Co-synthesis of phyllominerals with metallic particles and products obtained therefrom
A technology of layered minerals and granules, applied in the direction of non-metallic elements, silicon compounds, skin care preparations, etc., can solve the problems of difficult application of synthetic granules and suspensions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
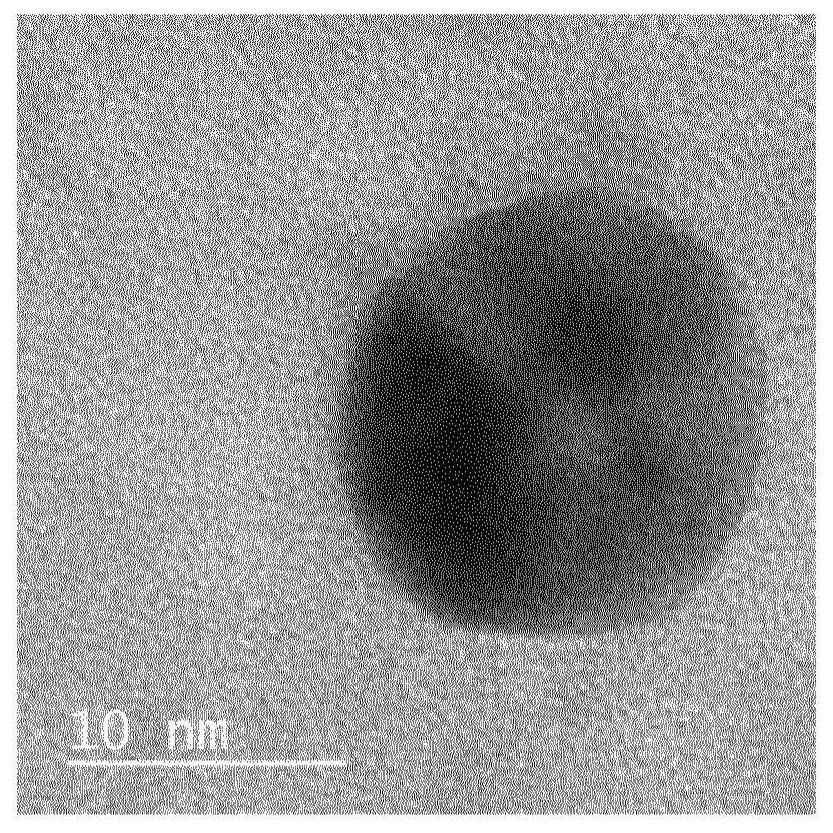
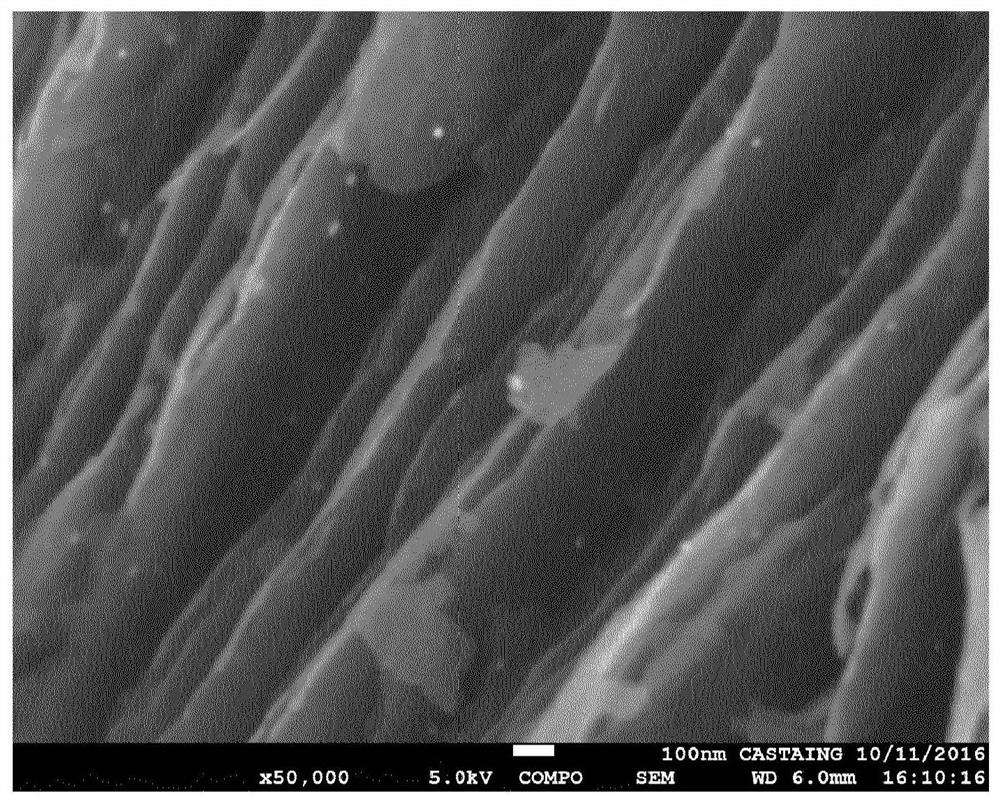
[0042] This example uses an aqueous dispersion of synthetic talc as the layered mineral source and gold nanoparticles as the noble metal source.
[0043] In a beaker, 6.3 mL of gold nanoparticle solution (0.05 mg / mL) was added to 32.6 g of an aqueous dispersion of synthetic talc (corresponding to 1.5 g of dry talc). The resulting mixture was diluted with 150 mL of distilled water, mixed and sonicated for several minutes. After sufficient dispersion, the suspension was centrifuged at 9000 rpm for 1 hour and 30 minutes. Finally, the supernatant was completely transparent and colorless, and the residue of the synthetic talc was reddish, indicating the presence of gold nanoparticles.
[0044] The theoretical loading of 1.5 g of talc is 0.315 mg of gold, corresponding to a loading of 210 ppm. Attempts to perform experiments at theoretical loadings above 3000 ppm resulted in a red supernatant after centrifugation, indicating that not all gold nanoparticles were incorporated into t...
Embodiment 2
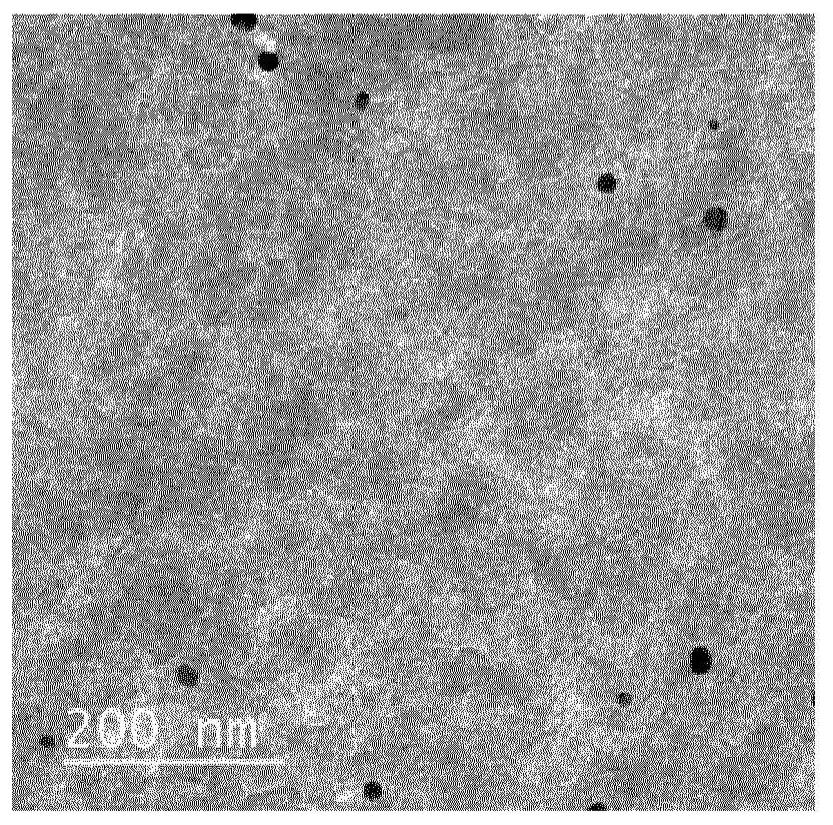
[0046] In this example, hydrated sodium metasilicate and magnesium acetate were used as layered mineral sources for in-situ formation of talc, and chloroauric acid was used as a noble metal source for in-situ formation of gold.
[0047] In a first beaker (A), 42.4 g (0.2 mol) of sodium metasilicate pentahydrate was dissolved in 300 mL of distilled water under magnetic stirring and sonication. Add 103.5 g of anhydrous sodium acetate. In a second beaker (B), 32.17 g (0.15 mol) of magnesium acetate tetrahydrate was dissolved in 100 mL of 1 M acetic acid under magnetic stirring and sonication. 0.8 mL of 10 mg / mL HAuCl 4 The trihydrate solution was added to beaker (B). The contents of beaker (B) were quickly added to the contents of beaker (A) with manual stirring to obtain a white suspension. The resulting aqueous suspension was treated in a hydrothermal reactor at 300° C. under autogenous pressure (85 bar) for 6 hours. At the end of the hydrothermal treatment, a red gel was o...
Embodiment 3
[0050] This example uses hydrated sodium metasilicate and magnesium acetate as layered mineral sources for in situ formation of talc, and a mixture of chloroauric acid and chloroplatinic acid as noble metal sources for in situ formation of gold and platinum.
[0051] In a first beaker (A), 42.4 g (0.2 mol) of sodium metasilicate pentahydrate was dissolved in 300 mL of distilled water under magnetic stirring and sonication. Add 103.5 g of anhydrous sodium acetate. In a second beaker (B), 32.17 g (0.15 mol) of magnesium acetate tetrahydrate was dissolved in 100 mL of 1 M acetic acid under magnetic stirring and sonication. 1.90 mL of 10 mg / mLHAuCl 4 trihydrate solution and 2.45 mL of 10.25 mg / mL H 2 PtCl 6 The hexahydrate solution was added to beaker (B). The contents of beaker (B) were quickly added to the contents of beaker (A) with manual stirring to obtain a white suspension. The resulting aqueous suspension was treated in a hydrothermal reactor at 300° C. under autogeno...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com