Method for increasing yield of ascomycin by using polyhydroxybutyrate as intracellular carbon library
A technology of polyhydroxybutyric acid and ascomycin, applied in the field of Streptomyces genetic engineering, can solve the problem that the impact of antibiotic production has not been reported, and achieve the effect of increasing production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
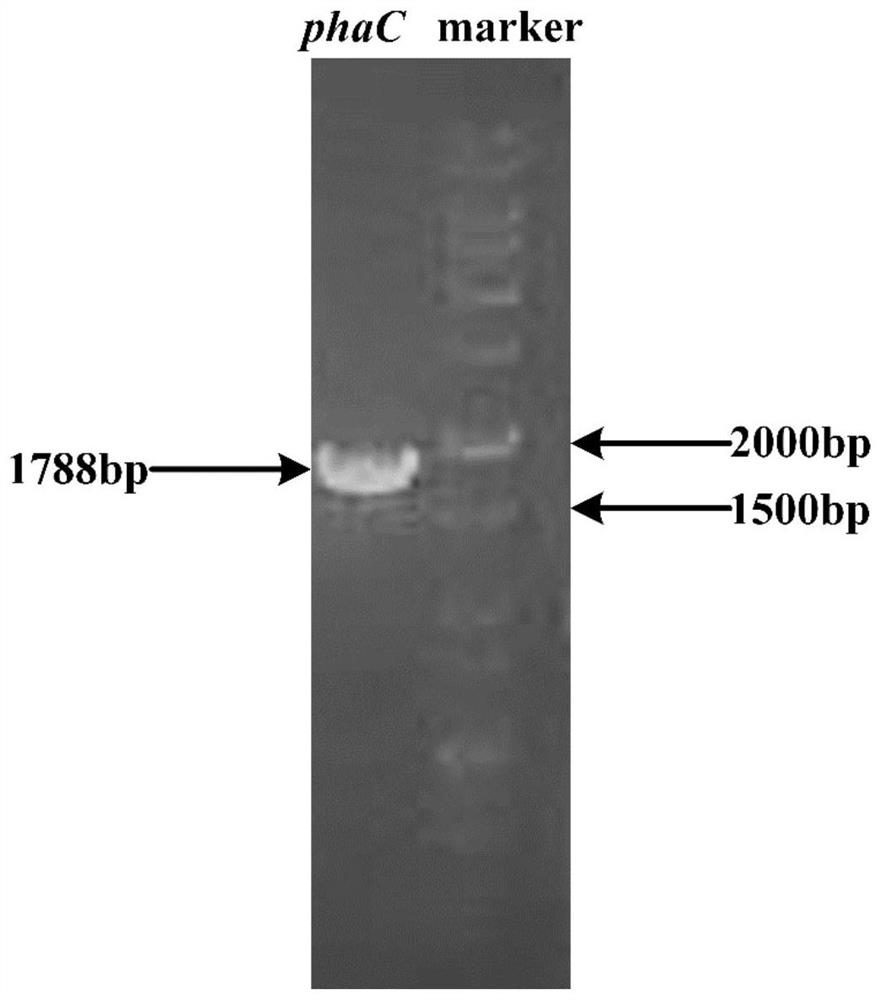
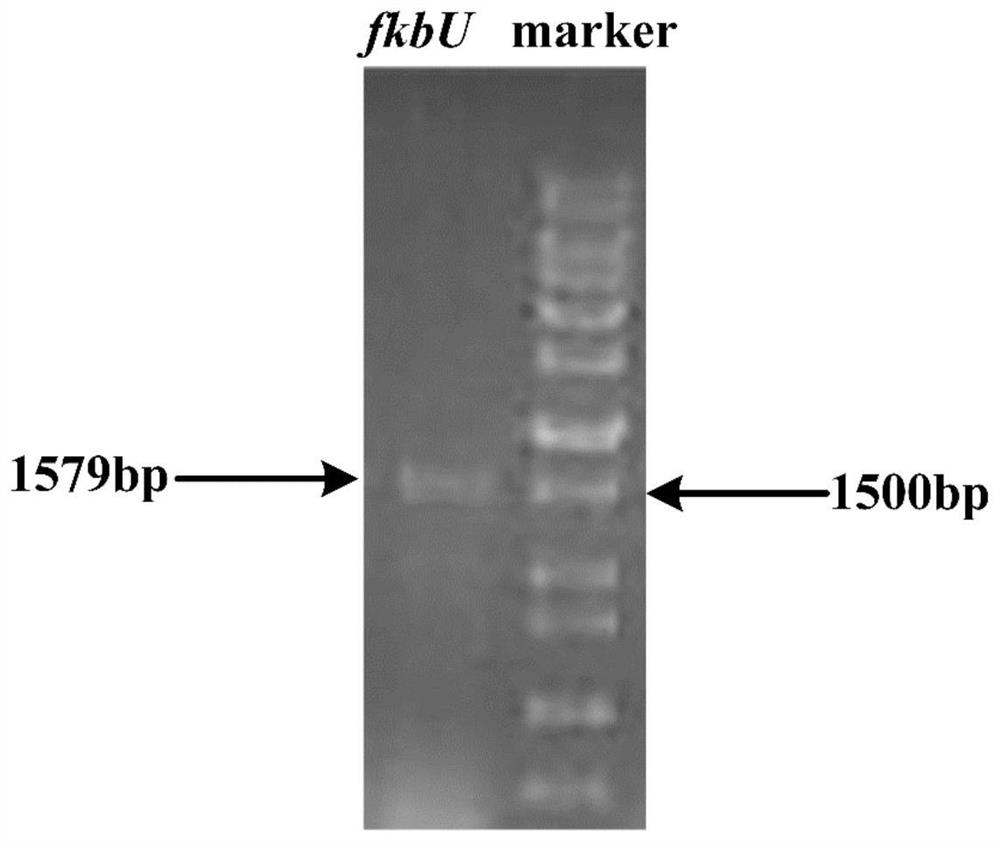
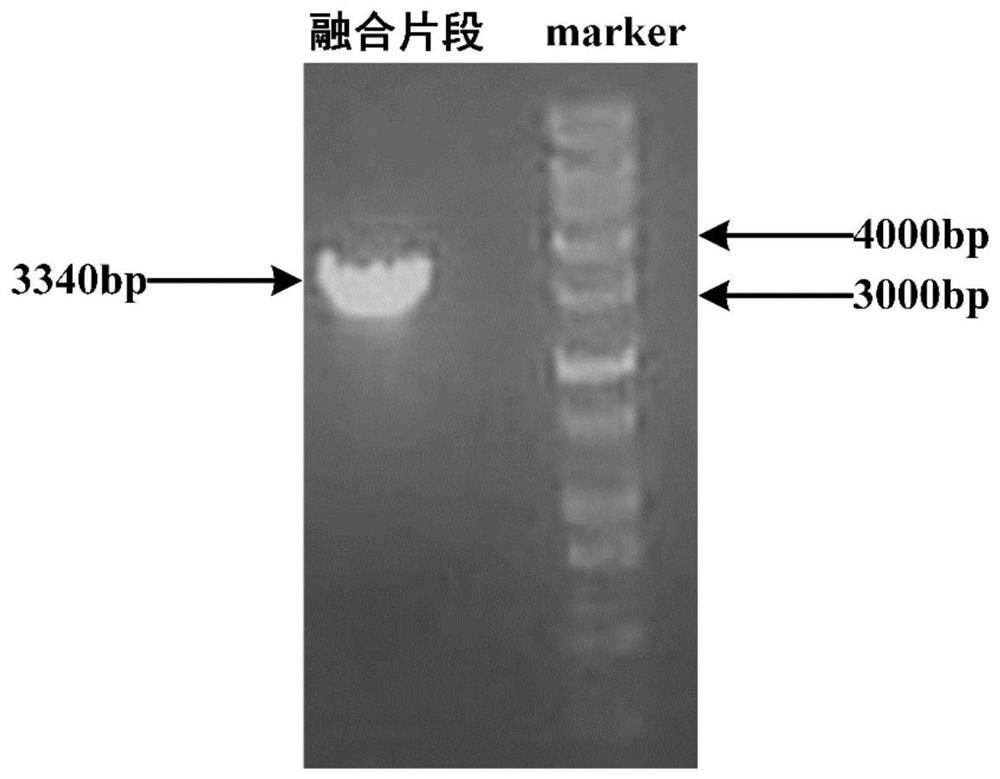
[0036] 1. Amplification and verification of PHB synthesis gene phaC.
[0037] (1) Design and synthesis of phaC gene amplification primers. According to the nucleic acid sequence of the PHB synthetic gene phaC (as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1), the amplification primers containing the restriction site and the RBS sequence are designed as follows (the underlined line indicates the NdeI restriction site, and the double underscore indicates the RBS sequence). Synthesized by Jinweizhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0038] OphaC-fkbU-F1:GGAATTCCATATGGCGACCGGCAAAGGCGCGGCAG
[0039]
[0040] (2) Genome extraction of strain Ralstonia eutropha H16. Ralstonia eutropha H16 was cultured at 150rpm at 30°C for 16 hours in a seed medium adapted to its growth (Nutrient Broth medium formula: peptone 10g / L, beef extract 3g / L, sodium chloride 5g / L, PH7.0) , to obtain fresh seed liquid for the extraction of genome; the fresh seed liquid was centrifuged at 12000rpm for 2 minutes to collect the thalline, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com