Soy sauce brewing process
A technology and technology of soy sauce, which is applied in the field of seasoning processing, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of raw materials, and achieve the effect of improving protein utilization rate, significant social and economic benefits, and increasing the content of glutamic acid in soy sauce
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
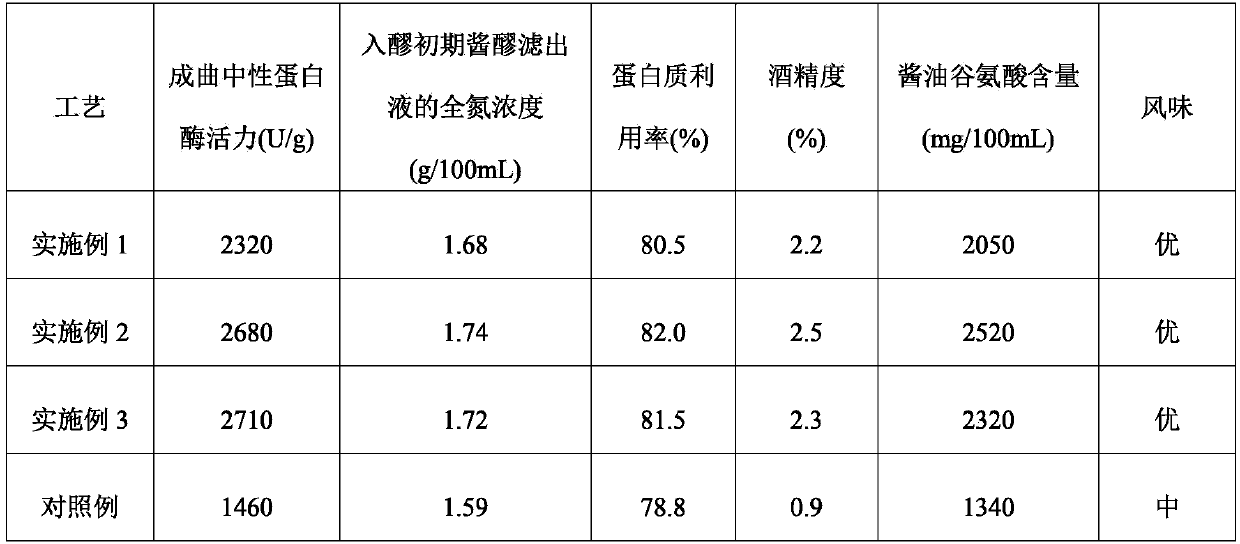
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] S1. Processing of protein raw materials: firstly, the protein raw materials are subjected to the wetting process and the steaming process to obtain cooked protein raw materials, and then the cooked protein raw materials are broken into protein granules with a diameter of 9 mm or less, and the protein granules are cooled. Protein raw materials are generally seeds rich in protein, such as soybean, soybean meal, soybean cake, etc. The protein raw material can be a single raw material, or can be obtained by mixing different kinds of raw materials. Among them, when performing the moistening process, add 1.05 to 1.30 times the weight of water to the protein raw material, and use a moistening auger to stir for 10 to 40 minutes; The raw material is cooked, and the cooking pressure is 1.0-1.4 MPa to obtain the cooked protein raw material.
[0042] Specifically, step S1 includes the following sub-steps:
[0043] S11 Moisturizing: soybean meal is selected as the protein raw mater...
Embodiment 2
[0080] S1. Processing of protein raw materials: firstly, the protein raw materials are subjected to the wetting process and the steaming process to obtain cooked protein raw materials, and then the cooked protein raw materials are broken into protein granules with a diameter of 9 mm or less, and the protein granules are cooled. Among them, when performing the moistening process, add 1.05 to 1.30 times the weight of water to the protein raw material, and use a moistening auger to stir for 10 to 40 minutes; The raw material is cooked, and the cooking pressure is 1.0-1.4 MPa to obtain the cooked protein raw material.
[0081] Specifically, step S1 includes the following sub-steps:
[0082] S11 Moisturizing: soybean meal is selected as the protein raw material, 1.25 times the weight of water is added to the soybean meal, and the water is mixed with a water auger for 20 minutes;
[0083] S12 Cooking: Use a rotary high-pressure cooking pot to cook the moistened soybean meal at a co...
Embodiment 3
[0111] S1. Processing of protein raw materials: firstly, the protein raw materials are subjected to the wetting process and the steaming process to obtain cooked protein raw materials, and then the cooked protein raw materials are broken into protein granules with a diameter of 9 mm or less, and the protein granules are cooled. Among them, when performing the moistening process, add 1.05 to 1.30 times the weight of water to the protein raw material, and use a moistening auger to stir for 10 to 40 minutes; The raw material is cooked, and the cooking pressure is 1.0-1.4 MPa to obtain the cooked protein raw material.
[0112] Specifically, step S1 includes the following sub-steps:
[0113] S11 Moisturizing: soybean meal is selected as the protein raw material, 1.30 times the weight of water is added to the soybean meal, and the water is mixed with a water auger for 10 minutes;
[0114] S12 Cooking: Use a rotary high-pressure cooking pot to cook the moistened soybean meal at a co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com