Alloy movable conduit for sodium-cooled fast reactor control rod driving mechanism and manufacturing method
A driving mechanism, sodium-cooled fast reactor technology, applied in the control of nuclear reactions, reactors, nuclear power generation, etc., can solve the problems of technical difficulties in smelting and manufacturing, high deformation resistance, high degree of alloying of GH1059 alloy, and improve radiation swelling resistance. performance, the effect of improving corrosion resistance, good microstructure and mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] An alloy moving conduit for a sodium-cooled fast reactor control rod drive mechanism provided in this embodiment has the following chemical composition and mass percentage: C: 0.063%, Si: 0.10%, Mn: 1.51%, P: 0.005%, S: 0.005%, Cr: 16.44%, Ni: 36.30%, Cu: 0.03%, Mo: 3.40%, W: 0.063%, Al: 0.08%, N: 0.018%, Co: 0.005%, B: 0.0017%, Zr: 0.010%, Y: 0.001%, Sn: 0.0002%, As: 0.0007%, Pb: 0.0001%, Bi: 0.0001%, and the balance is Fe and trace elements.
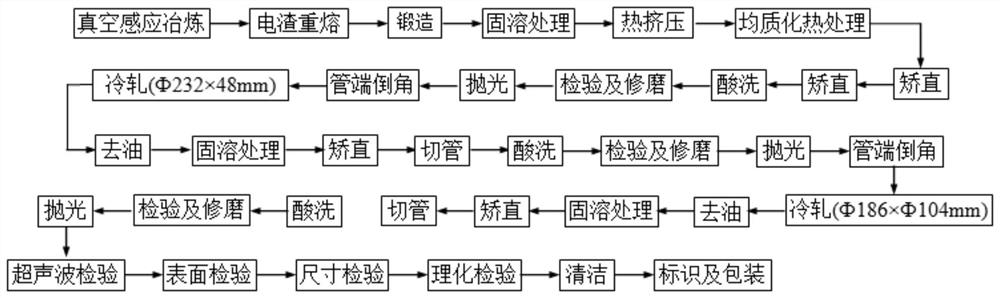
[0056] The manufacturing method comprises the steps of:
[0057] (1) Smelting
[0058] The alloy material is smelted by vacuum induction at a smelting temperature of 1480°C, cast into an alloy ingot of Ф440mm, and then smelted into an alloy ingot of Ф620 / Ф720mm by using a 6-ton protective atmosphere electroslag remelting furnace;
[0059] (2) Forging
[0060] The alloy ingot obtained in step (1) is opened with a 2,000-ton rapid forging unit, the initial forging temperature is 1100-1150°C, and the final forging temperature is ...
Embodiment 2
[0086] The difference between the alloy moving conduit for the control rod driving mechanism of a sodium-cooled fast reactor provided in this embodiment and the embodiment 1 is that its chemical composition and mass percentage are as follows: C: 0.060%, Si: 0.11%, Mn: 1.53% , P: 0.005%, S: 0.005%, Cr: 16.40%, Ni: 36.30%, Cu: 0.02%, Mo: 3.25%, W: 0.07%, Al: 0.073%, N: 0.02%, Co: 0.005% , B: 0.0019%, Zr: 0.010%, Y: 0.001%, Sn: 0.0002%, As: 0.0008%, Pb: 0.0001%, Bi: 0.0001%, Sb: 0.001%, and the balance is Fe and trace elements.
[0087] The inner and outer surface roughness Ra of the product is ≤1.6μm; the outer diameter is ±1.00mm, the inner diameter is ±1.00mm; the tensile property at 20°C: R m =590MPa, R p0.2 =264MPa, A 50 =49.0%, Z=75%, R m Indicates the tensile strength, R p0.2 Represents the yield strength, A represents the elongation after fracture, Z represents the reduction of area; high temperature tensile properties: at 100°C, R m =553MPa, R p0.2 =233MPa,A 50 =4...
Embodiment 3
[0089] The difference between the alloy moving conduit for the control rod driving mechanism of a sodium-cooled fast reactor provided in this embodiment and the embodiment 1 is that its chemical composition and mass percentage are as follows: C: 0.060%, Si: 0.10%, Mn: 1.54 %, P: 0.005%, S: 0.001%, Cr: 16.27%, Ni: 36.18%, Cu: 0.03%, Mo: 3.26%, W: 0.07%, Al: 0.048%, N: 0.012%, Co: 0.001 %, B: 0.001%, Zr: 0.0010%, Y: 0.001%, Sn: 0.001%, As: 0.0007%, Pb: 0.0001%, Bi: 0.0001%, Sb: 0.001%, and the balance is Fe and trace elements.
[0090] The inner and outer surface roughness Ra of the product is ≤1.6μm; the outer diameter is ±1.00mm, the inner diameter is ±1.00mm; the tensile property at 20°C: R m =592MPa, R p0.2 =266MPa, A 50 =48.5%, Z=75%, R m Indicates the tensile strength, R p0.2 Represents the yield strength, A represents the elongation after fracture, Z represents the reduction of area; high temperature tensile properties: at 100°C, R m =552MPa, R p0.2 =231MPa, A 50 =...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile properties | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com