Methods for reducing or shutting down lactation in non-human mammals and reagents therefor
A non-human mammal, lactation technology, applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, chemical instruments and methods, animal/human proteins, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0132] Example 1. Mutant mouse line that produces lactation failure
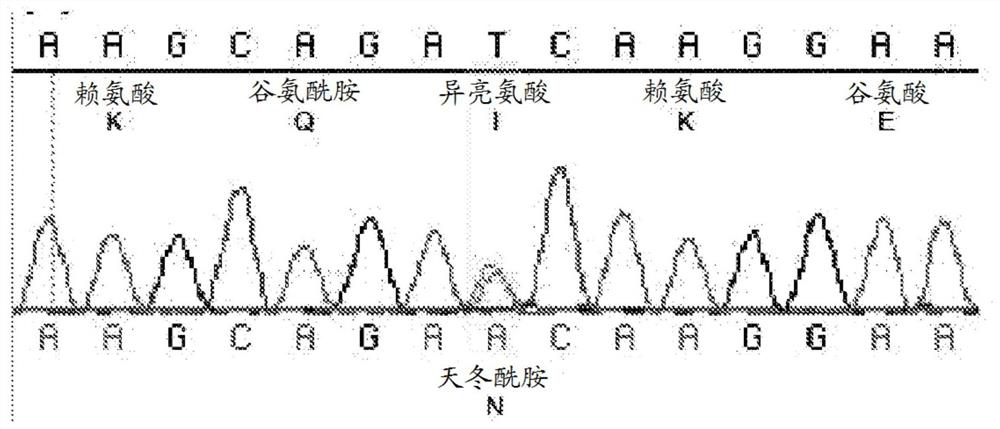
[0133] 1. Generation of OAS2 mutant mouse line
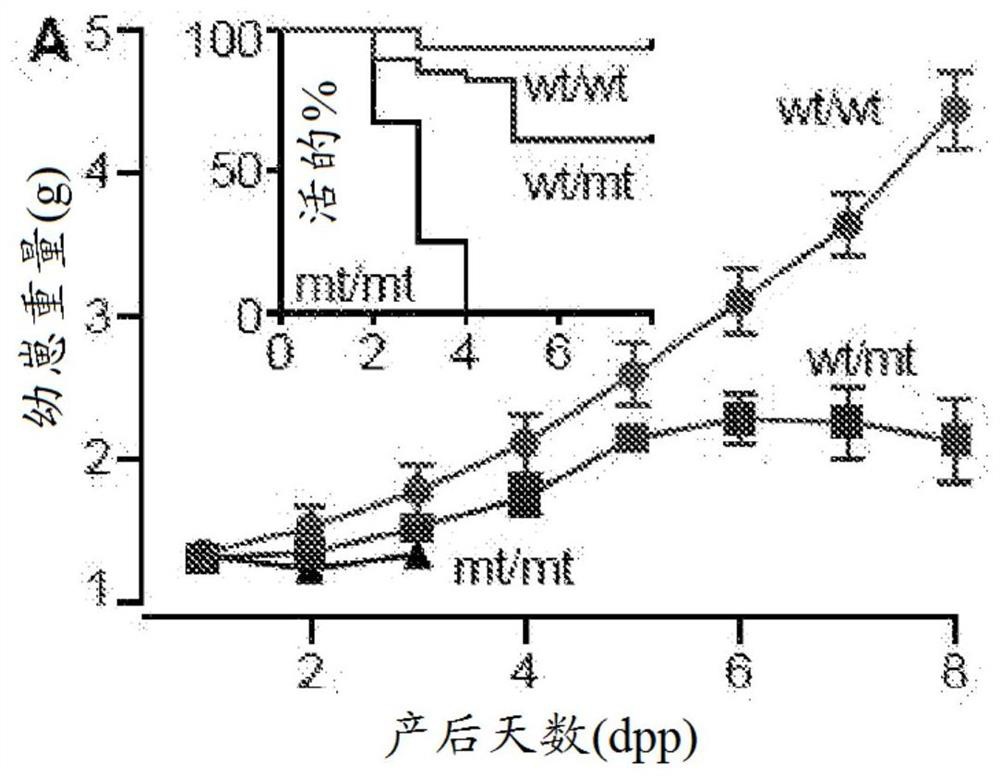
[0134] Using N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU) mutagenesis and screening for lactation failure, a mouse line was established, in which heterozygous (wt / mt) female mice showed partial penetrance of poor lactation. Produce litters that cannot thrive ( figure 1 ), and homozygous (mt / mt) female mice experience complete failure of lactation ( figure 1 ), provides a dominant inheritance model.
[0135] 1.1 Mice
[0136] All mice were raised in the Australian Phenomics Facility and Garvan Institute under specific pathogen-free conditions, and all animal procedures were passed through the Australian National University or Gavin / Approved by Garvan / St Vincent's Animal Ethics and Experimentation Committees. All animals were fed and drank ad libitum, and were reared in a 12-hour day / night cycle at 22°C and 80% relative humidity.
[0137] ENU mutagenesis and lineage construction wer...
Embodiment 2
[0157] Example 2. Characterization of OAS2 mutant mouse line
[0158] 2.1 Method
[0159] 2.1.1 Histopathology and organ pathology analysis
[0160] A complete analysis of histology and pathology of the Jersey strain was carried out by the Australian Phenotypic Network (APN) Histopathology and Organ Pathology Service Center of the University of Melbourne. Macroscopic and microscopic examinations of female sib pairs at eight and 31 weeks composed of mt / mt and wt / wt siblings. For breast tissue, ovary, fallopian tube, bicornuate uterus, cervix, bladder, liver / gallbladder, cecum, colon, spleen / pancreas, mesenteric lymph nodes, stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, kidney / adrenal glands, salivary glands / lymph nodes , Thymus, lung, heart, skin, eyes, brain, spinal cord, skeletal muscle, skeletal tissue / hind limbs for macro and micro examination.
[0161] 2.1.2 Expression in OAS2 mutant mouse milk protein
[0162] Quantitative PCR was performed on the mRNA of milk protein expressed in the ...
Embodiment 3
[0196] Example 3. Infusion of poly(I:C) into the breast of lactating mice
[0197] In this example, the inventors demonstrated that poly(I:C) (a representative OAS2 activator) can reduce or stop lactation when administered to lactating mice via intramammary infusion. The results showed that the administration of poly(I:C) resulted in lactation failure, premature degeneration, and mammary alveolar remodeling, so that the mammary glands infused in the previous pregnancy could recover and become fully capable of lactating after subsequent pregnancy.
[0198] 3.1 Method
[0199] Dilute the poly(I:C) stock solution with a concentration of 10 mg / ml in sterile saline according to the manufacturer's instructions, and then heat to 50°C. From this stock solution, the treatment and control solutions for injection into mouse mammary glands were prepared as follows:
[0200] Table 3: Injection master mix of 25ng / μl poly(I:C)
[0201]
[0202]
[0203] Table 4: Injection master mix for vehicle con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com