Gradient type microporous broadband wave-absorbing material and supercritical limited foaming type preparation method thereof
A wave absorbing material and a gradient type technology are applied in the field of gradient type microporous broadband wave absorbing material and its supercritical restricted foaming type preparation, which can solve the problems of narrow wave absorbing frequency band, high wave absorbing material density and high cost. To achieve the effect of improving mechanical properties, good control flexibility, and increasing nucleation density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
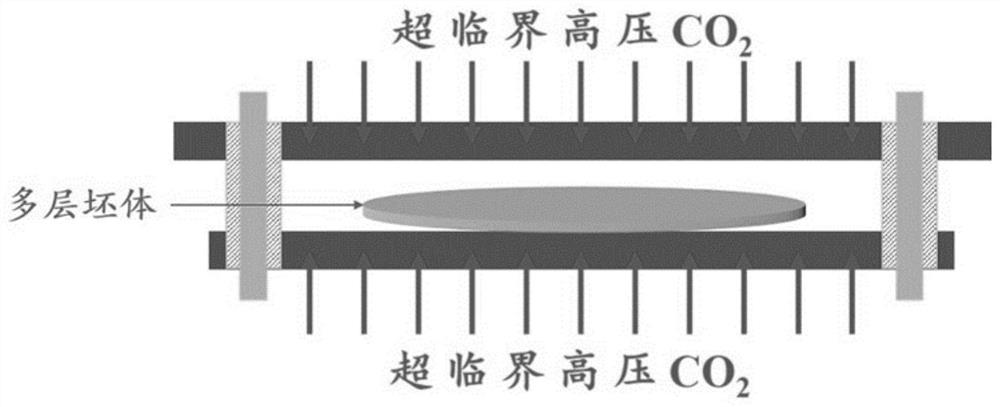
[0036] A gradient type microporous broadband wave-absorbing material, the preparation method of which comprises the following steps:
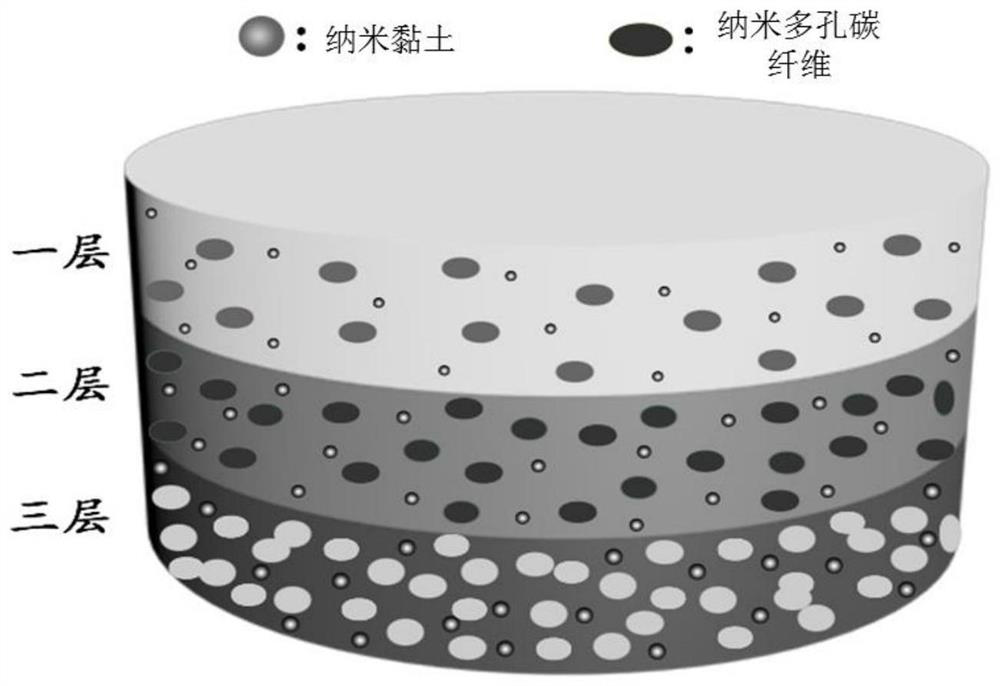
[0037] S1. Prefabricated sheet: Mix nanoporous carbon fiber, polymethylmethacrylate and nanoclay according to the preset mass ratio of 1:98:1, 3:95:2 and 5:92:3 respectively, and extrude through twin-screw extruder (extruder temperature: 190-220°C, rotating speed: 85r / min) for blending, granulation, drying, and injection molding to obtain three groups of prefabricated sheets with a thickness of 0.5mm in different mass ratios. Heterogeneous nucleation can be induced by adding nanoclay nucleating agent, further improving the foaming performance of the gradient microporous broadband absorbing material, and the nano-size effect of the nano-viscosity dispersed in the substrate helps to improve the absorbing material. absorption rate.
[0038] Wherein, the nanoporous carbon fiber is prepared through the following steps:
[0039] First, the mass rat...
Embodiment 2
[0048] A gradient-type microporous broadband wave-absorbing material, compared with Example 1, the difference is that step S1 includes: prefabricated sheet: nanoporous carbon fiber, polymethyl methacrylate and nanoclay respectively by preset mass Mixing at a ratio of 2:97:1, 5:93:2 and 8:88:4, blending and granulation through a twin-screw extruder (extruder temperature: 190-220°C, speed: 85r / min) , and after drying, three groups of prefabricated sheets with a thickness of 0.5 mm in different mass ratios were obtained by injection molding. Others are substantially the same as in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0050] A gradient-type microporous broadband wave-absorbing material, compared with Example 1, the difference is that step S1 includes: prefabricated sheet: nanoporous carbon fiber, polymethyl methacrylate and nanoclay respectively by preset mass Mixing at a ratio of 1:98:1, 3:95:2 and 5:92:3, blending and granulation through a twin-screw extruder (extruder temperature: 190-220°C, speed: 85r / min) , after drying, three groups of prefabricated sheets with a thickness of 1 mm in different mass ratios were obtained by injection molding. Others are substantially the same as in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
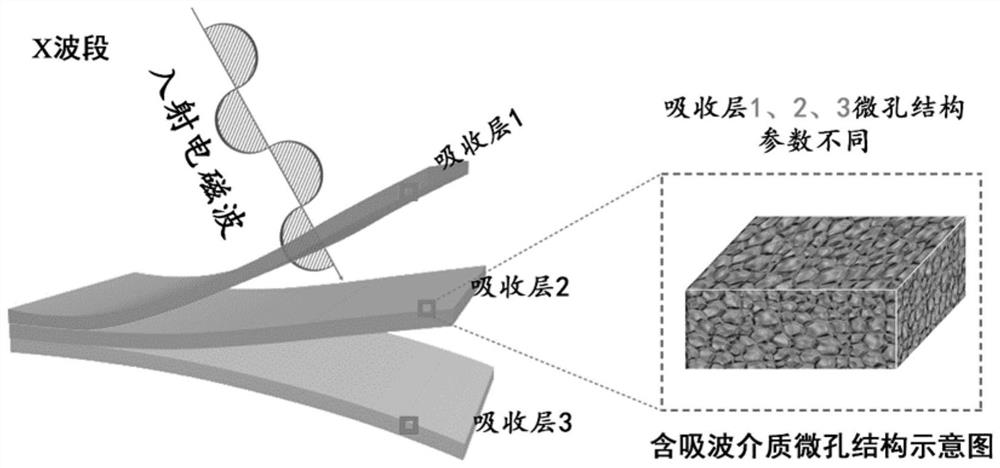
[0051] As described in Examples 1 to 3, by adjusting the thickness of the prefabricated sheet, the content of the absorbing medium and the nucleating agent, microporous structures with different structural parameters can be obtained, thereby realizing multi-layer broadband absorbing in different frequency bands, so The wave-absorbing frequency band has good cont...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com