Time domain A/D converter group
A converter and time-domain technology, applied in analog-to-digital converters, analog-to-digital conversion, code conversion, etc., can solve the problem of increased area, increased power consumption, and A/D converters that cannot be high-speed and low-power. Achieving high dynamic range of sensors, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0138] (A / D converter using two reference voltage signals)
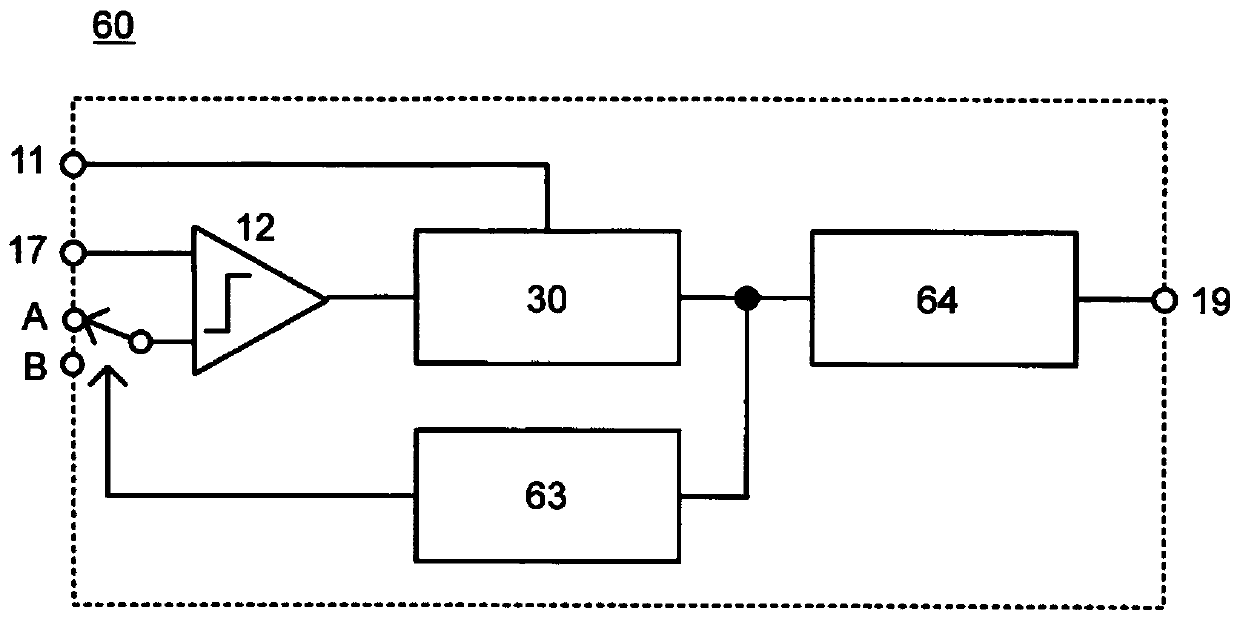
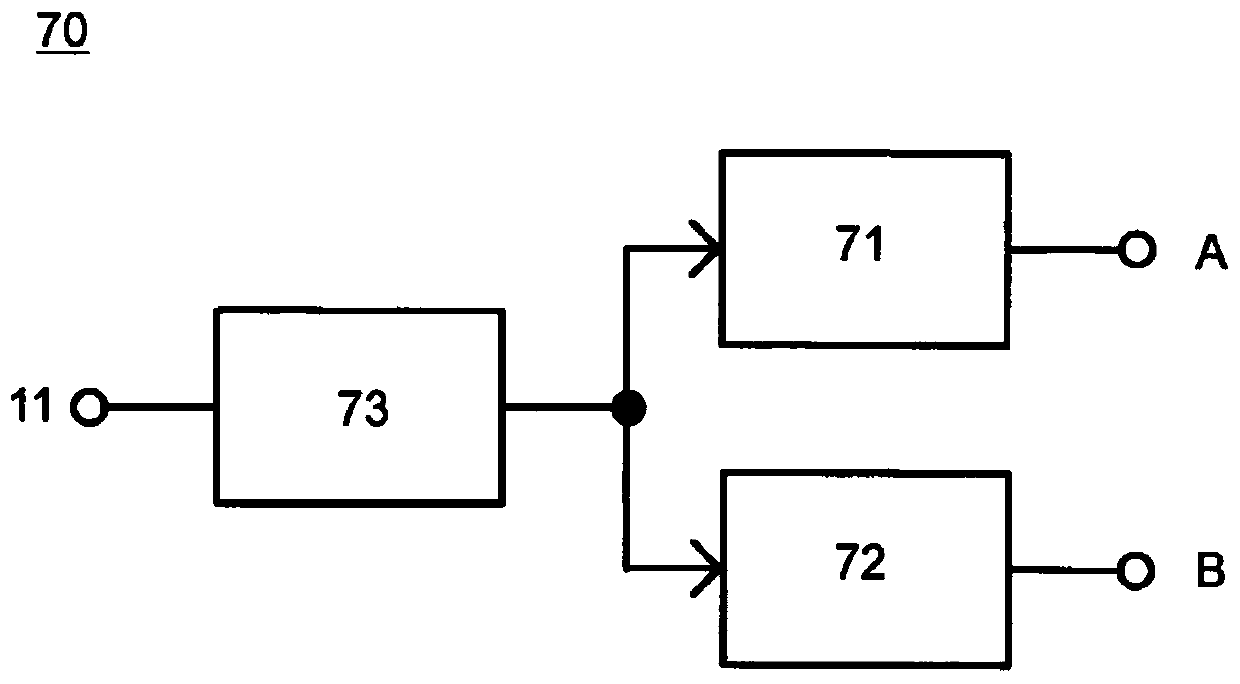
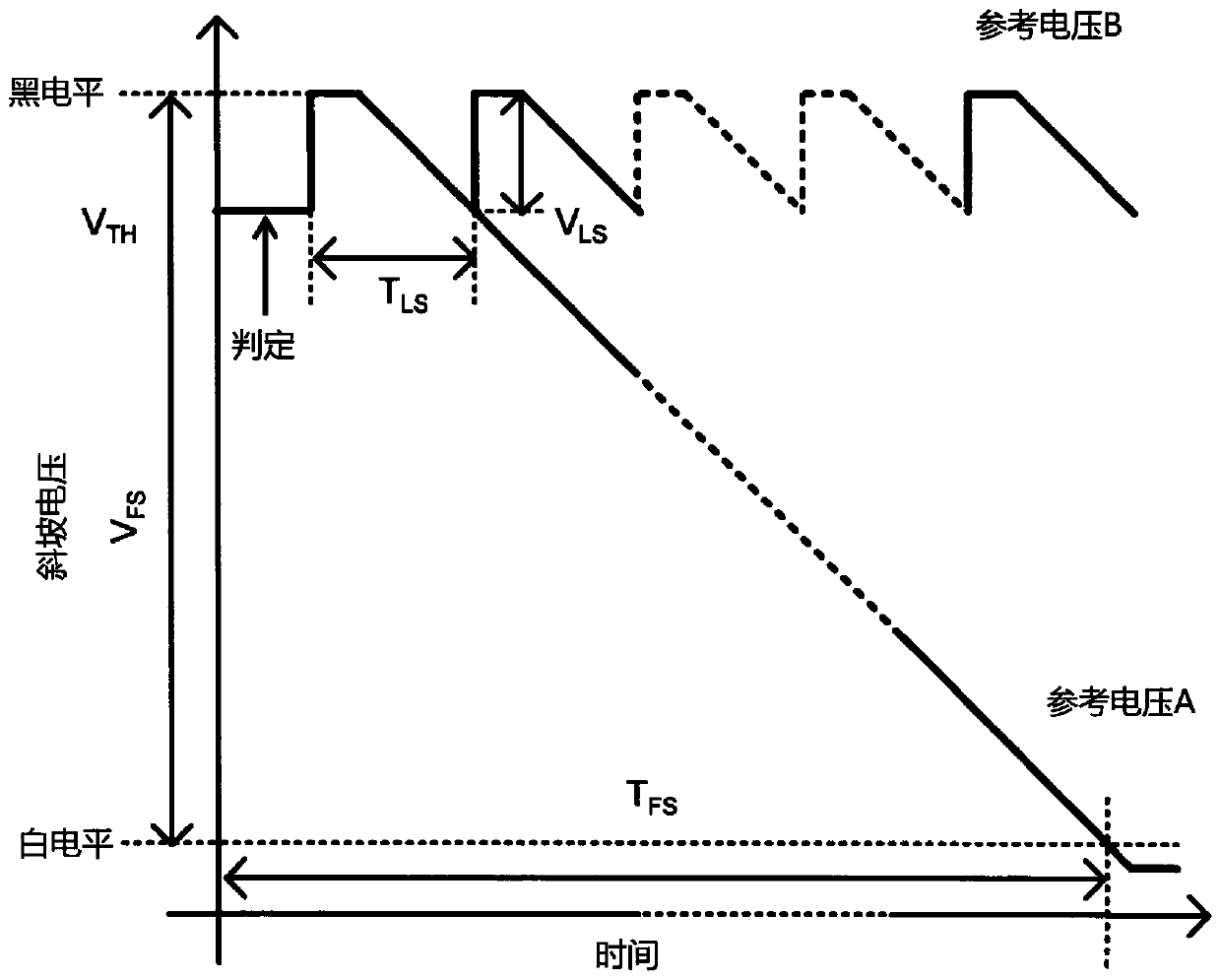
[0139] figure 1 The A / D converter 60 according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure is shown. The A / D converter 60 according to the first embodiment includes a comparator 12, an internal A / D converter 30, a reference voltage selection circuit 63, and an accumulation adder-subtractor 64, wherein the reference voltage selection circuit 63 has two kinds of ramp signals Serving as a reference voltage and switching between the reference voltages, the accumulative adder-subtractor 64 is used to perform accumulative addition or accumulative subtraction on a plurality of converted values and output the averaged output as an A / D converted value.
[0140] In the A / D converter 60 according to the first embodiment, the comparator 12 compares the pixel signal with the ramp signal as the reference voltage signal, generates a comparison output at the time when the two signals intersect, and controls the counter to ...
no. 2 approach
[0194] (A time-domain A / D conversion module including multiple A / D converters using a multi-phase clock formed by a DLL circuit)
[0195] Figure 14 A time-domain A / D conversion module including a plurality of A / D converters according to an embodiment of the present disclosure is shown. The A / D conversion module 10 includes a DLL (delay locked loop) circuit 20, and also includes a plurality of comparators 12-1, 12-2, ..., 12-n (n is a natural number, hereinafter, without distinguishing each comparator 12) and a plurality of internal A / D converters 30-1, 30-2, . A plurality of A / D converters 14-1, 14-2, . / D converter 14).
[0196] The DLL circuit 20 includes a plurality of delay circuits 21-1, 21-2, 21-3, and 21-4 (hereinafter referred to as delay circuits 21 when the respective delay circuits are not distinguished), a phase comparator (PD) 22, a charge pump (CP) and low pass filter (LPF) 23 . Four-stage delay circuits 21 - 1 , 21 - 2 , 21 - 3 , and 21 - 4 arranged in ser...
no. 3 approach
[0207] (conversion from polyphase clock signal to Gray code)
[0208] Figure 17 An A / D conversion module according to a third embodiment of the present disclosure is shown. The A / D conversion module 90 according to the third embodiment differs from the A / D conversion module 10 according to the second embodiment in that it further includes a Gray circuit between the DLL circuit 20 and the internal A / D converter 30 Code converter 50. The same description as the second embodiment is omitted, and the parts different from the A / D conversion module 10 according to the second embodiment are described here.
[0209] The Gray code converter 50 converts the multiphase clock signal 15 output from the DLL circuit 20 from a thermometer code (thermometric code) into a Gray code, and then inputs it to a latch or a trigger of a TDC unit constituting each internal A / D converter 30. Device 31. By configuring in this way, the number of latches constituting the TDC can be greatly reduced, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com