Method for transferring solar cell substrate
A technology of solar cells and transfer methods, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve problems such as corrosion, influence on bonding quality, complexity, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing manufacturing costs, reducing battery costs, and improving service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
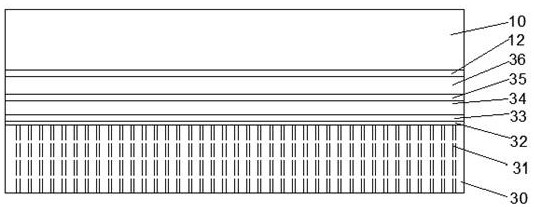
[0050] Such as Figure 1-Figure 3As shown, the present invention provides a method for transferring a solar cell substrate, comprising the following steps
[0051] S1: Growth of battery structure, using MOCVD equipment to grow battery epitaxial layer 36 on GaAs substrate 10, said battery epitaxial layer 36 includes N-GaAs buffer layer, GaInP etch stop layer 12, N-GaAs contact Layer 13 , GaInP top cell 14 , first tunnel junction 15 , GaAs middle cell 16 , second tunnel junction 17 , InGaAs bottom cell 18 and P-InGaAs contact layer 19 .
[0052] S2: Evaporate the metal bonding layer on the surface of the battery epitaxial layer 36 and the flexible substrate 34, and the grown battery epitaxial layer 36 and the flexible substrate 34 are cleaned with organic ultrasonic waves, and the battery epitaxial layer is sequentially evaporated by electron beams respectively metal bond layer 35, flexible substrate metal bond and layer 33,
[0053] Evaporation of the bonding layer of the bat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com