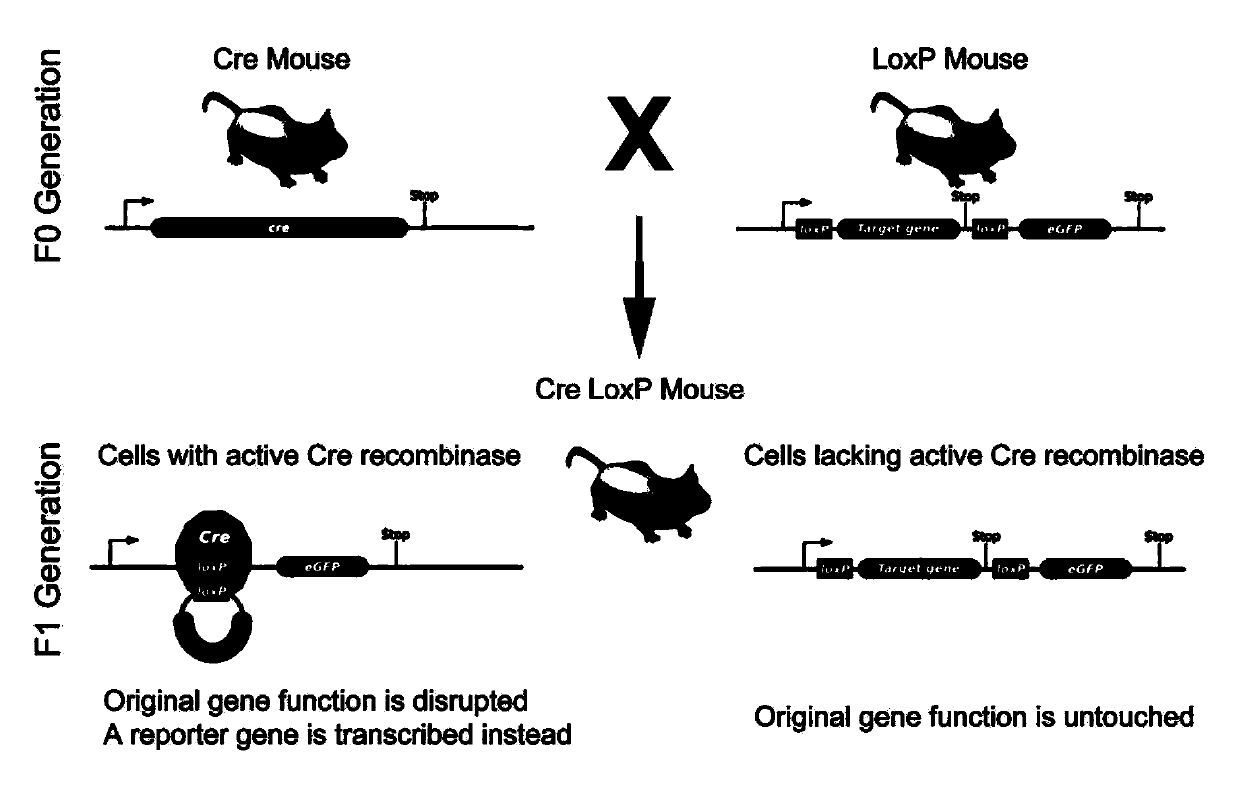
Method for screening acute radiation gastrointestinal syndrome treatment targets
A therapeutic target and radioactive technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of cells susceptible to radiation damage, no treatment for intestinal radiation damage, unpredictable radiation treatment effectiveness, etc., and achieve the effect of promoting stem cell proliferation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Construction of CreERT-loxP conditionally overexpressed transgenic mice
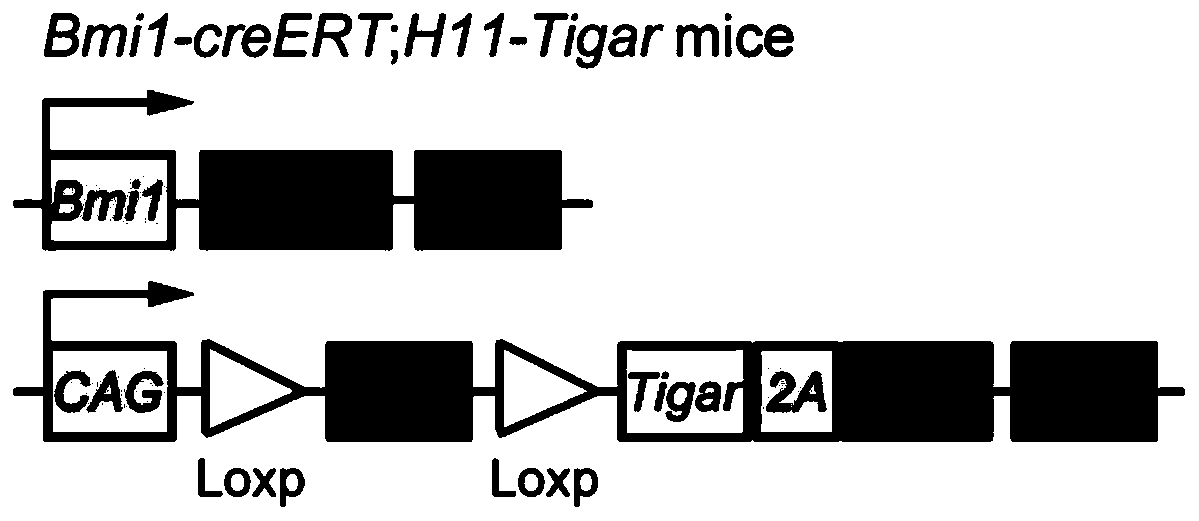
[0039] In order to effectively promote the proliferation of crypt quiescent stem cells, this technical scheme uses Bmi1-CreERT; loxP conditionally overexpressed transgenic mice, and genetically intervened the mouse crypt quiescent stem cells, using TIGAR as the target gene, through tamoxifen Induce the expression of TIGAR protein in crypt quiescent stem cells, such as figure 2 shown.
[0040] In mice with the above genotypes, TIGAR can be overexpressed only in crypt quiescent stem cells through Bmi1, a crypt quiescent stem cell-specific promoter.
[0041] The writing method of the above mouse is: Bmi1-creERT; H11-Tigar. Specifically, Bmi1 is a specific promoter of crypt quiescent stem cells. Cre is a gene encoding a recombinase, which can be translated into a recombinase to cut a specific gene sequence. ERT encodes the estrogen receptor. When creERT is translated as a whole, the re...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2: Induction of target gene overexpression after irradiation with ionizing radiation
[0045] Since it takes a certain amount of time from drug injection to the overexpression of TIGAR in crypt quiescent stem cells (for the CreERT-loxP animal model, it is usually 18-24hr), we irradiated the whole abdomen of mice with 15 Gy X-rays ( image 3 ) immediately after intraperitoneal injection of the drug (tamoxifen, single injection, 4.5mg / 20g mouse body weight).
[0046] On the 1st, 3rd, and 5th day after the mice were irradiated, the mice were sacrificed, and the intestinal tissues were made into frozen sections to observe the expression of TIGAR protein in the quiescent stem cells in the crypts, as shown in Figure 4 shown. Since TIGAR and green fluorescent protein (EGFP) are expressed simultaneously during the design and construction of transgenic mice, the expression level of green fluorescent protein can be used to indicate the expression level of TIGAR. One d...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: Evaluation of Radiation Treatment Effect
[0048] In order to evaluate the radiation rescue effect of TIGAR overexpression, the survival rate of mice and HE staining of intestinal tissue sections were used to evaluate. In the survival rate experiment, mice in the control group (insert the Tigar gene downstream of the loxP-STOP-loxP sequence to obtain the loxP-STOP-loxP-Tigar sequence, insert the above sequence into the H11 site of the mouse genome to obtain the H11-Tigar small rats) and intestinal crypt quiescent stem cell TIGAR overexpressed mice received 15Gy X-ray whole-abdominal irradiation ( image 3 ), intraperitoneal injection of tamoxifen (single injection, 4.5mg / 20g mouse body weight) was carried out immediately after irradiation. After the injection, continue to feed the mice, and observe the survival of the mice, such as Figure 5 shown.
[0049] It can be seen that the mice in the control group (H11-Tigar mice, WT) all died of radiation gast...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap