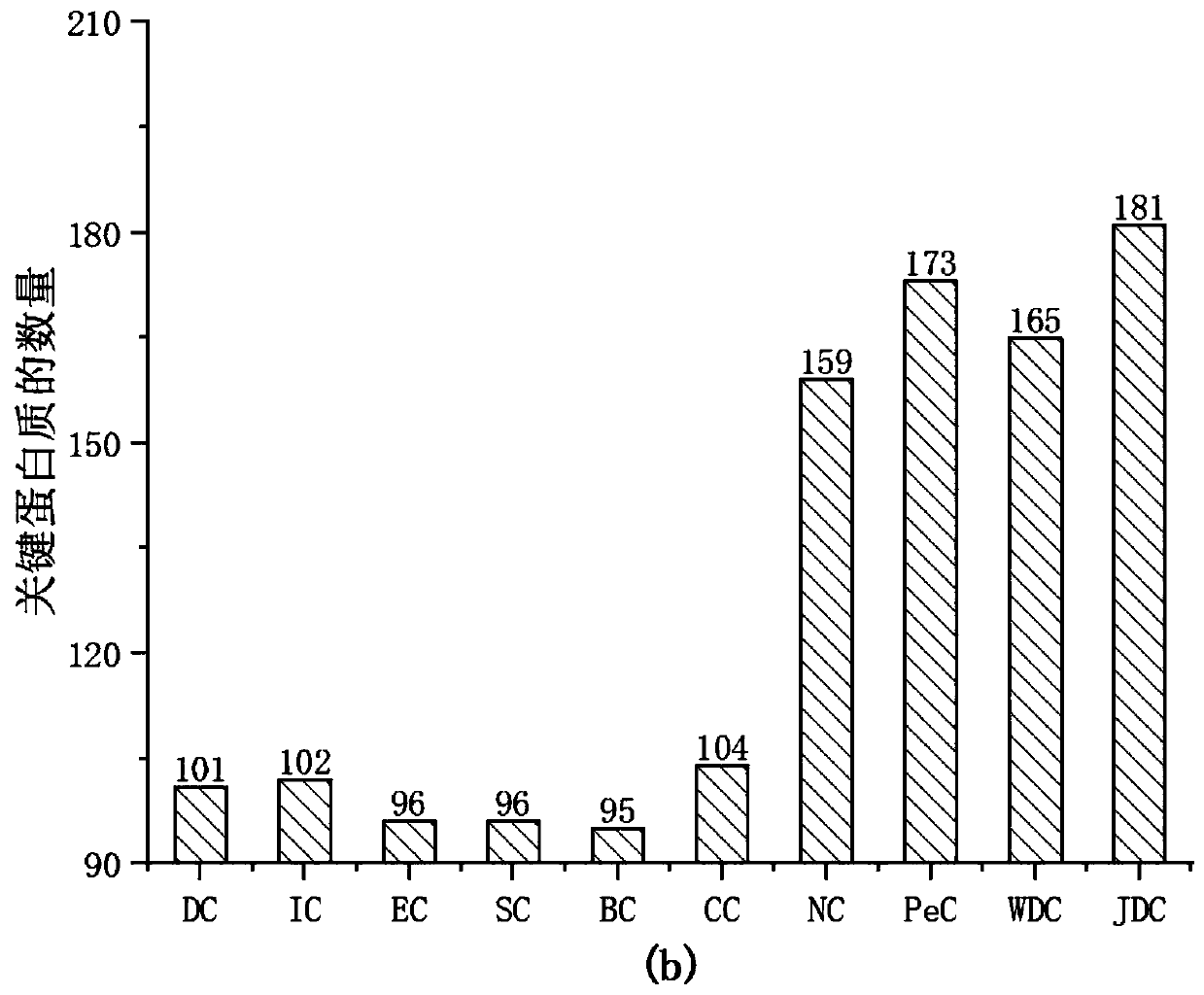
[0063]In order to verify the performance of the JDC method of the present invention, 9 key protein prediction methods were selected for comparison. The nine prediction methods are: (Degree Centrality, DC) degree centrality method; (Information Centrality, IC) information centrality; (Eigenvector Centrality, EC) information vector centrality; (Subgraph Centrality, SC) subgraph centrality; ( Betweenness Centrality, BC) betweenness centrality; (ClosenessCentrality, CC) proximity centrality; (Edge Clustering Cofficient Centrality, NC), a key protein measurement method based on the edge clustering coefficient, (Integratioin of gene expression profiles and PPIdata, PeC) based on Key protein measurement method of gene expression data and PPI network data; (Integratioin of gene expression profiles and PPI data and add the parameters to adjust the proportion, P&E) key protein measurement method based on weighted centrality. And selected Top1%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20% and 25% of the proteins ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] ROC curve comparison and multiple performance evaluations of key protein identification methods based on protein clustering properties and active co-expression.
[0066] To evaluate the global performance of each method, ROC curves were used for comparison. Compare the result as Figure 8 As shown, under the Yeast data, the area under the curve (AUC) of JDC was 0.6992, and the areas under the curve (AUC) of WDC and NC were 0.6884 and 0.6889, respectively. Compared with WDC and NC, the method of JDC improves by 0.0108 and 0.0103, respectively. The difference between JDC, WDC and PeC is how to weight the PPI network. Although LI and Tang introduced the PCC correlation coefficient to weight the PPI network on the basis of ECC, it effectively suppressed false positives and false negatives. However, the "activity" and "inactivity" of gene expression at different moments are ignored when introducing gene expression data. For this reason, the present invention proposes to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com