Method and device for detecting somatic cell copy number variation in specified genome region
A copy number variation and genome technology, applied in the field of genes, to achieve accurate detection results, reduce false positives, and improve accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
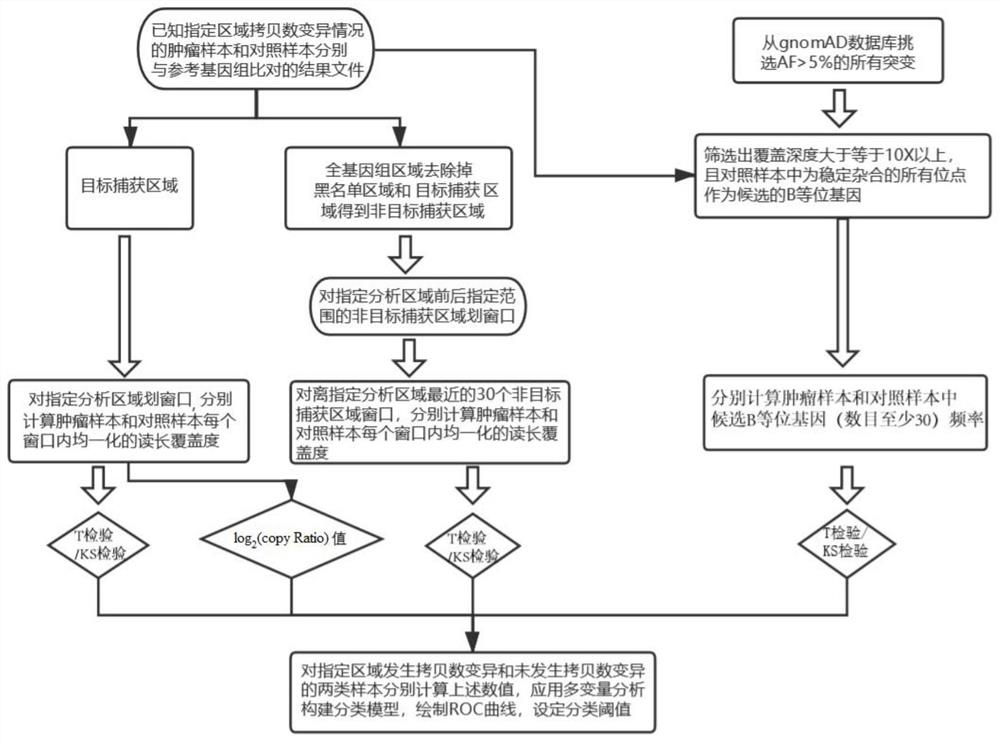
[0054] This embodiment provides a method for detecting somatic copy number variation in a designated genomic region, the flow chart of which is as follows figure 1 shown, including:
[0055] (1) Obtain tumor samples with known copy number variation in specified genomic regions, and use the paired samples as control samples; compare the sequencing data of tumor samples and control samples with the reference genome to obtain comparison result files;
[0056] In this example, 8 tumor tissue samples (non-small cell lung cancer were selected in this example) were selected, and the paired samples (control samples) were white blood cells from the peripheral blood of the same patient, and were performed using the Gene+Seq 2000 sequencing platform Whole exome sequencing. The sequencing data were compared with the human reference genome (GRCh37) by BWA-MEM software, and the comparison result file was obtained. It is known that in the specified genomic region (each sample has a specifi...
Embodiment 2
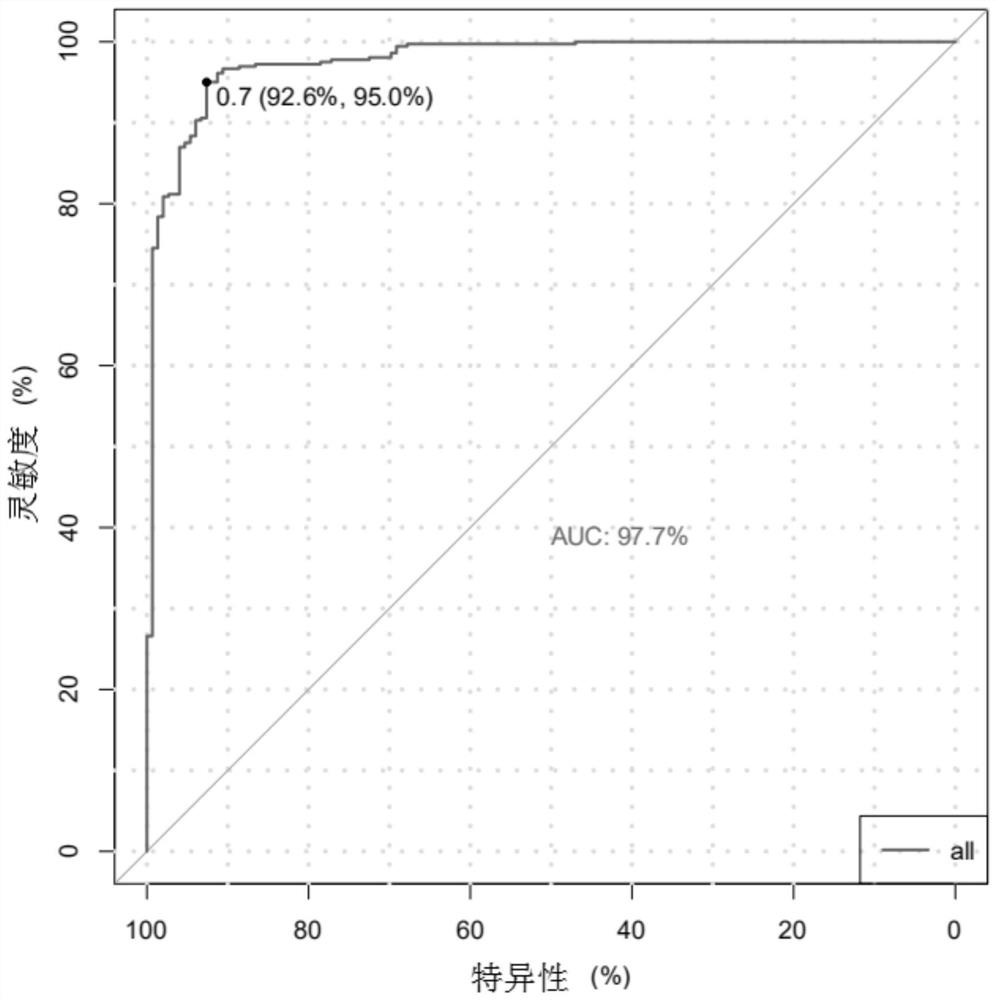
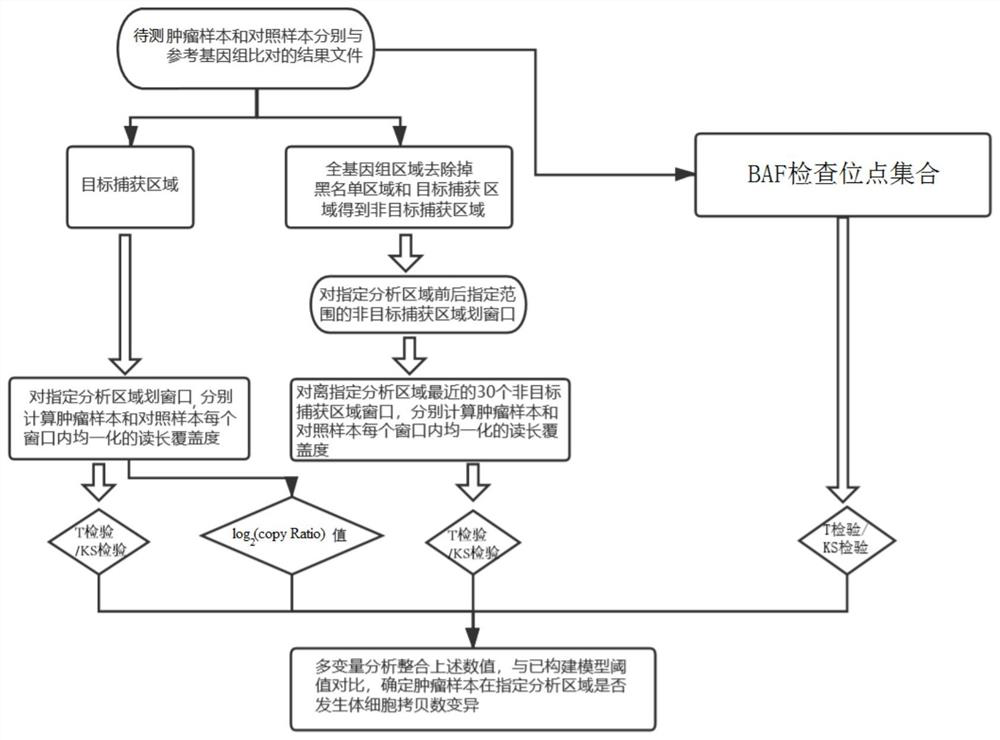
[0073] In this example, the tumor samples and paired samples with known copy number variation of the specified genomic region are used as the verification set, and the detection process is as follows: image 3 As shown, detect according to the method in embodiment 1, including:
[0074] (1) Compare the sequencing data of the tumor sample to be detected and the control sample with the reference genome to obtain a comparison result file;
[0075] The tumor tissue sample number is 190031660FD (provided by Genega), and its paired control is the peripheral blood leukocyte 190031660BD (provided by Genega) of the same patient. Gene+Seq 2000 sequencing platform was used for whole exome sequencing respectively. The sequencing data were compared with the human reference genome (GRCh37) by BWA-MEM software, and the comparison result file was obtained. Detection of CDKN2A gene (chromosome 9, position information on the genome is 21968174-21975187), PTEN gene (chromosome 10, position info...
Embodiment 3
[0094] This embodiment provides a device for detecting somatic copy number variation in a specified genomic region, comprising:
[0095] The comparison unit is used to compare the sequencing data of the tumor sample and the control sample with the reference genome to obtain a comparison result file; the copy number variation of the specified genomic region of the tumor sample is known, and the paired sample is used as a control sample;
[0096] The difference significance P value calculation unit of the normalized read length coverage is used to divide the window in the target capture area or non-target capture area of the specified genomic region based on the comparison result file, and calculate the difference between the tumor sample and the control sample in each The normalized read-length coverage within the window, and then calculate the significant difference P value of the normalized read-length coverage of the tumor sample and the control sample, corresponding to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com