Method for improving rooting ability of pinus massoniana based on endogenous hormones
A technology of endogenous hormones and rooting ability, applied in horticultural methods, botany equipment and methods, plant regeneration, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in rooting of subculture shoots, large differences in plant regeneration efficiency, and poor physiological activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Present embodiment is the method that the endogenous hormone of Pinus massoniana is researched, specifically as follows:
[0024] 1. Experimental materials:
[0025] Taking Tongmian pine as the research object, the national excellent masson pine geographic provenance, the 5 dominant tree method was used to select the best stand in the 15-30-year-old Tongmian pine stand in the state-owned Paiyangshan Forest Farm in Guangxi. The new twigs of the selected excellent trees in the same year were used as spikes, and the half-year-old masson pine tissue culture seedlings were used as rootstocks, and were grafted according to conventional methods. After the grafting survived, remove the top shoots of the grafted seedlings, and use 500mg·L -1 GA3 was sprayed every other week to promote germination, and sprayed 3 to 4 times in a row. When the grafted seedling sprouts grow to 1cm, spray once a week with 0.5% urea, and when the sprouts reach 3-5cm in length, pick vigorous sprouts ...
Embodiment 2
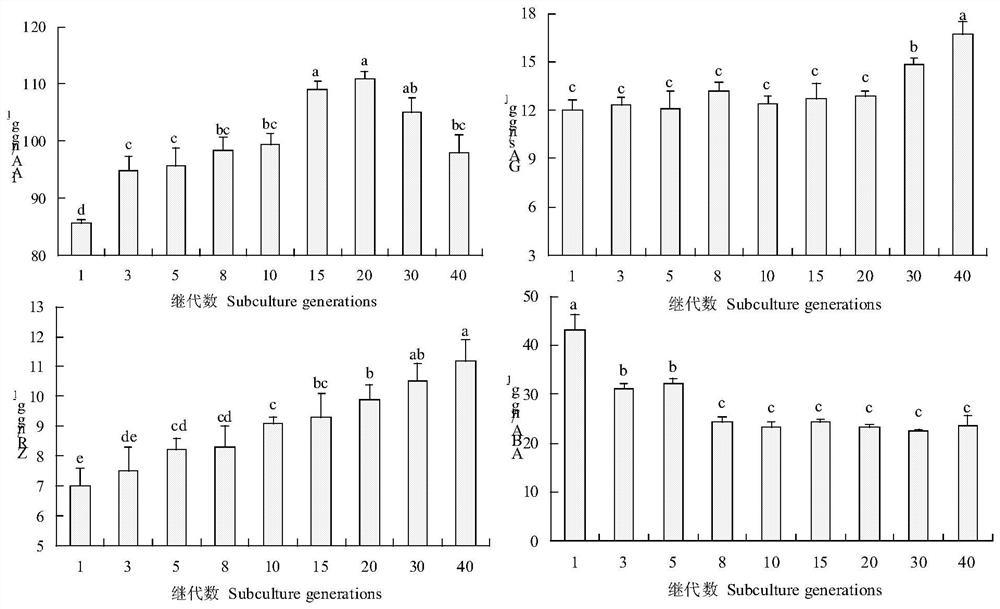
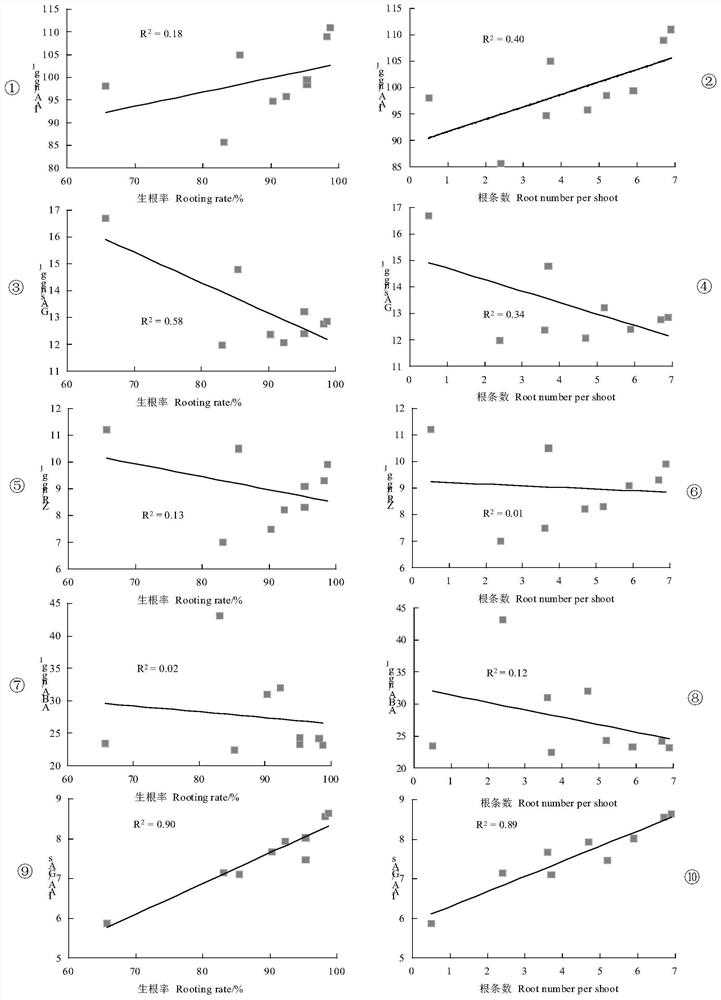
[0036] According to the statistical analysis of Example 1, the applicant found that the ratio of IAA / GAs has a certain influence on the rooting of subcultured shoots. Selecting the rooting agent according to the above ratio can accurately match the content of the rooting agent, greatly improving the rooting ability of the subcultured buds. Application In the long-term study of human beings, it was found that for the explant of the secondary shoot of Pinus massoniana:
[0037] The endogenous hormone 7≤IAA / GAs≤8 of the subcultured shoots of Pinus massoniana subcultured for 1-10 times;
[0038] The endogenous hormone IAA / GAs of the subcultured shoots of Pinus massoniana subcultured for 11-20 times>8;
[0039] The endogenous hormone IAA / GAs of the subcultured shoots of Pine massoniana subcultured 21-40 times<7;
[0040] Among them, the number of subcultures with the most significant differences in rooting rate, root number, and endogenous hormone levels was (1 time: 35-40d, 20 ti...
Embodiment 3
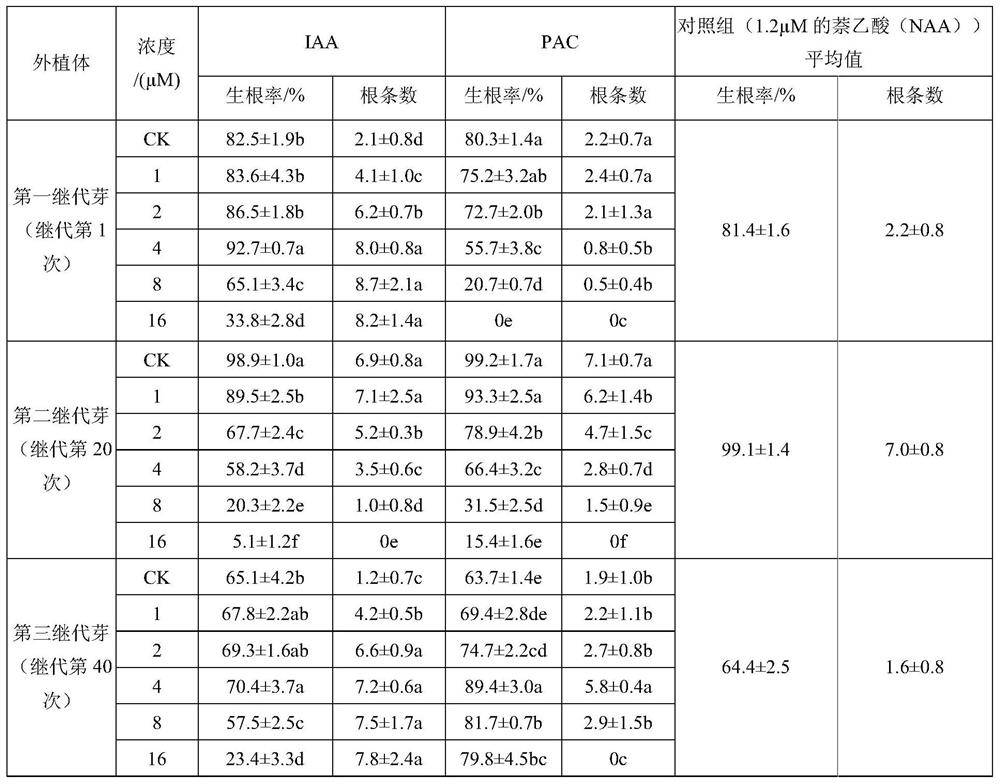
[0065] In the long-term research work, the applicant found that, in addition to the above-mentioned rooting agents, the rooting agents abscisic acid (ABA), forchlorfenuron (CPPU) and isopentenyl adenine (iP) also have an effect on the secondary buds of Pinus massoniana. Great impact; there is a significant difference in the concentration of the first, second and third generation buds, so the applicant carries out further research on the concentration of ABA, CPPU and iP respectively on the first, second and third generation buds, For details, see Table 6-11:
[0066] Table 6 rooting agent is to the orthogonal experiment factor level of first subgeneration bud
[0067]
[0068]
[0069] Table 7 Orthogonal test results
[0070] Number of trials Factor A Factor B Factor C Rooting rate (%) Number of roots 1 1 1 1 92.5±0.8a 8.3±1.0a 2 1 2 2 95.3±1.2a 8.1±0.4a 3 1 3 3 75.6±1.7c 5.3±0.5c 4 2 1 2 97.6±0.3a 7.9±0.4a 5 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com