Semantic high-precision map construction and positioning method based on point-line feature fusion laser
A feature fusion and map construction technology, applied in structured data retrieval, geographic information database, electromagnetic wave re-radiation, etc., can solve the problems of high dependence on 3D high-precision maps, mismatching and unsuccessful high-precision maps, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
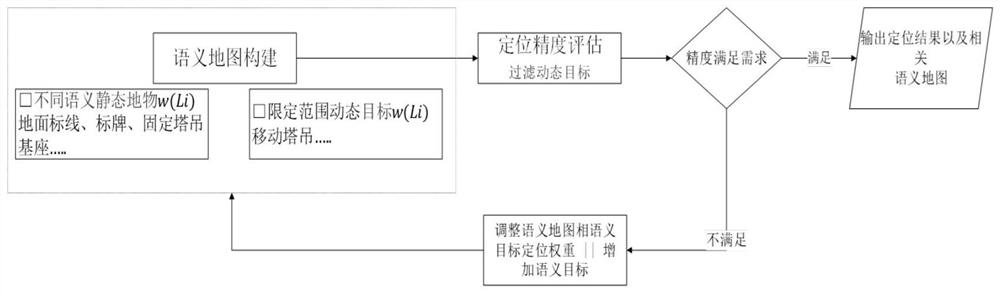
[0072] This embodiment provides a method for constructing a semantic high-precision map.
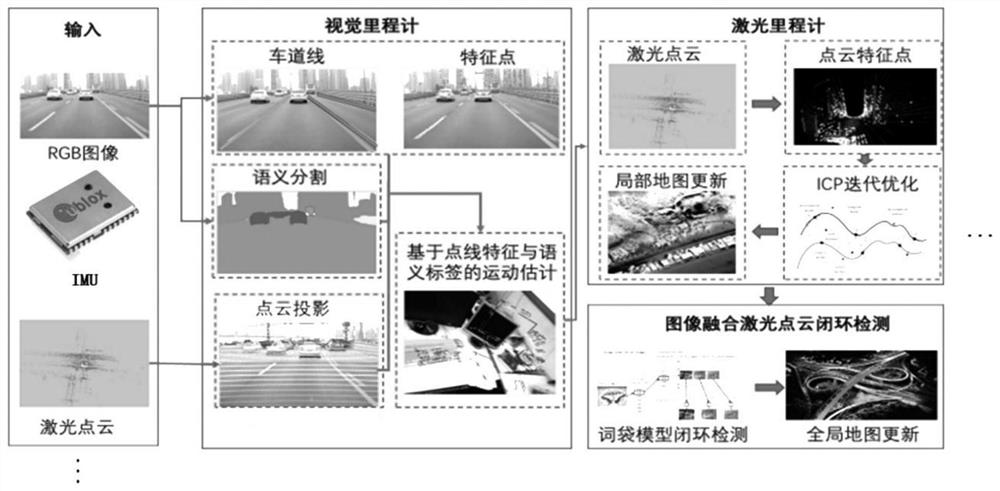
[0073] like figure 1 As shown, the basic process of this method is: input of image, point cloud, gps, IMU and other data → visual odometry → laser odometry → global map update, where visual odometry includes semantic segmentation, lane line detection, and feature point extraction → Obtain point, line features, semantic information → motion estimation (moving target elimination, pose estimation), laser odometer includes pose optimization (ICP iterative optimization, local map update). In this embodiment, improvements are mainly aimed at moving target elimination, pose estimation and optimization steps. Specifically include:
[0074] 1. Moving target removal
[0075] 1) Use the semantic segmentation network (such as FCN, Segnet, RefineNet, PSPNet, Deeplab v1&v2&v3, etc.) to perform semantic segmentation on the visual images collected by the camera, and use Hough, brief, etc. for feature...
Embodiment 2
[0103] This embodiment is mainly aimed at the positioning of dynamic scenes such as port areas and underground parking lots.
[0104] First, analyze the problems existing in conventional methods in the positioning of port areas and underground parking lots.
[0105] The port has the following characteristics: 1) The gantry crane in the unloading and loading area of the port is mobile, and its position may change at any time, so laser matching and positioning based on a fixed map cannot be applied; 2) The GPS signal under the gantry crane is weak, and the lateral positioning accuracy is difficult to guarantee The accuracy of unloading and loading is required, so GPS positioning cannot be used; 3) The position of the container in the unloading area will change with time, so the traditional visual matching or laser matching cannot be successful, and the map needs to be updated continuously, which improves the operational efficiency Complexity.
[0106] The underground parking ...
Embodiment 3
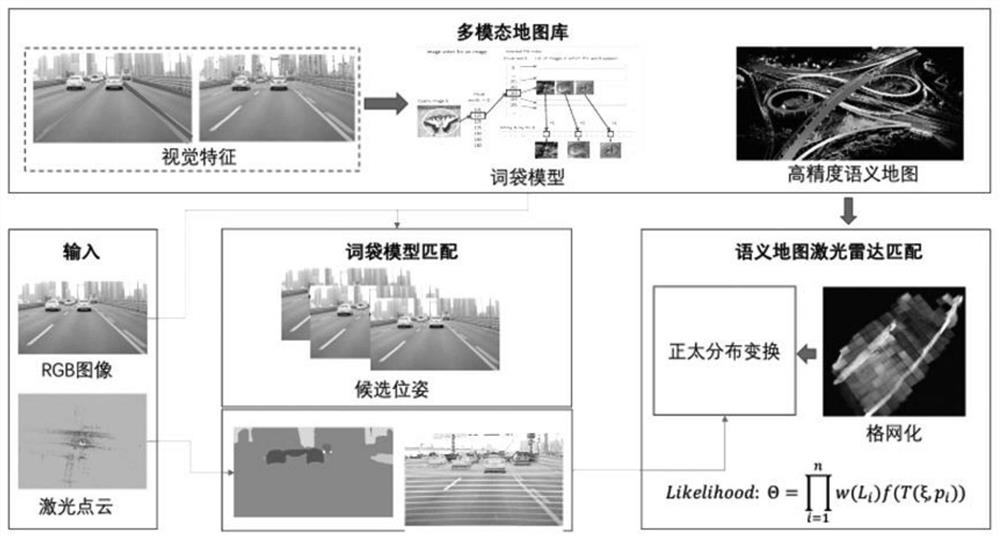
[0123] This embodiment provides a lane lateral positioning method based on the semantic high-precision map library constructed in Embodiment 1 and integrating low-precision GPS for closed scenes such as high speeds.
[0124] This method takes advantage of the characteristics of high efficiency, robustness and strong structure of lane line extraction, and applies it to the lateral positioning of unmanned vehicles on high-speed sections. Its core technical process is as follows: Figure 4 shown.
[0125] This method first extracts the lane line from the input visual image, and performs grayscale binarization processing to obtain the lane line binary image; then performs distance transformation on the binary image to obtain a distance map; at the same time, according to the GPS given The positioning information is obtained from the map library to obtain the vector high-precision lane line map of the current position, and the distance transformation is also performed on the lane l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com